NURS-FPX4020 Improving the Quality of Care and Patient Safety _Master Healthcare Excellence
Published: 2025-10-14
Modified: 2025-10-14
Samples Solutions
Introduction:
The Improving Quality of Care and Patient Safety NURS-FPX4020 course emphasizes strategies to enhance healthcare outcomes and ensure patient safety. ThisOwlisdom Nursing Coursework Help provides key insights into quality improvement and effective care practices.
NURS-FPX 4020 Assessment One: Enhancing Quality and Safety
Instructions for NURS-FPX 4020 Assessment One: Enhancing Quality and Safety
Healthcare organizations and professionals strive to create safe environments for patients; however, due to the complexity of the healthcare system, maintaining safety can be a challenge. Since nurses comprise the largest group of healthcare professionals, a great deal of responsibility falls into the hands of practicing nurses. Quality improvement (QI) measures and safety improvement plans are effective interventions for reducing medical errors and sentinel events, including medication errors, falls, infections, and deaths. A 2000 Institute of Medicine (IOM) report indicated that almost one million people are harmed annually in the United States (Kohn et al., 2000), and 210,000–440,000 die as a result of medical errors (Allen, 2013).
The role of the baccalaureate nurse includes identifying and explaining specific patient risk factors, incorporating evidence-based solutions to improve patient safety, and coordinating care. A solid foundation of knowledge and understanding of safety organizations such as Quality and Safety Education for Nurses (QSEN), the Institute of Medicine (IOM), and The Joint Commission and its National Patient Safety Goals (NPSGs) program is vital to practicing nurses in providing and promoting safe and effective patient care.
You are encouraged to complete the Identifying Safety Risks and Solutions activity. This activity offers an opportunity to review a case study and practice identifying safety risks and possible solutions. We have found that learners who complete course activities and review resources are more successful with first submissions. Completing course activities is also a way to demonstrate engagement in the course.
References
Allen, M. (2013). How many die from medical mistakes in U.S. hospitals? https://www.npr.org/sections/health-shots/2013/09/20/224507654/how-many-die-from-medical-mistakes-in-u-s-hospitals.
Kohn, L. T., Corrigan, J., & Donaldson, M. S. (Eds.). (2000). To err is human: Building a safer health system. National Academy Press.
Professional Context
As a baccalaureate-prepared nurse, you will be responsible for implementing quality improvement (QI) and patient safety measures in healthcare settings. Effective quality improvement measures result in systemic and organizational changes, ultimately leading to the development of a patient safety culture.
The purpose of this assessment is to better understand the role of the baccalaureate-prepared nurse in enhancing quality improvement (QI) measures that address a safety quality issue in a healthcare setting. This will be within the specific context of patient safety risks in a healthcare setting of your choice. You will do this by exploring the professional guidelines and best practices for improving and maintaining patient safety in healthcare settings from organizations such as QSEN and the IOM.
Looking through the lens of these professional best practices to examine the current policies and procedures in place at your chosen organization and the impact on safety measures for patients surrounding a specific safety quality issue, you will consider the role of the nurse in driving quality and safety improvements. You will identify stakeholders in QI improvement and safety measures, as well as consider evidence-based strategies to enhance the quality of care and promote safety in the context of your chosen healthcare setting.
As a baccalaureate-prepared nurse, you will be responsible for implementing quality improvement (QI) and patient safety measures in health care settings. Effective quality improvement measures result in systemic and organizational changes, ultimately leading to the development of a patient safety culture.
The purpose of this assessment is to better understand the role of the baccalaureate-prepared nurse in enhancing quality improvement (QI) measures that address a safety quality issue in a health care setting. This will be within the specific context of patient safety risks at a healthcare setting of your choice. You will do this by exploring the professional guidelines and best practices for improving and maintaining patient safety in health care settings from organizations such as QSEN and the IOM.
Looking through the lens of these professional best practices to examine the current policies and procedures in place at your chosen organization and the impact on safety measures for patients surrounding a specific safety quality issue, you will consider the role of the nurse in driving quality and safety improvements. You will identify stakeholders in QI improvement and safety measures, as well as consider evidence-based strategies to enhance the quality of care and promote medication administration safety in the context of your chosen health care setting.
Scenario
Select one of the safety quality issues presented in the Download Assessment 01 Supplement: Enhancing Quality and Safety [PDF]resource and incorporate evidence-based strategies to support communication and ensure safe and effective care.
Instructions
For this assessment, you will analyze a safety quality issue in a health care setting and identify a quality improvement (QI) initiative.
Be sure that your plan addresses the following, which corresponds to the grading criteria in the scoring guide. Please study the scoring guide carefully so that you know what is needed for a distinguished score.
- Explain factors leading to a specific patient-safety risk in a health care setting.
- Explain evidence-based and best-practice solutions to improve patient safety and reduce costs.
- Explain how nurses can help coordinate care to increase patient safety and reduce costs.
- Identify stakeholders with whom nurses would coordinate to drive safety enhancements with a specific safety quality issue.
- Communicate using writing that is clear, logical, and professional, with correct grammar and spelling, using current APA style.
Additional Requirements
- Length of submission: 3–5 pages, plus title and reference pages.
- Number of references: Cite a minimum of 4 sources of scholarly or professional evidence that support your findings and considerations. Resources should be no more than 5 years old.
- APA formatting: References and citations are formatted according to the current APA style.
Competencies Measured
By completing this assessment, you will demonstrate your proficiency in the course competencies through the following assessment scoring guide criteria:
- Competency 1: Analyze the elements of a successful quality improvement initiative.
- Explain evidence-based and best-practice solutions to improve patient safety and reduce costs.
- Competency 2: Analyze factors that lead to patient safety risks.
- Explain factors leading to a specific patient-safety risk in a health care setting.
- Competency 4: Explain the nurse’s role in coordinating care to enhance quality and reduce costs.
- Explain how nurses can help coordinate care to increase patient safety and reduce costs.
- Identify stakeholders with whom nurses would coordinate to drive safety enhancements with a specific safety quality issue.
- Competency 5: Apply professional, scholarly, evidence-based strategies to communicate in a manner that supports safe and effective patient care.
- Organize content so ideas flow logically with smooth transitions; contains few errors in grammar or punctuation, word choice, and spelling.
- Apply APA formatting to in-text citations and references exhibiting nearly flawless adherence to APA format.
Resources
Use the resources linked below to help complete this assessment.
Collapse All
Collaboration and Leadership
The following readings may help you in completing this assessment’s activities:
- Assessment 1: Collaboration and Leadership reading list.
Quality Improvement Initiatives
The following readings may help you in completing this assessment’s activities:
- Assessment 1: Quality Improvement Initiatives reading list.
Quality and Safety Education
The following readings may help you in completing this assessment’s activities:
- Assessment 1: Quality and Safety Education reading list
Quality and Safety Case Studies
Consider reviewing the following case studies as you complete your assessment:
- Assessment 1: Quality and Safety Case Studies reading list.
Program Resources
Capella Writing Center
- Writing Center.
- Access the various resources in the Capella Writing Center to help you better understand and improve your writing.
APA Style and Format
- Capella University follows the style and formatting guidelines in the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association, known informally as the APA manual. Refer to the Writing Center’s APA Module for tips on proper use of APA style and format.
Capella University Library
- BSN Program Library Research Guide.
- The library research guide will be useful in guiding you through the Capella University Library, offering tips for searching the literature and other references for your assessments.
Activity
Click the linked title below, Identifying Safety Risks and Solutions, to complete this formative activity, which offers an opportunity to review a case study and practice identifying safety risks and possible solutions. These skills will be necessary to complete the Enhancing Quality and Safety assessment successfully. This is for your own practice and self-assessment.
This tool needs to be loaded in a new browser window
Introduction to NURS 4020 Assessment One
Welcome to NURS-FPX 4020 Assessment One: Enhancing Quality and Safety! Healthcare organizations and professionals strive to maintain safe patient environments, but complexities within the system often pose challenges. Nurses, the largest group of healthcare providers, are crucial in ensuring patient safety. This How-To NURS-FPX 4020 Guide provides strategies and guidelines for addressing safety quality issues, incorporating evidence-based solutions, coordinating care, and communicating effectively within healthcare settings.
Select one of the safety quality issues presented in the Assessment 01 Supplement: Enhancing Quality and Safety.
Selecting a Safety Quality Issue
To start the NURS-FPX 4020 Assessment One: Enhancing Quality and Safety, we will select a safety quality issue in healthcare.
- Read the Assessment 01 Supplement to identify various safety quality issues.
- Choose one issue that resonates with your interests or seems significant.
- Consider the impact of the chosen issue on patient safety and healthcare costs.
Example
Responding promptly to patients experiencing deteriorating conditions in healthcare settings presents a multifaceted challenge. Considine et al. (2021) highlight issues within emergency departments despite the presence of Rapid Response Systems, indicating inconsistent recognition and action regarding clinical decline. These systems’ complexity and varying implementation across healthcare facilities may contribute to this problem. Bucknall et al. (2022) delve into the role of nurses in detecting early signs of patient deterioration, emphasizing their crucial function. However, they also underscore the obstacles nurses face, including high workloads and staffing limitations, which hinder their ability to monitor and respond effectively.
Gertz et al. (2022) noted that the COVID-19 pandemic exacerbated challenges in healthcare. Their study suggests that pandemic-related disruptions led to delays in medical treatment as healthcare systems grappled with overwhelming demand and had to adapt their care priorities. These circumstances likely contributed to slowed responses to deteriorating patients, with limited resources and unprecedented challenges that medical staff face.
Ullah et al. (2022) provide further insights by examining the workload associated with vital signs-based monitoring. Their research in a New Zealand hospital setting indicates that the monitoring and response process for deteriorating patients is labor-intensive. This suggests that time constraints and physical workload may impede timely responses, particularly in settings with limited resources.
The consequences of delayed responses to patient deterioration are significant. Firstly, patient safety and outcomes are directly affected. As evidenced by the studies, failure to promptly recognize and address clinical deterioration can result in adverse events, heightened morbidity, and, in severe cases, mortality. Swift interventions are essential in halting or reversing a patient’s decline, and any delay can reduce the effectiveness of the intervention, leading to more severe health consequences.
Additionally, delayed responses often necessitate more intricate and aggressive treatments. As a patient’s condition deteriorates, interventions become more invasive, pose significant risks, and require increased resources. This not only impacts the patient’s prognosis but also escalates healthcare expenditures. Prolonged hospital stays, additional interventions, and potential legal ramifications for healthcare institutions are financial burdens stemming from delayed responses.
Incorporate evidence-based strategies to support communication, ensure safe and effective care, and reduce costs.
Incorporating Evidence-Based Strategies
Next, we will incorporate evidence-based strategies.
- Research evidence-based solutions related to the selected issue.
- Utilize reputable sources such as academic journals, professional organizations, and government reports.
- Evaluate the effectiveness of different strategies in improving patient safety and reducing costs.
- Justify the chosen strategies based on their applicability and success in similar healthcare settings.
Example
Scholarly research offers essential strategies for promptly responding to patients experiencing deterioration in healthcare settings. Considine et al. (2021) emphasize the critical importance of structured approaches in identifying and managing clinical decline, particularly within emergency departments. Rapid Response Systems (RRSs) are valuable tools in aiding healthcare practitioners in the early detection of deteriorating patient conditions and prompt intervention. Implementing such systems significantly enhances patient safety by providing clear protocols for monitoring patients and determining appropriate interventions.
Bucknall and colleagues (2022) provide a compelling analysis of facilitation interventions to enhance nurses’ ability to respond to clinical deterioration. Their study underscores the vital role of ongoing education and support for nurses in adhering to clinical practice guidelines. Establishing a culture of continuous learning and active engagement within clinical settings markedly improves nurses’ capacity to detect and address early signs of patient deterioration, thereby mitigating risks associated with delayed responses.
Ullah et al. (2022) discuss the potential of technology in monitoring patients and facilitating prompt action in response to deteriorating health conditions. Utilizing electronic systems for monitoring vital signs and alerting healthcare providers to abnormalities offers a promising approach. These systems provide real-time information and expedite decision-making processes, enabling healthcare practitioners to respond swiftly to changes in patient status. Transitioning from traditional manual monitoring to technological solutions streamlines processes and alleviates pressure on nurses, allowing them to dedicate more time to patient care.
Hospitals must implement explicit and up-to-date protocols to ensure timely intervention in cases of patient deterioration. These protocols, grounded in robust evidence, should undergo regular review to align with contemporary standards of care. Hospitals can promote consistency in patient management by establishing clear thresholds for intervention and delineating definitive action plans. These guidelines must empower nurses and healthcare professionals to act promptly upon observing signs of patient decline, providing them with the necessary resources and support for effective execution.
Explain how nurses can help coordinate care to increase patient safety and reduce costs.
Coordinating Care to Increase Patient Safety
Here, we will explore how to coordinate care to increase patient safety.
- Explain the role of nurses in coordinating care to enhance patient safety.
- Highlight the importance of effective communication and collaboration among healthcare team members.
- Discuss how nurses can streamline processes and implement standardized protocols to reduce errors and improve outcomes.
- Provide examples of successful care coordination initiatives impacting patient safety and cost reduction.
Example
Nurses play a pivotal role in safeguarding patient safety, particularly in detecting and managing deteriorating health conditions. Studies by Bucknall et al. (2022) and Ullah et al. (2022) underscore the indispensable role of nursing in this vital aspect of healthcare. Beyond routine vital signs monitoring, nurses are instrumental in the early identification of worsening illnesses, aiming to prevent adverse health events by promptly addressing even subtle changes in patients’ conditions.
Moreover, nurses are central in facilitating swift and appropriate interventions. Upon identifying potential risks, nurses are responsible for effectively communicating this information to the medical team and initiating necessary medical responses (Bucknall et al., 2022). This role necessitates quick decision-making and clear communication of the situation’s urgency, positioning nurses as pivotal links between patients and the broader medical team (Bucknall et al., 2022; Ullah et al., 2022).
Identify stakeholders with whom nurses would coordinate to drive safety enhancements with a specific safety quality issue.
Identifying Stakeholders for Safety Enhancements
This section of NURS-FPX 4020 Assessment One: Enhancing Quality and Safety will identify stakeholders for safety enhancements.
- Identify critical stakeholders involved in addressing the chosen safety quality issue.
- Consider healthcare providers, administrators, patients, families, regulatory agencies, and quality improvement teams.
- Explain how collaboration with stakeholders can drive safety enhancements and facilitate the implementation of evidence-based strategies.
- Highlight the importance of engaging stakeholders throughout the improvement process to ensure sustainability and effectiveness.
Example
Nurses’ engagement in interdisciplinary teamwork and collaboration enhances patient care. Nurses collaborating with various healthcare professionals, including physicians and specialists, foster a holistic approach to patient treatment and management. Additionally, nurses are crucial in partnering with hospital management to drive improvements in patient safety systems. Their involvement in proposing policy revisions, developing safety protocols, and advocating for essential patient monitoring and care resources is indispensable. These contributions by nurses are instrumental in shaping healthcare environments that prioritize patient safety and deliver high-quality care.
Stakeholders in Quality Improvement
Various stakeholders play interconnected yet distinct roles in healthcare quality improvement. Healthcare professionals, such as physicians and nurses, are on the front lines and deeply involved in patient care and safety. Their direct experiences and perspectives are crucial for identifying improvement opportunities and implementing changes. Equally important are hospital administrators and policymakers, who have the authority to implement broad reforms, allocate resources, and establish policies that significantly influence the quality and safety of patient care.
Collaborative Strategies for Safety Enhancement
Collaboration among all stakeholders is essential for enhancing safety. Research by Considine et al. (2021) and Bucknall et al. (2022) emphasizes the importance of multidisciplinary cooperation in recognizing and managing patient deterioration. This collaboration goes beyond individual responsibilities, encouraging collective efforts that leverage diverse skills and perspectives to improve patient outcomes.
The integration of efforts from both clinical staff and administrative bodies is vital. Healthcare professionals provide the practical knowledge and experience to identify and address patient safety risks. At the same time, hospital management and policymakers support these safety measures through training investments, infrastructure improvements, and protocol revisions to align with contemporary best practices (Bucknall et al., 2022).
Closing
In conclusion, NURS-FPX 4020 Assessment One: Enhancing Quality and Safety How-To Guide equips students with the essential tools to address safety quality issues in healthcare. Nurses can significantly enhance patient safety and reduce costs by selecting relevant issues, incorporating evidence-based strategies, fostering care coordination, identifying stakeholders, and communicating effectively. Remember, proficiency in these competencies is achievable through dedication, critical thinking, and adherence to professional standards.
References
Bucknall, T., Considine, J., Harvey, G., Graham, I. D., Rycroft‐Malone, J., Mitchell, I., Saultry, B., Watts, J. J., Mohebbi, M., Mudiyanselage, S. B., Lotfaliany, M., & Hutchinson, A. (2022). Prioritizing Nurses’ Responses To deteriorating Patient Observations (PRONTO): a pragmatic cluster randomized controlled trial evaluating the effectiveness of a facilitation intervention on recognition and response to clinical deterioration. BMJ Quality & Safety, bmjqs-013785. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjqs2021-013785
Considine, J., Fry, M., Curtis, K., & Shaban, R. Z. (2021). Systems for recognition and response to deteriorating emergency department patients: a scoping review. Scandinavian Journal of Trauma, Resuscitation and Emergency Medicine, 29(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13049-021-00882-6
Gertz, A., Pollack, C. C., Schultheiss, M. D., & Brownstein, J. S. (2022). Delayed medical care and underlying health in the United States during the COVID-19 pandemic: A cross-sectional study. Preventive Medicine Reports, 28, 101882. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmedr.2022.101882
Ullah, E., Albrett, J., Khan, O., Matthews, C., Perry, I., GholamHosseini, H., & Lu, J. (2022). Workload involved in vital signs-based monitoring & responding to deteriorating patients: A single-site experience from a regional New Zealand hospital. Heliyon, 8(10), e10955. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e10955
NURS-FPX 4020 Assessment 2: Root-Cause Analysis and Safety Improvement Plan
Instructions for NURS-FPX 4020 Assessment 2: Root-Cause Analysis and Safety Improvement Plan
Root-Cause Analysis and Safety Improvement Plan
For this assessment, you can use a supplied template to conduct a root-cause analysis. The completed assessment will be a scholarly paper focusing on a quality or safety issue in a health care setting of your choice, as well as a safety improvement plan.
Collapse All
Introduction
As patient safety concerns continue to be addressed in the health care settings, nurses can play an active role in implementing safety improvement measures and plans. Often, root-cause analyses are conducted and safety improvement plans are created to address sentinel or adverse events such as medication errors, patient falls, wrong-site surgery events, and hospital-acquired infections. Performing a root-cause analysis offers a systematic approach for identifying causes of problems, including process and system-check failures. Once the causes of failures have been determined, a safety improvement plan can be developed to prevent recurrences. The baccalaureate nurse’s role as a leader is to create safety improvement plans as well as disseminate vital information to staff nurses and other health care professionals to protect patients and improve outcomes.
As you prepare for this assessment, it would be an excellent choice to complete the Quality and Safety Improvement Plan Knowledge Base activity and to review the various assessment resources, all of which will help you build your knowledge of key concepts and terms related to quality and safety improvement. The terms and concepts will be helpful as you prepare your Root-Cause Analysis and Safety Improvement Plan. Activities are not graded and demonstrate course engagement.
Professional Context
Nursing practice is governed by health care policies and procedures as well as state and national regulations developed to prevent problems. Nurses must participate in gathering and analyzing data to determine causes of patient safety issues, in solving problems, and in implementing quality improvements.
Scenario
For this assessment, use the specific safety concern identified in your previous assessment as the subject of a root-cause analysis and safety improvement plan.
Instructions
The purpose of this assessment is to demonstrate your understanding of and ability to analyze the root cause of a specific safety concern in a health care setting. You will create a plan to improve the safety of patients related to the safety quality issue presented in your Assessment Supplement PDF in Assessment 1. Based on the results of your analysis, using the literature and professional best practices as well as the existing resources at your chosen health care setting, provide a rationale for your plan.
Use the Root-Cause Analysis and Improvement Plan [DOCX] template to help you stay organized and concise. This will guide you step-by-step through the root cause analysis process.
Additionally, be sure that your plan addresses the following, which corresponds to the grading criteria in the scoring guide. Please study the scoring guide carefully so you understand what is needed for a distinguished score.
- Analyze the root cause of a specific patient safety issue in an organization.
- Apply evidence-based and best-practice strategies to address the safety issue.
- Create a feasible, evidence-based safety improvement plan to address a specific patient safety issue.
- Identify organizational resources that could be leveraged to improve your plan.
- Communicate in writing that is clear, logical, and professional, with correct grammar and spelling, using current APA style.
Example Assessment: You may use the following to give you an idea of what a Proficient or higher rating on the scoring guide would look like, but keep in mind that your Assessment 2 will focus on the quality issue you selected in Assessment 1.
- Assessment 2 Example [PDF] Download Assessment 2 Example [PDF].
Additional Requirements
- Length of submission: Use the provided Root-Cause Analysis and Improvement Plan template to create a 4–6 page root cause analysis and safety improvement plan about a specific patient safety issue.
- Number of references: Cite a minimum of 3 sources of scholarly or professional evidence that support your findings and considerations. Resources should be no more than 5 years old.
- APA formatting: Format references and citations according to current APA style.
Competencies Measured
By completing this assessment, you will demonstrate your proficiency in the course competencies through the following assessment scoring guide criteria:
- Competency 1: Analyze the elements of a successful quality improvement initiative.
- Apply evidence-based and best-practice strategies to address the safety issue.
- Create a feasible, evidence-based safety improvement plan to address a specific patient safety issue.
- Competency 2: Analyze factors that lead to patient safety risks.
- Analyze the root cause of a specific patient safety issue in an organization.
- Competency 3: Identify organizational interventions to promote patient safety.
- Identify organizational resources that could be leveraged to improve your plan.
- Competency 5: Apply professional, scholarly, evidence-based strategies to communicate in a manner that supports safe and effective patient care.
- Organize content so ideas flow logically with smooth transitions; contains few errors in grammar or punctuation, word choice, and spelling.
- Apply APA formatting to in-text citations and references exhibiting nearly flawless adherence to APA format.
Resources
Use the resources linked below to help complete this assessment.
Collapse All
Evidence-Based Practice
The following readings may help you in completing this assessment’s activities:
- Assessment 2: Evidence-Based Practice reading list.
Quality and Safety
The following readings may help you in completing this assessment’s activities:
- Assessment 2: Quality and Safety reading list.
Root-Cause Analysis
The following readings may help you in completing this assessment’s activities:
- Assessment 2: Root-Cause Analysis reading list.
Sentinel Events
The following readings may help you in completing this assessment’s activities:
- Assessment 2:Sentinel Events reading list.
Safety and Sentinel Event Case Studies
The following readings may help you in completing this assessment’s activities:
- Assessment 2:Safety and Sentinel Event Case Studies reading list.
Program Resources
Capella Writing Center
- Writing Center.
- Access the various resources in the Capella Writing Center to help you better understand and improve your writing.
APA Style and Format
- Capella University follows the style and formatting guidelines in the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association, known informally as the APA manual. Refer to the Writing Center’s APA Module for tips on proper use of APA style and format.
Capella University Library
- BSN Program Library Research Guide.
- The library research guide will be useful in guiding you through the Capella University Library, offering tips for searching the literature and other references for your assessments.
Activity
Click the linked title below, Quality and Safety Improvement Plan Knowledge Base, to complete this formative activity, which will help you check and build your knowledge of key concepts and terms related to quality and safety improvement. These terms and concepts will be useful as you prepare your Root Cause Analysis and Improvement Plan. This is for your own practice and self-assessment.
This tool needs to be loaded in a new browser window
Introduction to NURS 4020 Assessment Two
The NURS-FPX 4020 Assessment 2: Root-Cause Analysis and Safety Improvement Plan is designed to help you understand and analyze the root cause of a specific patient safety issue within a healthcare setting. By conducting a root-cause analysis, applying evidence-based strategies, and developing a feasible safety improvement plan, you will demonstrate your ability to improve patient safety and quality of care. This How-To NURS-FPX 4020 Guide provides step-by-step instructions on completing each part of the assignment, ensuring a clear, logical, and professional approach.
Analyze the root cause of a specific patient safety issue in an organization.
Conducting a Root-Cause Analysis
We will conduct a root-cause analysis to start the NURS-FPX 4020 Assessment 2: Root-Cause Analysis and Safety Improvement Plan.
- Identify the Problem: Clearly define the specific patient safety issue you focus on (e.g., medication errors, patient falls).
- Gather Data: Collect data related to the issue from your healthcare setting. This may include incident reports, patient records, and staff interviews.
- Analyze the Data: Use tools such as fishbone diagrams or the 5 Whys technique to systematically identify the root causes of the problem.
- Identify Contributing Factors: Determine the process and system failures contributing to the safety issue.
Example
The sentinel event under review, as described by Olson (2023), involves several critical incidents in Minnesota hospitals, leading to 21 preventable deaths and 178 serious injuries. This root cause analysis seeks to understand the factors contributing to these events, which include surgical errors, medication mishandling, and insufficient responses to patient conditions. Hospital administrators and quality assurance personnel identified these issues through adverse event reporting systems and internal audits. The events primarily impacted patients who received incorrect or delayed care, resulting in severe health complications and deaths, along with emotional distress. Additionally, healthcare providers faced scrutiny, prompting procedural reevaluations and potential legal implications.
Analysis of the Event and Relevant Findings
The sentinel events detailed by Olson (2023), involving a series of critical incidents in Minnesota hospitals, underscore the importance of identifying various underlying factors. These incidents led to severe outcomes, including preventable deaths and injuries, due to a range of errors, such as surgical mistakes, medication mishandling, and lapses in patient care.
Intended Procedure
Standard healthcare protocols for various procedures were either improperly followed or overlooked in these cases. This includes protocols for medication administration, surgical procedures, and general patient care guidelines.
Environmental Factors
As Olson (2023) noted, the healthcare environment was strained by high patient volumes and staff shortages, exacerbated by the pandemic. These conditions created a challenging operational environment, increasing the risk of errors.
Equipment and Resource Influence
Xie et al. (2021) highlight the impact of resource limitations, particularly staffing shortages, on patient safety. In these Minnesota incidents, inadequate staffing likely contributed to errors across multiple areas, including surgery and patient monitoring, due to rushed procedures and a lack of oversight.
Human Error Contribution
Various human errors contributed to these incidents, ranging from misinterpretation of medication labels and surgical plans to incorrect execution of medical procedures. Factors like fatigue, stress, or heavy workloads among healthcare staff could have influenced these errors.
Communication Factors
Wu and colleagues (2023) emphasize the importance of effective communication within healthcare environments. The reported adverse events in the Minnesota hospital episodes were likely caused by communication breakdowns among medical staff, including nurses, surgeons, pharmacists, and other healthcare professionals.
Root Causes Identified
Olson (2023) highlighted incidents in Minnesota hospitals where there was a pervasive failure to follow healthcare protocols, affecting various services such as medication administration, surgical procedures, and patient care. Staffing and resource shortages were key contributors to these incidents, as Olson (2023) and Xie et al. (2021) emphasized. These deficits increased risks and compromised patient care. Wu et al. (2023) identified inadequate communication within healthcare teams as a major factor. This breakdown led to errors in medication administration, surgical procedures, and care management, worsening the effects of the existing strains on the healthcare system.
Apply evidence-based and best-practice strategies to address the safety issue.
Applying Evidence-Based and Best-Practice Strategies
Next, we will apply evidence-based strategies.
- Research Best Practices: Review the literature and professional guidelines for the specific safety issue. Identify evidence-based strategies that have been proven effective.
- Evaluate Applicability: Assess how these strategies can be adapted to your healthcare setting. Consider the feasibility and potential impact of each strategy.
Example
Implementing evidence-based strategies to address drug mismanagement, surgical errors, and patient care deficiencies is essential, especially considering the serious errors identified in Minnesota hospitals by Olson (2023). These strategies should be grounded in current research and best practices from healthcare policies, recognizing the complex nature of these issues and providing a framework for mitigation and prevention.
Factors Leading to Safety Issues
Medication Errors. As identified in the root cause analysis, interruptions during medication administration significantly influenced medication errors. Strategies such as increasing staffing levels, reducing workloads, and enhancing communication channels should be implemented to minimize these errors. This approach aligns with the findings of Wu et al. (2023) and Olson (2023), which emphasize the importance of a stable environment for medication delivery.
Patient Falls. The PRONTO trial by Bucknall et al. (2022) underscores the importance of early detection and response to clinical deterioration to prevent incidents like patient falls. Nursing interventions are crucial in identifying at-risk patients through regular vital sign monitoring and adherence to clinical practice guidelines.
Wrong-Site Surgery. Gertz et al. (2022) highlight that issues related to workload and staffing levels contribute to wrong-site surgeries. Implementing standardized presurgical procedures and checklists can mitigate these issues. This ensures consistency and accuracy in surgical practices, reducing the likelihood of such critical errors.
Hospital-Acquired Infections. Ullah et al. (2022) emphasize the significant workload involved in monitoring patients and responding to signs of deterioration, which is crucial in preventing hospital-acquired infections. Hirschhorn et al. (2021) support that streamlining this process with electronic vital sign systems can significantly reduce infection risks.
Addressing Safety Issues through Best Practices
To reduce medication errors, creating a ‘no-interruption’ zone during medication preparation and utilizing electronic medication administration records (EMARs) can significantly decrease mistakes. Educating patients and their families about medication safety, as suggested by Wu et al. (2023), is also vital. Considine et al. (2021) recommend comprehensive Rapid Response Systems (RRS) in the Emergency Department and ongoing staff training and simulation exercises to minimize medication errors and enhance patient safety.
Improving environmental safety through non-slip flooring, assistive technology, and adequate lighting is essential. Including patients and their families in fall prevention strategies and providing continuous staff training on fall prevention and risk assessment are crucial steps.
The World Health Organization advises using a systematic surgical safety checklist to reduce the incidence of wrong-site surgery significantly. Preoperative conferences and involving patients in labeling the surgical site can also enhance safety.
Adhering strictly to infection control practices, such as personal protective equipment and regular hand washing, is essential to prevent hospital-acquired infections. Maintaining environmental cleanliness and educating staff on infection control are also critical. Ullah et al. (2022) propose that transitioning from hand-written to digital tracking of vital signs could reduce nurses’ workloads, allowing for more attentive patient care and lowering the incidence of hospital-acquired infections.
Create a feasible, evidence-based safety improvement plan to address a specific patient safety issue.
Creating a Safety Improvement Plan
Here, we will create a safety improvement plan.
- Set Goals: Define clear, measurable goals for your improvement plan. These should be specific to the identified safety issue.
- Develop Interventions: Based on your root-cause analysis and research, outline the interventions you will implement to address the root causes.
- Create an Implementation Plan: Detail the steps, timeline, and responsible parties for implementing each intervention.
- Monitor and Evaluate: Plan for ongoing monitoring and evaluation to measure the effectiveness of your interventions.
Example
A comprehensive improvement plan is proposed in response to the significant occurrences of medication errors, surgical errors, and patient care deficiencies in Minnesota hospitals. This plan is based on root cause analysis and is supported by recent research and best practices in healthcare.
Actions, New Processes, or Policies
We standardized Surgical Protocols and Checklists. The strategy recommends implementing standardized surgical protocols and checklists to prevent wrong-site and other surgical errors, as Gertz et al. (2022) highlighted.
Staff Training and Professional Development. The plan includes ongoing training programs for nurses and healthcare workers, focusing on early recognition of patient deterioration, adherence to clinical guidelines, and effective communication skills, in line with the recommendations of Bucknall et al. (2022).
Enhancement of Communication Protocols. Drawing from Olson (2023), the plan advocates for establishing clear and effective communication channels among healthcare professionals. This includes leveraging technology to ensure the timely sharing of critical test results and patient information.
Adoption of Technology for Patient Monitoring. Inspired by Ullah et al.’s (2022) findings, the strategy suggests integrating electronic monitoring systems for patient vital signs. This will reduce nurses’ manual workload and enable more accurate and timely responses to patient needs.
Goals or Desired Outcomes
Reduction in Specific Patient Safety Events. Significantly minimize medication errors, surgical mistakes, and patient care lapses, particularly focusing on wrong-site surgeries and medication mismanagement.
It enhanced Staff Competency in Patient Safety. Improve the medical staff’s ability to recognize and address patient safety issues, especially in surgery and drug administration.
It strengthened the Patient Safety Culture. In line with Wu et al. (2023), the plan aims to increase patient and family involvement in the care process, fostering a patient-centered care and safety culture.
Rough Timeline for Development and Implementation
Initial Phase (0-3 Months). Develop standardized surgical and medication protocols. Begin comprehensive staff training. Implement communication and electronic monitoring systems.
Intermediate Phase (4-6 Months). Pilot new protocols in selected departments. Continue staff training and evaluate the effectiveness of communication. Integrate electronic monitoring in key areas.
Final Phase (7-12 Months). Implement standardized protocols throughout the facility. Expand electronic monitoring to all departments. Maintain ongoing staff development and feedback mechanisms.
Evaluation and Adjustment (Post-12 Months). Regularly assess the new systems to reduce errors. Make adjustments based on feedback and outcomes.
This plan is built on scholarly evidence and practical strategies. It targets the root causes of identified patient safety issues. Its implementation is expected to significantly enhance patient safety and quality of care in healthcare.
Identify organizational resources that could be leveraged to improve your plan.
Identifying Organizational Resources
We will explore the organizational resources for this NURS-FPX 4020 Assessment 2: Root-Cause Analysis and Safety Improvement Plan section.
- Assess Resources: Identify existing resources within your organization that can support your safety improvement plan. This may include staff training programs, technology, and financial resources.
- Leverage Support: Determine how to utilize these resources to enhance your plan’s success. Engage key stakeholders and secure the necessary support.
Example
Existing Organizational Resources
Leveraging existing organizational resources is crucial for successfully implementing the safety improvement plan addressing critical incidents in Minnesota hospitals. This ensures the efficient use of available assets and facilitates the integration of new strategies.
Human Resources
Nursing Staff. Experienced nurses play a vital role in frontline healthcare, ensuring patient safety. Their expertise is crucial in mentoring new nurses, particularly in key practices such as medication administration and patient monitoring, fostering a strong safety culture.
Patient Safety Officers oversee safety protocols, especially in surgical settings, and coordinate strategies to address identified safety issues.
Interdisciplinary Teams. Collaboration among physicians, pharmacists, nurses, and other healthcare professionals ensures that complex care scenarios are managed with diverse expertise, essential for a comprehensive approach to patient safety.
Technological Resources
Electronic Health Records (EHR). EHRs are essential for ensuring the accuracy of surgical procedures, controlling medication errors, and monitoring patient data.
Patient Monitoring Systems. These technologies significantly reduce the likelihood of patient care errors and are crucial for the early detection of patient deterioration.
Educational and Training Materials
Online Learning Platforms. These platforms facilitate efficient staff training on new safety protocols and procedures related to medication management and surgical safety.
Simulation Training Tools. Simulation training provides hands-on experience managing patient safety scenarios, particularly in surgical settings.
Policy and Governance Frameworks
Safety Policies and Guidelines. Safety policies must be regularly updated and revised to align with the latest advancements in patient safety best practices.
Quality Improvement Committees. These committees are essential for guiding the execution of the safety improvement strategy, ensuring its alignment with the organization’s overarching goals.
Demonstration of Proficiency
Competency 1: Analyze the elements of a successful quality improvement initiative.
Competency 2: Analyze factors that lead to patient safety risks.
Competency 3: Identify organizational interventions to promote patient safety.
Competency 5: Apply professional, scholarly, evidence-based strategies to communicate in a manner that supports safe and effective patient care.
These competencies are designed to guide you through completing the assessment. They provide a framework to ensure that your work is thorough, evidence-based, and professionally communicated.
Closing
Completing the NURS-FPX 4020 Assessment 2: Root-Cause Analysis and Safety Improvement Plan will enhance your ability to identify and address patient safety issues through systematic analysis and strategic planning. Following this How-To Owlisdom Guide, you can create a comprehensive safety improvement plan that leverages organizational resources and adheres to best practices. The NURS-FPX 4020 Assessment 2: Root-Cause Analysis and Safety Improvement Plan demonstrates your proficiency in quality care and patient safety. It prepares you to take on leadership roles in healthcare settings, contributing to improved patient outcomes and safer care environments.
NURS-FPX 4020 Assessment Three: Improvement Plan In-Service Presentation
Instructions for NURS-FPX 4020 Assessment Three: Improvement Plan In-Service Presentation
Improvement Plan In-Service Presentation
For this assessment, you will develop an 8–14 slide PowerPoint presentation with thorough speaker’s notes designed for a hypothetical in-service session related to the improvement plan you developed in Assessment 2.
Collapse All
Introduction
As a practicing professional, you are likely to present educational in-services or training to staff pertaining to quality improvement (QI) measures of safety improvement interventions. Such in-services and training sessions should be presented creatively and innovatively to hold the audience’s attention and promote knowledge acquisition and skill application that changes practice for the better. The teaching sessions may include a presentation, audience participation via simulation or other interactive strategy, audiovisual media, and participant learning evaluation.
The use of in-services and/or training sessions has positive implications for nursing practice by increasing staff confidence when providing care to specific patient populations. It also allows for a safe and nonthreatening environment where staff nurses can practice their skills before a real patient event. Participation in learning sessions fosters a team approach, collaboration, patient safety, and greater patient satisfaction rates in the health care environment (Patel & Wright, 2018).
As you prepare to complete the assessment, consider the impact of in-service training on patient outcomes as well as practice outcomes for staff nurses. Be sure to support your thoughts on the effectiveness of educating and training staff to increase the quality of care provided to patients by examining the literature and established best practices.
You are encouraged to explore the AONE Nurse Executive Competencies Review activity before you develop the Improvement Plan In-Service Presentation. This activity will help you review your understanding of the AONE Nurse Executive Competencies—especially those related to competencies relevant to developing an effective training session and presentation. This is for your own practice and self-assessment, and demonstrates your engagement in the course.
Reference
Patel, S., & Wright, M. (2018). Development of interprofessional simulation in nursing education to improve teamwork and collaboration in maternal-child nursing. Journal of Obstetric, Gynecologic & Neonatal Nursing, 47(3), s16–s17.
Professional Context
As a baccalaureate-prepared nurse, you will often find yourself in a position to lead and educate other nurses. This colleague-to-colleague education can take many forms, from mentoring to informal explanations on best practices to formal in-service training. In-services are an effective way to train a large group. Preparing to run an in-service may be daunting, as the facilitator must develop his or her message around the topic while designing activities to help the target audience learn and practice. By improving understanding and competence around designing and delivering in-service training, a BSN practitioner can demonstrate leadership and prove him- or herself a valuable resource to others.
Scenario
For this assessment, build on the work that you have done in your first two assessments and create an agenda and PowerPoint of an educational in-service session that would help a specific staff audience learn, provide feedback, and understand their roles and practice new skills related to the safety improvement plan you created.
Instructions
The final deliverable for this assessment will be a PowerPoint presentation with detailed presenter’s notes representing the material you would deliver at an in-service session to raise awareness of your chosen safety improvement initiative, focusing on a specific patient safety issue, and to explain the need for such an initiative. Additionally, you must educate the audience as to their role and importance to the success of the initiative. This includes providing examples and practice opportunities to test out new ideas or practices related to the safety improvement initiative.
Be sure that your presentation addresses the following, which corresponds to the grading criteria in the scoring guide. Please study the scoring guide carefully so you understand what is needed for a distinguished score.
- Describe the purpose and goals of an in-service session focusing on a specific patient safety issue.
- Explain the need for and process to improve safety outcomes related to a specific patient safety issue.
- Explain to the audience their role and the importance of making the improvement plan successful.
- Create resources or activities to encourage skill development and process understanding related to a safety improvement initiative.
- Communicate with nurses in a respectful and informative way that clearly presents expectations and solicits feedback on communication strategies for future improvement.
There are various ways to structure an in-service session; below is just one example:
- Part 1: Agenda and Outcomes.
- Explain to your audience what they are going to learn or do, and what they are expected to take away.
- Part 2: Safety Improvement Plan.
- Give an overview of the current problem, focusing on a specific patient safety issue, the proposed plan, and what the improvement plan is trying to address.
- Explain why it is important for the organization to address the current situation.
- Part 3: Audience’s Role and Importance.
- Discuss how the staff audience will be expected to help implement and drive the improvement plan.
- Explain why they are critical to the success of the improvement plan, focusing on a specific patient safety issue.
- Describe how their work could benefit from embracing their role in the plan.
- Part 4: New Process and Skills Practice.
- Explain new processes or skills.
- Develop an activity that allows the staff audience to practice and ask questions about these new processes and skills.
- In the notes section of your PowerPoint, brainstorm potential responses to likely questions or concerns.
- Part 5: Soliciting Feedback.
- Describe how you would solicit feedback from the audience on the improvement plan and the in-service.
- Explain how you might integrate this feedback for future improvements.
Remember to account for activity and discussion time.
For tips on developing PowerPoint presentations, refer to:
- Capella University Library: PowerPoint Presentations.
- Guidelines for Effective PowerPoint Presentations [PPTX].
Additional Requirements
- Presentation length: There is no required length; use just enough slides to address all the necessary elements. Remember to use short, concise bullet points on the slides and expand on your points in the presenter’s notes. If you use 2 or 3 slides to address each of the parts in the above example, your presentation would be at least 10 slides and no more than 15 slides (not including the title, conclusion, or reference slides).
- Speaker notes: Speaker notes (located under each slide) should reflect what you would actually say if you were delivering the presentation to an audience. This presentation does NOT require audio or a transcript. Another presenter would be able to use the presentation by following the speaker’s notes.
- APA format: Use APA formatting for in-text citations. Include an APA-formatted reference slide at the end of your presentation.
- Number of references: Cite a minimum of 3 sources of scholarly or professional evidence to support your assertions. Resources should be no more than 5 years old.
Competencies Measured
By completing this assessment, you will demonstrate your proficiency in the course competencies through the following assessment scoring guide criteria:
- Competency 1: Analyze the elements of a successful quality improvement initiative.
- Explain the need for and process to improve safety outcomes related to a specific patient safety issue.
- Create resources or activities to encourage skill development and process understanding related to a safety improvement initiative.
- Competency 4: Explain the nurse’s role in coordinating care to enhance quality and reduce costs.
- Describe the purpose and goals of an in-service session focusing on a specific patient safety issue.
- Explain to the audience their role and the importance of making the improvement plan successful.
- Competency 5: Apply professional, scholarly, evidence-based strategies to communicate in a manner that supports safe and effective patient care.
- Slides are easy to read and error-free. Detailed speaker notes are provided. Speaker notes are clear, organized, and professionally presented.
- Organize content with a clear purpose or goals and with relevant and evidence-based sources (published within 5 years).
Resources
Use the resources linked below to help complete this assessment.
Collapse All
Leadership Competencies
The following readings may help you in completing this assessment’s activities:
- Assessment 3: Leadership Competencies reading list.
Evidence and Value-Based Decision Making
The following readings may help you in completing this assessment’s activities:
- Assessment 3: Evidence and Value-Based Decision Making reading list.
Facilitating Learning
The following readings may help you in completing this assessment’s activities:
- Assessment 3: Facilitating Learning Reading List.
Program Resources
Capella Writing Center
- Writing Center.
- Access the various resources in the Capella Writing Center to help you better understand and improve your writing.
APA Style and Format
- Capella University follows the style and formatting guidelines in the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association, known informally as the APA manual. Refer to the Writing Center’s APA Module for tips on proper use of APA style and format.
Capella University Library
- BSN Program Library Research Guide.
- The library research guide will be useful in guiding you through the Capella University Library, offering tips for searching the literature and other references for your assessments.
PowerPoint
Refer to these helpful Campus resources for PowerPoint tips:
- Capella University Library: PowerPoint Presentations.
- Guidelines for Effective PowerPoint Presentations [PPTX].
Activity
Click the linked title below, AONE Nurse Executive Competencies Review, to complete this formative activity, which will help you review your understanding of the AONE Nurse Executive Competencies—especially those related to competencies relevant to developing an effective training session and presentation. This is for your own practice and self-assessment.
This tool needs to be loaded in a new browser window
Introduction to NURS 4020 Assessment Three
The NURS-FPX 4020 Assessment Three: Improvement Plan In-Service Presentation focuses on developing an educational in-service session to improve patient safety through quality improvement initiatives. As healthcare professionals, presenting effective training sessions to staff promotes knowledge acquisition and enhances patient care quality. This How-To NURS-FPX 4020 Guide outlines the key components for a successful in-service session, emphasizing the importance of clear communication, staff engagement, and interactive learning strategies.
Describe the purpose and goals of an in-service session focusing on a specific patient safety issue.
Purpose and Goals of an In-Service Session
To start the NURS-FPX 4020 Assessment Three: Improvement Plan In-Service Presentation, we will first discuss the purpose and goals of an in-service session.
Understanding the Patient Safety Issue
- Clearly define the specific patient safety issue that will be addressed.
- Provide background information and context to ensure all participants understand the issue.
Example

Setting Clear Objectives
- Identify the goals you aim to achieve with the in-service session.
- Ensure the objectives are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
Example

Explain the need for and process to improve safety outcomes related to a specific patient safety issue.
Need for and Process to Improve Safety Outcomes
Next, we will discuss the need and the processes to improve safety outcomes.
Identifying the Safety Issue
- Conduct a thorough root-cause analysis to understand the underlying factors contributing to the safety issue.
- Use evidence-based research to support your findings.
Example
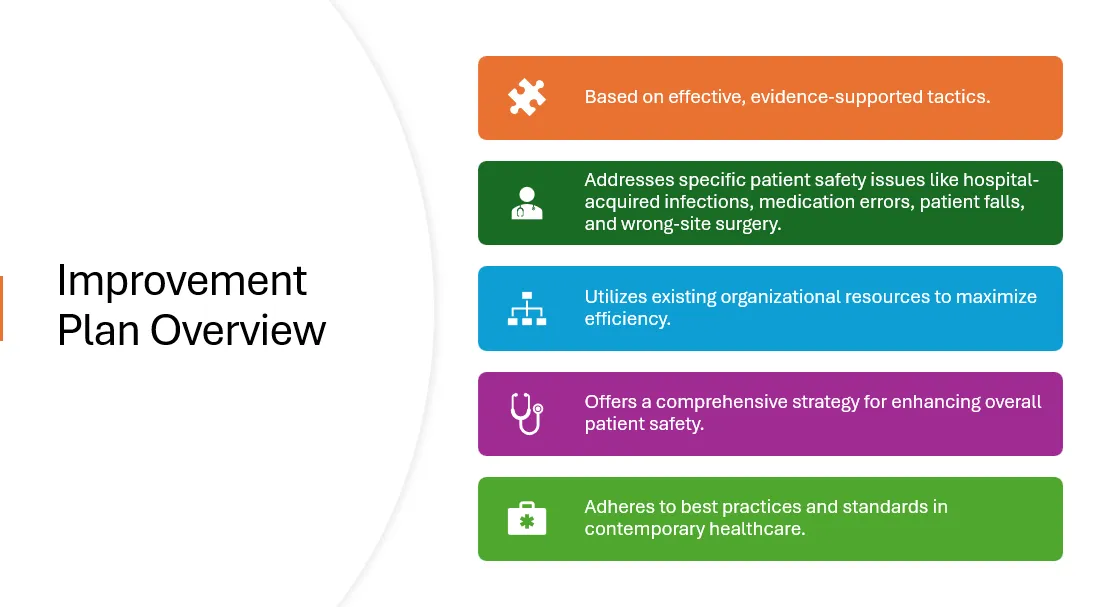
Developing an Improvement Plan
- Outline a step-by-step process to address the identified safety issue.
- Include strategies that have been proven effective in similar settings.
Example

Explain to the audience their role and the importance of making the improvement plan successful.
Role and Importance of Staff in the Improvement Plan
Here, we will explore the role and importance of staff in the improvement plan.
Engaging Staff in the Process
- Highlight the importance of staff participation in the success of the improvement plan.
- Use motivational techniques to encourage active involvement.
Defining Roles and Responsibilities
- Clearly define the roles of each staff member in implementing the improvement plan.
- Provide specific examples of how each role contributes to overall success.
Example

Create resources or activities to encourage skill development and process understanding related to a safety improvement initiative.
Resources and Activities for Skill Development
This section will discuss the resources and activities for skill development.
Creating Effective Training Materials
- Develop resources such as handouts, slides, and videos that reinforce the training objectives.
- Ensure the materials are easily accessible and user-friendly.
Implementing Interactive Learning Strategies
- Incorporate simulations, role-playing, and other interactive activities to enhance learning.
- Encourage hands-on practice to build confidence and competence.
Example

Communicate with nurses respectfully and informatively, clearly presenting expectations and soliciting feedback on communication strategies for future improvement.
Effective Communication with Nurses
For this segment of Assessment Three, we will discuss effective communication with the nurses.
Strategies for Clear and Respectful Communication
- Use simple, concise language to ensure understanding.
- Be respectful and empathetic in all communications to foster a positive learning environment.
Soliciting Feedback for Continuous Improvement
- Create opportunities for participants to provide feedback on the training session.
- Use the feedback to make necessary adjustments and improvements.
Example

Demonstration of Proficiency
- Analyzing Quality Improvement Initiatives
- Coordinating Care to Enhance Quality and Reduce Costs
- Applying Scholarly Communication Strategies
Closing
Completing the NURS-FPX 4020 Assessment Three: Improvement Plan In-Service Presentation will equip you with the skills necessary to develop and deliver effective in-service training sessions that improve patient safety and quality of care. By understanding the importance of clear communication, staff engagement, and interactive learning, you will be better prepared to lead initiatives that foster a culture of continuous improvement in healthcare settings. Remember, the competencies required are attainable with practice and dedication, providing you with a strong foundation for professional growth and excellence in patient care. In the upcoming NURS 4020 Assessment Four, we will discuss the improvement plan toolkit.
NURS-FPX 4020 ASSESSMENT FOUR: Improvement Plan Tool Kit
Instructions for NURS-FPX 4020 Assessment Four: Improvement Plan Tool Kit
ImprovementPlan Tool Kit
For this assessment, you will develop a Word document or an online resource repository of at least 12 annotated professional or scholarly resources that you consider critical for the audience of your safety improvement plan to understand or implement to ensure the success of the plan.
Collapse All
Introduction
Communication in the health care environment consists of an information-sharing experience, whether through oral or written messages (Chard & Makary, 2015). As health care organizations and nurses strive to create a culture of safety and quality care, the importance of interprofessional collaboration, the development of tool kits, and the use of wikis becomes more relevant and vital. In addition to the dissemination of information and evidence-based findings and the development of tool kits, continuous support for and availability of such resources are critical. Among the most popular methods to promote ongoing dialogue and information sharing are blogs, wikis, websites, and social media. Nurses know how to support people in times of need or crisis and how to support one another in the workplace; wikis in particular enable nurses to continue that support beyond the work environment. Here, they can be free to share their unique perspectives, educate others, and promote health care wellness at local and global levels (Kaminski, 2016).
You are encouraged to complete the Determining the Relevance and Usefulness of Resources activity prior to developing the repository. This activity will help you determine which resources or research will be most relevant to address a particular need. This may be useful as you consider how to explain the purpose and relevance of the resources you are assembling for your toolkit. The activity is for your own practice and self-assessment, and demonstrates course engagement.
References
Chard, R., & Makary, M. A. (2015). Transfer-of-care communication: Nursing best practices. AORN Journal, 102(4), 329–342.
Kaminski, J. (2016). Why should all nurses/be authors? Canadian Journal of Nursing Informatics, 11(4), 1–7.
Professional Context
Nurses are often asked to implement processes, concepts, or practices—sometimes with little preparatory communication or education. One way to encourage the sustainability of quality and process improvements is to assemble an accessible, user-friendly toolkit for knowledge and process documentation. Creating a resource repository or tool kit is also an excellent way to follow up on an educational or in-service session, as it can help to reinforce attendees’ new knowledge as well as the understanding of its value. By practicing creating a simple online tool kit, you can develop valuable technology skills to improve your competence and efficacy. This technology is easy to use, and resources are available to guide you.
Scenario
For this assessment, build on the work done in your first three assessments and create an online tool kit or resource repository that will help the audience of your in-service understand the research behind your safety improvement plan about a specific patient safety issue and put the plan into action.
Preparation
Google Sites is recommended for this assessment; the tools are free to use and should offer you a blend of flexibility and simplicity as you create your online tool kit. Please note that this requires a Google account; use your Gmail or Google Docs login, or create an account following the directions under the “Create Account” menu.
Refer to the resources on the following list to help you get started with Google Sites:
- Assessment 4: Google Sites reading list.
Instructions
Using Google Sites, assemble an online resource tool kit containing at least 12 annotated resources that you consider critical to the success of your safety improvement initiative. These resources should enable nurses and others to implement and maintain the safety improvement you have developed.
It is recommended that you focus on the 3 or 4 most critical categories or themes with respect to your safety improvement initiative. For example, for an initiative that concerns improving workplace safety for practitioners, you might choose broad themes such as general organizational safety and quality best practices; environmental safety and quality risks; individual strategies to improve personal and team safety; and process best practices for reporting and improving environmental safety issues.
Following the recommended scheme, you would collect 3 resources on average for each of the 4 categories, focusing on a specific patient safety issue. Each resource listing should include the following:
- An APA-formatted citation of the resource with a working link.
- A description of the information, skills, or tools provided by the resource.
- A brief explanation of how the resource can help nurses better understand or implement the safety improvement initiative regarding a specific patient safety issue.
- A description of how nurses can use this resource and when its use may be appropriate.
Remember that you must make your site “public” so that your faculty can access it. Check out the Google Sites resources for more information.
Here is an example entry:
- Merret, A., Thomas, P., Stephens, A., Moghabghab, R., & Gruneir, M. (2011). A collaborative approach to fall prevention. Canadian Nurse, 107(8), 24–29.
- This article presents the Geriatric Emergency Management-Falls Intervention Team (GEM-FIT) project. It shows how a collaborative nurse-led project can be implemented and used to improve collaboration and interdisciplinary teamwork, as well as improve the delivery of health care services. This resource is likely more useful to nurses as a resource for strategies and models for assembling and participating in an interdisciplinary team than for specific fall-prevention strategies. It is suggested that this resource be reviewed prior to creating an interdisciplinary team for a collaborative project in a health care setting.
Additionally, be sure that your plan addresses the following, which corresponds to the grading criteria in the scoring guide. Please study the scoring guide carefully so you understand what is needed for a distinguished score.
- Identify necessary resources to support the implementation and continued sustainability of a safety improvement initiative pertaining to a specific patient safety issue.
- Analyze the usefulness of resources to the role group responsible for implementing quality and safety improvements, focusing on a specific patient safety issue.
- Analyze the value of resources to reduce patient safety risk related to a specific patient safety issue.
- Present reasons and relevant situations for the use of the resource tool kit by its target audience.
- Communicate in a clear, logically structured, and professional manner that applies current APA style and formatting.
Example Assessment: You may use the following example to give you an idea of what a Proficient or higher rating on the scoring guide would look like, but keep in mind that your toolkit will focus on promoting safety with the quality issue you selected in Assessment 1. Note that you do not have to submit your bibliography in addition to the Google Site; the example bibliography is merely for your reference.
- Assessment 4 Example [PDF] Download Assessment 4 Example [PDF].
To submit your online tool kit assessment, paste the link to your Google Site in the assessment submission box.
Example Google Site: You may use the example found on the Assessment 4: Google Sites reading list, Resources for Improved Heparin Infusion Safety, to give you an idea of what a Proficient or higher rating on the scoring guide would look like for this assessment but keep in mind that your tool kit will focus on promoting safety with the quality issue you selected in Assessment 1
Note: If you experience technical or other challenges in completing this assessment, please contact your faculty member.
Competencies Measured
By completing this assessment, you will demonstrate your proficiency in the course competencies through the following assessment scoring guide criteria:
- Competency 1: Analyze the elements of a successful quality improvement initiative.
- Analyze the usefulness of resources to the role group responsible for implementing quality and safety improvements, focusing on a specific patient safety issue.
- Competency 2: Analyze factors that lead to patient safety risks.
- Analyze the value of resources to reduce patient safety risk related to a specific patient safety issue.
- Competency 3: Identify organizational interventions to promote patient safety.
- Identify necessary resources to support the implementation and continued sustainability of a safety improvement initiative pertaining to a specific patient safety issue.
- Competency 5: Apply professional, scholarly, evidence-based strategies to communicate in a manner that supports safe and effective patient care.
- Present reasons and relevant situations for the resource tool kit to be used by its target audience.
- Communicate the resource tool kit in a clear, logically structured, and professional manner that applies current APA style and formatting.
Resources
Use the resources linked below to help complete this assessment.
Collapse All
Collaborationand Teamwork
The following readings may help you in completing this assessment’s activities:
- Assessment 4: Collaboration and Teamwork reading list.
Wikis, Blogs, and Google Sites
The following readings may help you in completing this assessment’s activities:
Wikis
- Assessment 4: Wikis reading list.
Blogs
- Assessment 4:Blogs.
Google Sites
Refer to the resources on this list to help you build your tool kit:
- Assessment 4: Google Sites reading list.
Building Professional Efficacy and Visibility
The following readings may help you in completing this assessment’s activities:
- Assessment 4:Building Professional Efficacy and Visibility reading list.
Evaluating Resources
- Assessment 4: Evaluating Resources.
- This reading may help you in completing this assessment’s activities:
- Think Critically About Source Quality.
- This Capella University Library guide offers a method to help you determine which resources to include in your tool kit.
Program Resources
Capella Writing Center
- Writing Center.
- Access the various resources in the Capella Writing Center to help you better understand and improve your writing.
APA Style and Format
- Capella University follows the style and formatting guidelines in the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association, known informally as the APA manual. Refer to the Writing Center’s APA Module for tips on proper use of APA style and format.
Capella University Library
- BSN Program Library Research Guide.
- The library research guide will be useful in guiding you through the Capella University Library, offering tips for searching the literature and other references for your assessments.
Activity
Click the linked title below, Determining the Relevance and Usefulness of Resources to complete this formative activity, which will help you determine which resources or research will be most relevant to address a particular need. This may be useful as you consider how to explain the purpose and relevance of the resources you are assembling for your toolkit.
This is for your own practice and self-assessment.
This tool needs to be loaded in a new browser window
Introduction to NURS 4020 Assessment Four
In NURS-FPX 4020 Assessment Four: Improvement Plan Tool Kit, you will develop a comprehensive resource repository to support a safety improvement plan. This How-To NURS-FPX 4020 Guide will provide structured steps to create a Word document or an online repository of at least 12 annotated professional or scholarly resources. These resources are crucial for understanding and implementing your safety improvement initiative effectively. This task emphasizes the importance of communication, collaboration, and continuous support within healthcare environments to foster a culture of safety and quality care.
An APA-formatted citation of the resource with a working link. A description of the resource’s information, skills, or tools. A brief explanation of how the resource can help nurses better understand or implement the safety improvement initiative regarding a specific patient safety issue. A description of how nurses can use this resource and when its use may be appropriate.
Identifying Critical Categories/Themes
We will identify critical categories or themes to start the NURS-FPX 4020 Assessment Four: Improvement Plan Tool Kit.
- Focus on 3 or 4 critical categories related to your safety improvement initiative.
- Examples of categories might include organizational safety and quality best practices, environmental safety risks, individual personal and team safety strategies, and process best practices for reporting safety issues.
- Ensure these categories are broad enough to encompass various aspects of the safety issue but specific enough to provide targeted resources.
- Reflect on the primary goals of your safety improvement initiative.
- Identify key themes that are central to achieving these goals.
- Write down these categories and ensure they align with your objective.
Selecting and Annotating Resources
Next, we will select and create annotated resources for the categories or themes.
- Each resource must be cited in APA format and include a working link.
- Use reliable citation tools or guides to format your citations correctly.
- Double-check the links to ensure they are functional.
- Provide a summary of the resource’s information, skills, or tools.
- Explain how the resource can help nurses understand or implement the safety improvement initiative.
- Describe how and when nurses can use this resource effectively.
Example
Massey, D., Chaboyer, W., & Anderson, V. (2016). What factors influence ward nurses’ recognition of and response to patient deterioration? An integrative review of the literature. Nursing Open, 4(1), 6–23. https://doi.org/10.1002/nop2.53
The integrative analysis of ward nurses’ awareness and response to patient deterioration provides valuable insights into utilizing resources for those responsible for quality and safety improvements. The essential components of the resource toolkit include highlighted issues such as patient assessment, patient knowledge, access to support, environmental factors, non-technical skills, education, and emotional responses. The analysis indicates that these areas are crucial for enhancing nurses’ abilities and reactions to patient deterioration. This resource is vital due to the complex issues associated with early detection and response to clinical deterioration. Nurses can use the toolkit to enhance their non-technical skills, access necessary support, and manage emotional reactions during patient deterioration cases. The resource toolkit is vital for reducing patient safety concerns, offering a structured approach for nurses to recognize and respond to deterioration. Nurses should utilize these resources daily to improve patient safety through prompt evaluations and actions.
NOTE: I will provide an annotated bibliography for one resource and three resources in the sample solution. By following the guidelines, write an annotated bibliography for the necessary resources.
Demonstration of Proficiency
Competency 1: Analyze the elements of a successful quality improvement initiative.
Competency 2: Analyze factors that lead to patient safety risks.
Competency 3: Identify organizational interventions to promote patient safety.
Competency 5: Apply professional, scholarly, evidence-based strategies to communicate in a manner that supports safe and effective patient care.
These competencies guide you to systematically approach and solve the assignment, ensuring a thorough and professional outcome.
Closing
Completing the NURS-FPX 4020 Assessment Four: Improvement Plan Tool Kit will equip you to create a valuable resource repository that can significantly enhance patient safety and quality care in healthcare settings. The key takeaways include understanding the importance of structured communication, the relevance of annotated resources, and the impact of accessible, well-organized information on the success of safety improvement initiatives. NURS-FPX 4020 Assessment Four: Improvement Plan Tool Kit How-To Owlisdom Guide provides a detailed, step-by-step approach to developing a resource repository for a safety improvement plan. By adhering to these guidelines, you can ensure that your repository is comprehensive, relevant, and accessible, supporting the ongoing efforts to enhance patient safety and quality care in healthcare settings.
Introduction:
The Improving Quality of Care and Patient Safety NURS-FPX4020 course emphasizes strategies to enhance healthcare outcomes and ensure patient safety. ThisOwlisdom Nursing Coursework Help provides key insights into quality improvement and effective care practices.
NURS-FPX 4020 Assessment One: Enhancing Quality and Safety
Instructions for NURS-FPX 4020 Assessment One: Enhancing Quality and Safety
Healthcare organizations and professionals strive to create safe environments for patients; however, due to the complexity of the healthcare system, maintaining safety can be a challenge. Since nurses comprise the largest group of healthcare professionals, a great deal of responsibility falls into the hands of practicing nurses. Quality improvement (QI) measures and safety improvement plans are effective interventions for reducing medical errors and sentinel events, including medication errors, falls, infections, and deaths. A 2000 Institute of Medicine (IOM) report indicated that almost one million people are harmed annually in the United States (Kohn et al., 2000), and 210,000–440,000 die as a result of medical errors (Allen, 2013).
The role of the baccalaureate nurse includes identifying and explaining specific patient risk factors, incorporating evidence-based solutions to improve patient safety, and coordinating care. A solid foundation of knowledge and understanding of safety organizations such as Quality and Safety Education for Nurses (QSEN), the Institute of Medicine (IOM), and The Joint Commission and its National Patient Safety Goals (NPSGs) program is vital to practicing nurses in providing and promoting safe and effective patient care.
You are encouraged to complete the Identifying Safety Risks and Solutions activity. This activity offers an opportunity to review a case study and practice identifying safety risks and possible solutions. We have found that learners who complete course activities and review resources are more successful with first submissions. Completing course activities is also a way to demonstrate engagement in the course.
References
Allen, M. (2013). How many die from medical mistakes in U.S. hospitals? https://www.npr.org/sections/health-shots/2013/09/20/224507654/how-many-die-from-medical-mistakes-in-u-s-hospitals.
Kohn, L. T., Corrigan, J., & Donaldson, M. S. (Eds.). (2000). To err is human: Building a safer health system. National Academy Press.
Professional Context
As a baccalaureate-prepared nurse, you will be responsible for implementing quality improvement (QI) and patient safety measures in healthcare settings. Effective quality improvement measures result in systemic and organizational changes, ultimately leading to the development of a patient safety culture.
The purpose of this assessment is to better understand the role of the baccalaureate-prepared nurse in enhancing quality improvement (QI) measures that address a safety quality issue in a healthcare setting. This will be within the specific context of patient safety risks in a healthcare setting of your choice. You will do this by exploring the professional guidelines and best practices for improving and maintaining patient safety in healthcare settings from organizations such as QSEN and the IOM.
Looking through the lens of these professional best practices to examine the current policies and procedures in place at your chosen organization and the impact on safety measures for patients surrounding a specific safety quality issue, you will consider the role of the nurse in driving quality and safety improvements. You will identify stakeholders in QI improvement and safety measures, as well as consider evidence-based strategies to enhance the quality of care and promote safety in the context of your chosen healthcare setting.
As a baccalaureate-prepared nurse, you will be responsible for implementing quality improvement (QI) and patient safety measures in health care settings. Effective quality improvement measures result in systemic and organizational changes, ultimately leading to the development of a patient safety culture.
The purpose of this assessment is to better understand the role of the baccalaureate-prepared nurse in enhancing quality improvement (QI) measures that address a safety quality issue in a health care setting. This will be within the specific context of patient safety risks at a healthcare setting of your choice. You will do this by exploring the professional guidelines and best practices for improving and maintaining patient safety in health care settings from organizations such as QSEN and the IOM.
Looking through the lens of these professional best practices to examine the current policies and procedures in place at your chosen organization and the impact on safety measures for patients surrounding a specific safety quality issue, you will consider the role of the nurse in driving quality and safety improvements. You will identify stakeholders in QI improvement and safety measures, as well as consider evidence-based strategies to enhance the quality of care and promote medication administration safety in the context of your chosen health care setting.
Scenario
Select one of the safety quality issues presented in the Download Assessment 01 Supplement: Enhancing Quality and Safety [PDF]resource and incorporate evidence-based strategies to support communication and ensure safe and effective care.
Instructions
For this assessment, you will analyze a safety quality issue in a health care setting and identify a quality improvement (QI) initiative.
Be sure that your plan addresses the following, which corresponds to the grading criteria in the scoring guide. Please study the scoring guide carefully so that you know what is needed for a distinguished score.
- Explain factors leading to a specific patient-safety risk in a health care setting.
- Explain evidence-based and best-practice solutions to improve patient safety and reduce costs.
- Explain how nurses can help coordinate care to increase patient safety and reduce costs.
- Identify stakeholders with whom nurses would coordinate to drive safety enhancements with a specific safety quality issue.
- Communicate using writing that is clear, logical, and professional, with correct grammar and spelling, using current APA style.
Additional Requirements
- Length of submission: 3–5 pages, plus title and reference pages.
- Number of references: Cite a minimum of 4 sources of scholarly or professional evidence that support your findings and considerations. Resources should be no more than 5 years old.
- APA formatting: References and citations are formatted according to the current APA style.
Competencies Measured
By completing this assessment, you will demonstrate your proficiency in the course competencies through the following assessment scoring guide criteria:
- Competency 1: Analyze the elements of a successful quality improvement initiative.
- Explain evidence-based and best-practice solutions to improve patient safety and reduce costs.
- Competency 2: Analyze factors that lead to patient safety risks.
- Explain factors leading to a specific patient-safety risk in a health care setting.
- Competency 4: Explain the nurse’s role in coordinating care to enhance quality and reduce costs.
- Explain how nurses can help coordinate care to increase patient safety and reduce costs.
- Identify stakeholders with whom nurses would coordinate to drive safety enhancements with a specific safety quality issue.
- Competency 5: Apply professional, scholarly, evidence-based strategies to communicate in a manner that supports safe and effective patient care.
- Organize content so ideas flow logically with smooth transitions; contains few errors in grammar or punctuation, word choice, and spelling.
- Apply APA formatting to in-text citations and references exhibiting nearly flawless adherence to APA format.
Resources
Use the resources linked below to help complete this assessment.
Collapse All
Collaboration and Leadership
The following readings may help you in completing this assessment’s activities:
- Assessment 1: Collaboration and Leadership reading list.
Quality Improvement Initiatives
The following readings may help you in completing this assessment’s activities:
- Assessment 1: Quality Improvement Initiatives reading list.
Quality and Safety Education
The following readings may help you in completing this assessment’s activities:
- Assessment 1: Quality and Safety Education reading list
Quality and Safety Case Studies
Consider reviewing the following case studies as you complete your assessment:
- Assessment 1: Quality and Safety Case Studies reading list.
Program Resources
Capella Writing Center
- Writing Center.
- Access the various resources in the Capella Writing Center to help you better understand and improve your writing.
APA Style and Format
- Capella University follows the style and formatting guidelines in the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association, known informally as the APA manual. Refer to the Writing Center’s APA Module for tips on proper use of APA style and format.
Capella University Library
- BSN Program Library Research Guide.
- The library research guide will be useful in guiding you through the Capella University Library, offering tips for searching the literature and other references for your assessments.
Activity
Click the linked title below, Identifying Safety Risks and Solutions, to complete this formative activity, which offers an opportunity to review a case study and practice identifying safety risks and possible solutions. These skills will be necessary to complete the Enhancing Quality and Safety assessment successfully. This is for your own practice and self-assessment.
This tool needs to be loaded in a new browser window
Introduction to NURS 4020 Assessment One
Welcome to NURS-FPX 4020 Assessment One: Enhancing Quality and Safety! Healthcare organizations and professionals strive to maintain safe patient environments, but complexities within the system often pose challenges. Nurses, the largest group of healthcare providers, are crucial in ensuring patient safety. This How-To NURS-FPX 4020 Guide provides strategies and guidelines for addressing safety quality issues, incorporating evidence-based solutions, coordinating care, and communicating effectively within healthcare settings.
Select one of the safety quality issues presented in the Assessment 01 Supplement: Enhancing Quality and Safety.
Selecting a Safety Quality Issue
To start the NURS-FPX 4020 Assessment One: Enhancing Quality and Safety, we will select a safety quality issue in healthcare.
- Read the Assessment 01 Supplement to identify various safety quality issues.
- Choose one issue that resonates with your interests or seems significant.
- Consider the impact of the chosen issue on patient safety and healthcare costs.
Example
Responding promptly to patients experiencing deteriorating conditions in healthcare settings presents a multifaceted challenge. Considine et al. (2021) highlight issues within emergency departments despite the presence of Rapid Response Systems, indicating inconsistent recognition and action regarding clinical decline. These systems’ complexity and varying implementation across healthcare facilities may contribute to this problem. Bucknall et al. (2022) delve into the role of nurses in detecting early signs of patient deterioration, emphasizing their crucial function. However, they also underscore the obstacles nurses face, including high workloads and staffing limitations, which hinder their ability to monitor and respond effectively.
Gertz et al. (2022) noted that the COVID-19 pandemic exacerbated challenges in healthcare. Their study suggests that pandemic-related disruptions led to delays in medical treatment as healthcare systems grappled with overwhelming demand and had to adapt their care priorities. These circumstances likely contributed to slowed responses to deteriorating patients, with limited resources and unprecedented challenges that medical staff face.
Ullah et al. (2022) provide further insights by examining the workload associated with vital signs-based monitoring. Their research in a New Zealand hospital setting indicates that the monitoring and response process for deteriorating patients is labor-intensive. This suggests that time constraints and physical workload may impede timely responses, particularly in settings with limited resources.
The consequences of delayed responses to patient deterioration are significant. Firstly, patient safety and outcomes are directly affected. As evidenced by the studies, failure to promptly recognize and address clinical deterioration can result in adverse events, heightened morbidity, and, in severe cases, mortality. Swift interventions are essential in halting or reversing a patient’s decline, and any delay can reduce the effectiveness of the intervention, leading to more severe health consequences.
Additionally, delayed responses often necessitate more intricate and aggressive treatments. As a patient’s condition deteriorates, interventions become more invasive, pose significant risks, and require increased resources. This not only impacts the patient’s prognosis but also escalates healthcare expenditures. Prolonged hospital stays, additional interventions, and potential legal ramifications for healthcare institutions are financial burdens stemming from delayed responses.
Incorporate evidence-based strategies to support communication, ensure safe and effective care, and reduce costs.
Incorporating Evidence-Based Strategies
Next, we will incorporate evidence-based strategies.
- Research evidence-based solutions related to the selected issue.
- Utilize reputable sources such as academic journals, professional organizations, and government reports.
- Evaluate the effectiveness of different strategies in improving patient safety and reducing costs.
- Justify the chosen strategies based on their applicability and success in similar healthcare settings.
Example
Scholarly research offers essential strategies for promptly responding to patients experiencing deterioration in healthcare settings. Considine et al. (2021) emphasize the critical importance of structured approaches in identifying and managing clinical decline, particularly within emergency departments. Rapid Response Systems (RRSs) are valuable tools in aiding healthcare practitioners in the early detection of deteriorating patient conditions and prompt intervention. Implementing such systems significantly enhances patient safety by providing clear protocols for monitoring patients and determining appropriate interventions.
Bucknall and colleagues (2022) provide a compelling analysis of facilitation interventions to enhance nurses’ ability to respond to clinical deterioration. Their study underscores the vital role of ongoing education and support for nurses in adhering to clinical practice guidelines. Establishing a culture of continuous learning and active engagement within clinical settings markedly improves nurses’ capacity to detect and address early signs of patient deterioration, thereby mitigating risks associated with delayed responses.
Ullah et al. (2022) discuss the potential of technology in monitoring patients and facilitating prompt action in response to deteriorating health conditions. Utilizing electronic systems for monitoring vital signs and alerting healthcare providers to abnormalities offers a promising approach. These systems provide real-time information and expedite decision-making processes, enabling healthcare practitioners to respond swiftly to changes in patient status. Transitioning from traditional manual monitoring to technological solutions streamlines processes and alleviates pressure on nurses, allowing them to dedicate more time to patient care.
Hospitals must implement explicit and up-to-date protocols to ensure timely intervention in cases of patient deterioration. These protocols, grounded in robust evidence, should undergo regular review to align with contemporary standards of care. Hospitals can promote consistency in patient management by establishing clear thresholds for intervention and delineating definitive action plans. These guidelines must empower nurses and healthcare professionals to act promptly upon observing signs of patient decline, providing them with the necessary resources and support for effective execution.
Explain how nurses can help coordinate care to increase patient safety and reduce costs.
Coordinating Care to Increase Patient Safety
Here, we will explore how to coordinate care to increase patient safety.
- Explain the role of nurses in coordinating care to enhance patient safety.
- Highlight the importance of effective communication and collaboration among healthcare team members.
- Discuss how nurses can streamline processes and implement standardized protocols to reduce errors and improve outcomes.
- Provide examples of successful care coordination initiatives impacting patient safety and cost reduction.
Example
Nurses play a pivotal role in safeguarding patient safety, particularly in detecting and managing deteriorating health conditions. Studies by Bucknall et al. (2022) and Ullah et al. (2022) underscore the indispensable role of nursing in this vital aspect of healthcare. Beyond routine vital signs monitoring, nurses are instrumental in the early identification of worsening illnesses, aiming to prevent adverse health events by promptly addressing even subtle changes in patients’ conditions.
Moreover, nurses are central in facilitating swift and appropriate interventions. Upon identifying potential risks, nurses are responsible for effectively communicating this information to the medical team and initiating necessary medical responses (Bucknall et al., 2022). This role necessitates quick decision-making and clear communication of the situation’s urgency, positioning nurses as pivotal links between patients and the broader medical team (Bucknall et al., 2022; Ullah et al., 2022).
Identify stakeholders with whom nurses would coordinate to drive safety enhancements with a specific safety quality issue.
Identifying Stakeholders for Safety Enhancements
This section of NURS-FPX 4020 Assessment One: Enhancing Quality and Safety will identify stakeholders for safety enhancements.
- Identify critical stakeholders involved in addressing the chosen safety quality issue.
- Consider healthcare providers, administrators, patients, families, regulatory agencies, and quality improvement teams.
- Explain how collaboration with stakeholders can drive safety enhancements and facilitate the implementation of evidence-based strategies.
- Highlight the importance of engaging stakeholders throughout the improvement process to ensure sustainability and effectiveness.
Example
Nurses’ engagement in interdisciplinary teamwork and collaboration enhances patient care. Nurses collaborating with various healthcare professionals, including physicians and specialists, foster a holistic approach to patient treatment and management. Additionally, nurses are crucial in partnering with hospital management to drive improvements in patient safety systems. Their involvement in proposing policy revisions, developing safety protocols, and advocating for essential patient monitoring and care resources is indispensable. These contributions by nurses are instrumental in shaping healthcare environments that prioritize patient safety and deliver high-quality care.
Stakeholders in Quality Improvement
Various stakeholders play interconnected yet distinct roles in healthcare quality improvement. Healthcare professionals, such as physicians and nurses, are on the front lines and deeply involved in patient care and safety. Their direct experiences and perspectives are crucial for identifying improvement opportunities and implementing changes. Equally important are hospital administrators and policymakers, who have the authority to implement broad reforms, allocate resources, and establish policies that significantly influence the quality and safety of patient care.
Collaborative Strategies for Safety Enhancement
Collaboration among all stakeholders is essential for enhancing safety. Research by Considine et al. (2021) and Bucknall et al. (2022) emphasizes the importance of multidisciplinary cooperation in recognizing and managing patient deterioration. This collaboration goes beyond individual responsibilities, encouraging collective efforts that leverage diverse skills and perspectives to improve patient outcomes.
The integration of efforts from both clinical staff and administrative bodies is vital. Healthcare professionals provide the practical knowledge and experience to identify and address patient safety risks. At the same time, hospital management and policymakers support these safety measures through training investments, infrastructure improvements, and protocol revisions to align with contemporary best practices (Bucknall et al., 2022).
Closing
In conclusion, NURS-FPX 4020 Assessment One: Enhancing Quality and Safety How-To Guide equips students with the essential tools to address safety quality issues in healthcare. Nurses can significantly enhance patient safety and reduce costs by selecting relevant issues, incorporating evidence-based strategies, fostering care coordination, identifying stakeholders, and communicating effectively. Remember, proficiency in these competencies is achievable through dedication, critical thinking, and adherence to professional standards.
References
Bucknall, T., Considine, J., Harvey, G., Graham, I. D., Rycroft‐Malone, J., Mitchell, I., Saultry, B., Watts, J. J., Mohebbi, M., Mudiyanselage, S. B., Lotfaliany, M., & Hutchinson, A. (2022). Prioritizing Nurses’ Responses To deteriorating Patient Observations (PRONTO): a pragmatic cluster randomized controlled trial evaluating the effectiveness of a facilitation intervention on recognition and response to clinical deterioration. BMJ Quality & Safety, bmjqs-013785. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjqs2021-013785
Considine, J., Fry, M., Curtis, K., & Shaban, R. Z. (2021). Systems for recognition and response to deteriorating emergency department patients: a scoping review. Scandinavian Journal of Trauma, Resuscitation and Emergency Medicine, 29(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13049-021-00882-6
Gertz, A., Pollack, C. C., Schultheiss, M. D., & Brownstein, J. S. (2022). Delayed medical care and underlying health in the United States during the COVID-19 pandemic: A cross-sectional study. Preventive Medicine Reports, 28, 101882. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmedr.2022.101882
Ullah, E., Albrett, J., Khan, O., Matthews, C., Perry, I., GholamHosseini, H., & Lu, J. (2022). Workload involved in vital signs-based monitoring & responding to deteriorating patients: A single-site experience from a regional New Zealand hospital. Heliyon, 8(10), e10955. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e10955
NURS-FPX 4020 Assessment 2: Root-Cause Analysis and Safety Improvement Plan
Instructions for NURS-FPX 4020 Assessment 2: Root-Cause Analysis and Safety Improvement Plan
Root-Cause Analysis and Safety Improvement Plan
For this assessment, you can use a supplied template to conduct a root-cause analysis. The completed assessment will be a scholarly paper focusing on a quality or safety issue in a health care setting of your choice, as well as a safety improvement plan.
Collapse All
Introduction
As patient safety concerns continue to be addressed in the health care settings, nurses can play an active role in implementing safety improvement measures and plans. Often, root-cause analyses are conducted and safety improvement plans are created to address sentinel or adverse events such as medication errors, patient falls, wrong-site surgery events, and hospital-acquired infections. Performing a root-cause analysis offers a systematic approach for identifying causes of problems, including process and system-check failures. Once the causes of failures have been determined, a safety improvement plan can be developed to prevent recurrences. The baccalaureate nurse’s role as a leader is to create safety improvement plans as well as disseminate vital information to staff nurses and other health care professionals to protect patients and improve outcomes.
As you prepare for this assessment, it would be an excellent choice to complete the Quality and Safety Improvement Plan Knowledge Base activity and to review the various assessment resources, all of which will help you build your knowledge of key concepts and terms related to quality and safety improvement. The terms and concepts will be helpful as you prepare your Root-Cause Analysis and Safety Improvement Plan. Activities are not graded and demonstrate course engagement.
Professional Context
Nursing practice is governed by health care policies and procedures as well as state and national regulations developed to prevent problems. Nurses must participate in gathering and analyzing data to determine causes of patient safety issues, in solving problems, and in implementing quality improvements.
Scenario
For this assessment, use the specific safety concern identified in your previous assessment as the subject of a root-cause analysis and safety improvement plan.
Instructions
The purpose of this assessment is to demonstrate your understanding of and ability to analyze the root cause of a specific safety concern in a health care setting. You will create a plan to improve the safety of patients related to the safety quality issue presented in your Assessment Supplement PDF in Assessment 1. Based on the results of your analysis, using the literature and professional best practices as well as the existing resources at your chosen health care setting, provide a rationale for your plan.
Use the Root-Cause Analysis and Improvement Plan [DOCX] template to help you stay organized and concise. This will guide you step-by-step through the root cause analysis process.
Additionally, be sure that your plan addresses the following, which corresponds to the grading criteria in the scoring guide. Please study the scoring guide carefully so you understand what is needed for a distinguished score.
- Analyze the root cause of a specific patient safety issue in an organization.
- Apply evidence-based and best-practice strategies to address the safety issue.
- Create a feasible, evidence-based safety improvement plan to address a specific patient safety issue.
- Identify organizational resources that could be leveraged to improve your plan.
- Communicate in writing that is clear, logical, and professional, with correct grammar and spelling, using current APA style.
Example Assessment: You may use the following to give you an idea of what a Proficient or higher rating on the scoring guide would look like, but keep in mind that your Assessment 2 will focus on the quality issue you selected in Assessment 1.
- Assessment 2 Example [PDF] Download Assessment 2 Example [PDF].
Additional Requirements
- Length of submission: Use the provided Root-Cause Analysis and Improvement Plan template to create a 4–6 page root cause analysis and safety improvement plan about a specific patient safety issue.
- Number of references: Cite a minimum of 3 sources of scholarly or professional evidence that support your findings and considerations. Resources should be no more than 5 years old.
- APA formatting: Format references and citations according to current APA style.
Competencies Measured
By completing this assessment, you will demonstrate your proficiency in the course competencies through the following assessment scoring guide criteria:
- Competency 1: Analyze the elements of a successful quality improvement initiative.
- Apply evidence-based and best-practice strategies to address the safety issue.
- Create a feasible, evidence-based safety improvement plan to address a specific patient safety issue.
- Competency 2: Analyze factors that lead to patient safety risks.
- Analyze the root cause of a specific patient safety issue in an organization.
- Competency 3: Identify organizational interventions to promote patient safety.
- Identify organizational resources that could be leveraged to improve your plan.
- Competency 5: Apply professional, scholarly, evidence-based strategies to communicate in a manner that supports safe and effective patient care.
- Organize content so ideas flow logically with smooth transitions; contains few errors in grammar or punctuation, word choice, and spelling.
- Apply APA formatting to in-text citations and references exhibiting nearly flawless adherence to APA format.
Resources
Use the resources linked below to help complete this assessment.
Collapse All
Evidence-Based Practice
The following readings may help you in completing this assessment’s activities:
- Assessment 2: Evidence-Based Practice reading list.
Quality and Safety
The following readings may help you in completing this assessment’s activities:
- Assessment 2: Quality and Safety reading list.
Root-Cause Analysis
The following readings may help you in completing this assessment’s activities:
- Assessment 2: Root-Cause Analysis reading list.
Sentinel Events
The following readings may help you in completing this assessment’s activities:
- Assessment 2:Sentinel Events reading list.
Safety and Sentinel Event Case Studies
The following readings may help you in completing this assessment’s activities:
- Assessment 2:Safety and Sentinel Event Case Studies reading list.
Program Resources
Capella Writing Center
- Writing Center.
- Access the various resources in the Capella Writing Center to help you better understand and improve your writing.
APA Style and Format
- Capella University follows the style and formatting guidelines in the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association, known informally as the APA manual. Refer to the Writing Center’s APA Module for tips on proper use of APA style and format.
Capella University Library
- BSN Program Library Research Guide.
- The library research guide will be useful in guiding you through the Capella University Library, offering tips for searching the literature and other references for your assessments.
Activity
Click the linked title below, Quality and Safety Improvement Plan Knowledge Base, to complete this formative activity, which will help you check and build your knowledge of key concepts and terms related to quality and safety improvement. These terms and concepts will be useful as you prepare your Root Cause Analysis and Improvement Plan. This is for your own practice and self-assessment.
This tool needs to be loaded in a new browser window
Introduction to NURS 4020 Assessment Two
The NURS-FPX 4020 Assessment 2: Root-Cause Analysis and Safety Improvement Plan is designed to help you understand and analyze the root cause of a specific patient safety issue within a healthcare setting. By conducting a root-cause analysis, applying evidence-based strategies, and developing a feasible safety improvement plan, you will demonstrate your ability to improve patient safety and quality of care. This How-To NURS-FPX 4020 Guide provides step-by-step instructions on completing each part of the assignment, ensuring a clear, logical, and professional approach.
Analyze the root cause of a specific patient safety issue in an organization.
Conducting a Root-Cause Analysis
We will conduct a root-cause analysis to start the NURS-FPX 4020 Assessment 2: Root-Cause Analysis and Safety Improvement Plan.
- Identify the Problem: Clearly define the specific patient safety issue you focus on (e.g., medication errors, patient falls).
- Gather Data: Collect data related to the issue from your healthcare setting. This may include incident reports, patient records, and staff interviews.
- Analyze the Data: Use tools such as fishbone diagrams or the 5 Whys technique to systematically identify the root causes of the problem.
- Identify Contributing Factors: Determine the process and system failures contributing to the safety issue.
Example
The sentinel event under review, as described by Olson (2023), involves several critical incidents in Minnesota hospitals, leading to 21 preventable deaths and 178 serious injuries. This root cause analysis seeks to understand the factors contributing to these events, which include surgical errors, medication mishandling, and insufficient responses to patient conditions. Hospital administrators and quality assurance personnel identified these issues through adverse event reporting systems and internal audits. The events primarily impacted patients who received incorrect or delayed care, resulting in severe health complications and deaths, along with emotional distress. Additionally, healthcare providers faced scrutiny, prompting procedural reevaluations and potential legal implications.
Analysis of the Event and Relevant Findings
The sentinel events detailed by Olson (2023), involving a series of critical incidents in Minnesota hospitals, underscore the importance of identifying various underlying factors. These incidents led to severe outcomes, including preventable deaths and injuries, due to a range of errors, such as surgical mistakes, medication mishandling, and lapses in patient care.
Intended Procedure
Standard healthcare protocols for various procedures were either improperly followed or overlooked in these cases. This includes protocols for medication administration, surgical procedures, and general patient care guidelines.
Environmental Factors
As Olson (2023) noted, the healthcare environment was strained by high patient volumes and staff shortages, exacerbated by the pandemic. These conditions created a challenging operational environment, increasing the risk of errors.
Equipment and Resource Influence
Xie et al. (2021) highlight the impact of resource limitations, particularly staffing shortages, on patient safety. In these Minnesota incidents, inadequate staffing likely contributed to errors across multiple areas, including surgery and patient monitoring, due to rushed procedures and a lack of oversight.
Human Error Contribution
Various human errors contributed to these incidents, ranging from misinterpretation of medication labels and surgical plans to incorrect execution of medical procedures. Factors like fatigue, stress, or heavy workloads among healthcare staff could have influenced these errors.
Communication Factors
Wu and colleagues (2023) emphasize the importance of effective communication within healthcare environments. The reported adverse events in the Minnesota hospital episodes were likely caused by communication breakdowns among medical staff, including nurses, surgeons, pharmacists, and other healthcare professionals.
Root Causes Identified
Olson (2023) highlighted incidents in Minnesota hospitals where there was a pervasive failure to follow healthcare protocols, affecting various services such as medication administration, surgical procedures, and patient care. Staffing and resource shortages were key contributors to these incidents, as Olson (2023) and Xie et al. (2021) emphasized. These deficits increased risks and compromised patient care. Wu et al. (2023) identified inadequate communication within healthcare teams as a major factor. This breakdown led to errors in medication administration, surgical procedures, and care management, worsening the effects of the existing strains on the healthcare system.
Apply evidence-based and best-practice strategies to address the safety issue.
Applying Evidence-Based and Best-Practice Strategies
Next, we will apply evidence-based strategies.
- Research Best Practices: Review the literature and professional guidelines for the specific safety issue. Identify evidence-based strategies that have been proven effective.
- Evaluate Applicability: Assess how these strategies can be adapted to your healthcare setting. Consider the feasibility and potential impact of each strategy.
Example
Implementing evidence-based strategies to address drug mismanagement, surgical errors, and patient care deficiencies is essential, especially considering the serious errors identified in Minnesota hospitals by Olson (2023). These strategies should be grounded in current research and best practices from healthcare policies, recognizing the complex nature of these issues and providing a framework for mitigation and prevention.
Factors Leading to Safety Issues
Medication Errors. As identified in the root cause analysis, interruptions during medication administration significantly influenced medication errors. Strategies such as increasing staffing levels, reducing workloads, and enhancing communication channels should be implemented to minimize these errors. This approach aligns with the findings of Wu et al. (2023) and Olson (2023), which emphasize the importance of a stable environment for medication delivery.
Patient Falls. The PRONTO trial by Bucknall et al. (2022) underscores the importance of early detection and response to clinical deterioration to prevent incidents like patient falls. Nursing interventions are crucial in identifying at-risk patients through regular vital sign monitoring and adherence to clinical practice guidelines.
Wrong-Site Surgery. Gertz et al. (2022) highlight that issues related to workload and staffing levels contribute to wrong-site surgeries. Implementing standardized presurgical procedures and checklists can mitigate these issues. This ensures consistency and accuracy in surgical practices, reducing the likelihood of such critical errors.
Hospital-Acquired Infections. Ullah et al. (2022) emphasize the significant workload involved in monitoring patients and responding to signs of deterioration, which is crucial in preventing hospital-acquired infections. Hirschhorn et al. (2021) support that streamlining this process with electronic vital sign systems can significantly reduce infection risks.
Addressing Safety Issues through Best Practices
To reduce medication errors, creating a ‘no-interruption’ zone during medication preparation and utilizing electronic medication administration records (EMARs) can significantly decrease mistakes. Educating patients and their families about medication safety, as suggested by Wu et al. (2023), is also vital. Considine et al. (2021) recommend comprehensive Rapid Response Systems (RRS) in the Emergency Department and ongoing staff training and simulation exercises to minimize medication errors and enhance patient safety.
Improving environmental safety through non-slip flooring, assistive technology, and adequate lighting is essential. Including patients and their families in fall prevention strategies and providing continuous staff training on fall prevention and risk assessment are crucial steps.
The World Health Organization advises using a systematic surgical safety checklist to reduce the incidence of wrong-site surgery significantly. Preoperative conferences and involving patients in labeling the surgical site can also enhance safety.
Adhering strictly to infection control practices, such as personal protective equipment and regular hand washing, is essential to prevent hospital-acquired infections. Maintaining environmental cleanliness and educating staff on infection control are also critical. Ullah et al. (2022) propose that transitioning from hand-written to digital tracking of vital signs could reduce nurses’ workloads, allowing for more attentive patient care and lowering the incidence of hospital-acquired infections.
Create a feasible, evidence-based safety improvement plan to address a specific patient safety issue.
Creating a Safety Improvement Plan
Here, we will create a safety improvement plan.
- Set Goals: Define clear, measurable goals for your improvement plan. These should be specific to the identified safety issue.
- Develop Interventions: Based on your root-cause analysis and research, outline the interventions you will implement to address the root causes.
- Create an Implementation Plan: Detail the steps, timeline, and responsible parties for implementing each intervention.
- Monitor and Evaluate: Plan for ongoing monitoring and evaluation to measure the effectiveness of your interventions.
Example
A comprehensive improvement plan is proposed in response to the significant occurrences of medication errors, surgical errors, and patient care deficiencies in Minnesota hospitals. This plan is based on root cause analysis and is supported by recent research and best practices in healthcare.
Actions, New Processes, or Policies
We standardized Surgical Protocols and Checklists. The strategy recommends implementing standardized surgical protocols and checklists to prevent wrong-site and other surgical errors, as Gertz et al. (2022) highlighted.
Staff Training and Professional Development. The plan includes ongoing training programs for nurses and healthcare workers, focusing on early recognition of patient deterioration, adherence to clinical guidelines, and effective communication skills, in line with the recommendations of Bucknall et al. (2022).
Enhancement of Communication Protocols. Drawing from Olson (2023), the plan advocates for establishing clear and effective communication channels among healthcare professionals. This includes leveraging technology to ensure the timely sharing of critical test results and patient information.
Adoption of Technology for Patient Monitoring. Inspired by Ullah et al.’s (2022) findings, the strategy suggests integrating electronic monitoring systems for patient vital signs. This will reduce nurses’ manual workload and enable more accurate and timely responses to patient needs.
Goals or Desired Outcomes
Reduction in Specific Patient Safety Events. Significantly minimize medication errors, surgical mistakes, and patient care lapses, particularly focusing on wrong-site surgeries and medication mismanagement.
It enhanced Staff Competency in Patient Safety. Improve the medical staff’s ability to recognize and address patient safety issues, especially in surgery and drug administration.
It strengthened the Patient Safety Culture. In line with Wu et al. (2023), the plan aims to increase patient and family involvement in the care process, fostering a patient-centered care and safety culture.
Rough Timeline for Development and Implementation
Initial Phase (0-3 Months). Develop standardized surgical and medication protocols. Begin comprehensive staff training. Implement communication and electronic monitoring systems.
Intermediate Phase (4-6 Months). Pilot new protocols in selected departments. Continue staff training and evaluate the effectiveness of communication. Integrate electronic monitoring in key areas.
Final Phase (7-12 Months). Implement standardized protocols throughout the facility. Expand electronic monitoring to all departments. Maintain ongoing staff development and feedback mechanisms.
Evaluation and Adjustment (Post-12 Months). Regularly assess the new systems to reduce errors. Make adjustments based on feedback and outcomes.
This plan is built on scholarly evidence and practical strategies. It targets the root causes of identified patient safety issues. Its implementation is expected to significantly enhance patient safety and quality of care in healthcare.
Identify organizational resources that could be leveraged to improve your plan.
Identifying Organizational Resources
We will explore the organizational resources for this NURS-FPX 4020 Assessment 2: Root-Cause Analysis and Safety Improvement Plan section.
- Assess Resources: Identify existing resources within your organization that can support your safety improvement plan. This may include staff training programs, technology, and financial resources.
- Leverage Support: Determine how to utilize these resources to enhance your plan’s success. Engage key stakeholders and secure the necessary support.
Example
Existing Organizational Resources
Leveraging existing organizational resources is crucial for successfully implementing the safety improvement plan addressing critical incidents in Minnesota hospitals. This ensures the efficient use of available assets and facilitates the integration of new strategies.
Human Resources
Nursing Staff. Experienced nurses play a vital role in frontline healthcare, ensuring patient safety. Their expertise is crucial in mentoring new nurses, particularly in key practices such as medication administration and patient monitoring, fostering a strong safety culture.
Patient Safety Officers oversee safety protocols, especially in surgical settings, and coordinate strategies to address identified safety issues.
Interdisciplinary Teams. Collaboration among physicians, pharmacists, nurses, and other healthcare professionals ensures that complex care scenarios are managed with diverse expertise, essential for a comprehensive approach to patient safety.
Technological Resources
Electronic Health Records (EHR). EHRs are essential for ensuring the accuracy of surgical procedures, controlling medication errors, and monitoring patient data.
Patient Monitoring Systems. These technologies significantly reduce the likelihood of patient care errors and are crucial for the early detection of patient deterioration.
Educational and Training Materials
Online Learning Platforms. These platforms facilitate efficient staff training on new safety protocols and procedures related to medication management and surgical safety.
Simulation Training Tools. Simulation training provides hands-on experience managing patient safety scenarios, particularly in surgical settings.
Policy and Governance Frameworks
Safety Policies and Guidelines. Safety policies must be regularly updated and revised to align with the latest advancements in patient safety best practices.
Quality Improvement Committees. These committees are essential for guiding the execution of the safety improvement strategy, ensuring its alignment with the organization’s overarching goals.
Demonstration of Proficiency
Competency 1: Analyze the elements of a successful quality improvement initiative.
Competency 2: Analyze factors that lead to patient safety risks.
Competency 3: Identify organizational interventions to promote patient safety.
Competency 5: Apply professional, scholarly, evidence-based strategies to communicate in a manner that supports safe and effective patient care.
These competencies are designed to guide you through completing the assessment. They provide a framework to ensure that your work is thorough, evidence-based, and professionally communicated.
Closing
Completing the NURS-FPX 4020 Assessment 2: Root-Cause Analysis and Safety Improvement Plan will enhance your ability to identify and address patient safety issues through systematic analysis and strategic planning. Following this How-To Owlisdom Guide, you can create a comprehensive safety improvement plan that leverages organizational resources and adheres to best practices. The NURS-FPX 4020 Assessment 2: Root-Cause Analysis and Safety Improvement Plan demonstrates your proficiency in quality care and patient safety. It prepares you to take on leadership roles in healthcare settings, contributing to improved patient outcomes and safer care environments.
NURS-FPX 4020 Assessment Three: Improvement Plan In-Service Presentation
Instructions for NURS-FPX 4020 Assessment Three: Improvement Plan In-Service Presentation
Improvement Plan In-Service Presentation
For this assessment, you will develop an 8–14 slide PowerPoint presentation with thorough speaker’s notes designed for a hypothetical in-service session related to the improvement plan you developed in Assessment 2.
Collapse All
Introduction
As a practicing professional, you are likely to present educational in-services or training to staff pertaining to quality improvement (QI) measures of safety improvement interventions. Such in-services and training sessions should be presented creatively and innovatively to hold the audience’s attention and promote knowledge acquisition and skill application that changes practice for the better. The teaching sessions may include a presentation, audience participation via simulation or other interactive strategy, audiovisual media, and participant learning evaluation.
The use of in-services and/or training sessions has positive implications for nursing practice by increasing staff confidence when providing care to specific patient populations. It also allows for a safe and nonthreatening environment where staff nurses can practice their skills before a real patient event. Participation in learning sessions fosters a team approach, collaboration, patient safety, and greater patient satisfaction rates in the health care environment (Patel & Wright, 2018).
As you prepare to complete the assessment, consider the impact of in-service training on patient outcomes as well as practice outcomes for staff nurses. Be sure to support your thoughts on the effectiveness of educating and training staff to increase the quality of care provided to patients by examining the literature and established best practices.
You are encouraged to explore the AONE Nurse Executive Competencies Review activity before you develop the Improvement Plan In-Service Presentation. This activity will help you review your understanding of the AONE Nurse Executive Competencies—especially those related to competencies relevant to developing an effective training session and presentation. This is for your own practice and self-assessment, and demonstrates your engagement in the course.
Reference
Patel, S., & Wright, M. (2018). Development of interprofessional simulation in nursing education to improve teamwork and collaboration in maternal-child nursing. Journal of Obstetric, Gynecologic & Neonatal Nursing, 47(3), s16–s17.
Professional Context
As a baccalaureate-prepared nurse, you will often find yourself in a position to lead and educate other nurses. This colleague-to-colleague education can take many forms, from mentoring to informal explanations on best practices to formal in-service training. In-services are an effective way to train a large group. Preparing to run an in-service may be daunting, as the facilitator must develop his or her message around the topic while designing activities to help the target audience learn and practice. By improving understanding and competence around designing and delivering in-service training, a BSN practitioner can demonstrate leadership and prove him- or herself a valuable resource to others.
Scenario
For this assessment, build on the work that you have done in your first two assessments and create an agenda and PowerPoint of an educational in-service session that would help a specific staff audience learn, provide feedback, and understand their roles and practice new skills related to the safety improvement plan you created.
Instructions
The final deliverable for this assessment will be a PowerPoint presentation with detailed presenter’s notes representing the material you would deliver at an in-service session to raise awareness of your chosen safety improvement initiative, focusing on a specific patient safety issue, and to explain the need for such an initiative. Additionally, you must educate the audience as to their role and importance to the success of the initiative. This includes providing examples and practice opportunities to test out new ideas or practices related to the safety improvement initiative.
Be sure that your presentation addresses the following, which corresponds to the grading criteria in the scoring guide. Please study the scoring guide carefully so you understand what is needed for a distinguished score.
- Describe the purpose and goals of an in-service session focusing on a specific patient safety issue.
- Explain the need for and process to improve safety outcomes related to a specific patient safety issue.
- Explain to the audience their role and the importance of making the improvement plan successful.
- Create resources or activities to encourage skill development and process understanding related to a safety improvement initiative.
- Communicate with nurses in a respectful and informative way that clearly presents expectations and solicits feedback on communication strategies for future improvement.
There are various ways to structure an in-service session; below is just one example:
- Part 1: Agenda and Outcomes.
- Explain to your audience what they are going to learn or do, and what they are expected to take away.
- Part 2: Safety Improvement Plan.
- Give an overview of the current problem, focusing on a specific patient safety issue, the proposed plan, and what the improvement plan is trying to address.
- Explain why it is important for the organization to address the current situation.
- Part 3: Audience’s Role and Importance.
- Discuss how the staff audience will be expected to help implement and drive the improvement plan.
- Explain why they are critical to the success of the improvement plan, focusing on a specific patient safety issue.
- Describe how their work could benefit from embracing their role in the plan.
- Part 4: New Process and Skills Practice.
- Explain new processes or skills.
- Develop an activity that allows the staff audience to practice and ask questions about these new processes and skills.
- In the notes section of your PowerPoint, brainstorm potential responses to likely questions or concerns.
- Part 5: Soliciting Feedback.
- Describe how you would solicit feedback from the audience on the improvement plan and the in-service.
- Explain how you might integrate this feedback for future improvements.
Remember to account for activity and discussion time.
For tips on developing PowerPoint presentations, refer to:
- Capella University Library: PowerPoint Presentations.
- Guidelines for Effective PowerPoint Presentations [PPTX].
Additional Requirements
- Presentation length: There is no required length; use just enough slides to address all the necessary elements. Remember to use short, concise bullet points on the slides and expand on your points in the presenter’s notes. If you use 2 or 3 slides to address each of the parts in the above example, your presentation would be at least 10 slides and no more than 15 slides (not including the title, conclusion, or reference slides).
- Speaker notes: Speaker notes (located under each slide) should reflect what you would actually say if you were delivering the presentation to an audience. This presentation does NOT require audio or a transcript. Another presenter would be able to use the presentation by following the speaker’s notes.
- APA format: Use APA formatting for in-text citations. Include an APA-formatted reference slide at the end of your presentation.
- Number of references: Cite a minimum of 3 sources of scholarly or professional evidence to support your assertions. Resources should be no more than 5 years old.
Competencies Measured
By completing this assessment, you will demonstrate your proficiency in the course competencies through the following assessment scoring guide criteria:
- Competency 1: Analyze the elements of a successful quality improvement initiative.
- Explain the need for and process to improve safety outcomes related to a specific patient safety issue.
- Create resources or activities to encourage skill development and process understanding related to a safety improvement initiative.
- Competency 4: Explain the nurse’s role in coordinating care to enhance quality and reduce costs.
- Describe the purpose and goals of an in-service session focusing on a specific patient safety issue.
- Explain to the audience their role and the importance of making the improvement plan successful.
- Competency 5: Apply professional, scholarly, evidence-based strategies to communicate in a manner that supports safe and effective patient care.
- Slides are easy to read and error-free. Detailed speaker notes are provided. Speaker notes are clear, organized, and professionally presented.
- Organize content with a clear purpose or goals and with relevant and evidence-based sources (published within 5 years).
Resources
Use the resources linked below to help complete this assessment.
Collapse All
Leadership Competencies
The following readings may help you in completing this assessment’s activities:
- Assessment 3: Leadership Competencies reading list.
Evidence and Value-Based Decision Making
The following readings may help you in completing this assessment’s activities:
- Assessment 3: Evidence and Value-Based Decision Making reading list.
Facilitating Learning
The following readings may help you in completing this assessment’s activities:
- Assessment 3: Facilitating Learning Reading List.
Program Resources
Capella Writing Center
- Writing Center.
- Access the various resources in the Capella Writing Center to help you better understand and improve your writing.
APA Style and Format
- Capella University follows the style and formatting guidelines in the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association, known informally as the APA manual. Refer to the Writing Center’s APA Module for tips on proper use of APA style and format.
Capella University Library
- BSN Program Library Research Guide.
- The library research guide will be useful in guiding you through the Capella University Library, offering tips for searching the literature and other references for your assessments.
PowerPoint
Refer to these helpful Campus resources for PowerPoint tips:
- Capella University Library: PowerPoint Presentations.
- Guidelines for Effective PowerPoint Presentations [PPTX].
Activity
Click the linked title below, AONE Nurse Executive Competencies Review, to complete this formative activity, which will help you review your understanding of the AONE Nurse Executive Competencies—especially those related to competencies relevant to developing an effective training session and presentation. This is for your own practice and self-assessment.
This tool needs to be loaded in a new browser window
Introduction to NURS 4020 Assessment Three
The NURS-FPX 4020 Assessment Three: Improvement Plan In-Service Presentation focuses on developing an educational in-service session to improve patient safety through quality improvement initiatives. As healthcare professionals, presenting effective training sessions to staff promotes knowledge acquisition and enhances patient care quality. This How-To NURS-FPX 4020 Guide outlines the key components for a successful in-service session, emphasizing the importance of clear communication, staff engagement, and interactive learning strategies.
Describe the purpose and goals of an in-service session focusing on a specific patient safety issue.
Purpose and Goals of an In-Service Session
To start the NURS-FPX 4020 Assessment Three: Improvement Plan In-Service Presentation, we will first discuss the purpose and goals of an in-service session.
Understanding the Patient Safety Issue
- Clearly define the specific patient safety issue that will be addressed.
- Provide background information and context to ensure all participants understand the issue.
Example
Setting Clear Objectives
- Identify the goals you aim to achieve with the in-service session.
- Ensure the objectives are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
Example
Explain the need for and process to improve safety outcomes related to a specific patient safety issue.
Need for and Process to Improve Safety Outcomes
Next, we will discuss the need and the processes to improve safety outcomes.
Identifying the Safety Issue
- Conduct a thorough root-cause analysis to understand the underlying factors contributing to the safety issue.
- Use evidence-based research to support your findings.
Example
Developing an Improvement Plan
- Outline a step-by-step process to address the identified safety issue.
- Include strategies that have been proven effective in similar settings.
Example
Explain to the audience their role and the importance of making the improvement plan successful.
Role and Importance of Staff in the Improvement Plan
Here, we will explore the role and importance of staff in the improvement plan.
Engaging Staff in the Process
- Highlight the importance of staff participation in the success of the improvement plan.
- Use motivational techniques to encourage active involvement.
Defining Roles and Responsibilities
- Clearly define the roles of each staff member in implementing the improvement plan.
- Provide specific examples of how each role contributes to overall success.
Example
Create resources or activities to encourage skill development and process understanding related to a safety improvement initiative.
Resources and Activities for Skill Development
This section will discuss the resources and activities for skill development.
Creating Effective Training Materials
- Develop resources such as handouts, slides, and videos that reinforce the training objectives.
- Ensure the materials are easily accessible and user-friendly.
Implementing Interactive Learning Strategies
- Incorporate simulations, role-playing, and other interactive activities to enhance learning.
- Encourage hands-on practice to build confidence and competence.
Example
Communicate with nurses respectfully and informatively, clearly presenting expectations and soliciting feedback on communication strategies for future improvement.
Effective Communication with Nurses
For this segment of Assessment Three, we will discuss effective communication with the nurses.
Strategies for Clear and Respectful Communication
- Use simple, concise language to ensure understanding.
- Be respectful and empathetic in all communications to foster a positive learning environment.
Soliciting Feedback for Continuous Improvement
- Create opportunities for participants to provide feedback on the training session.
- Use the feedback to make necessary adjustments and improvements.
Example
Demonstration of Proficiency
- Analyzing Quality Improvement Initiatives
- Coordinating Care to Enhance Quality and Reduce Costs
- Applying Scholarly Communication Strategies
Closing
Completing the NURS-FPX 4020 Assessment Three: Improvement Plan In-Service Presentation will equip you with the skills necessary to develop and deliver effective in-service training sessions that improve patient safety and quality of care. By understanding the importance of clear communication, staff engagement, and interactive learning, you will be better prepared to lead initiatives that foster a culture of continuous improvement in healthcare settings. Remember, the competencies required are attainable with practice and dedication, providing you with a strong foundation for professional growth and excellence in patient care. In the upcoming NURS 4020 Assessment Four, we will discuss the improvement plan toolkit.
NURS-FPX 4020 ASSESSMENT FOUR: Improvement Plan Tool Kit
Instructions for NURS-FPX 4020 Assessment Four: Improvement Plan Tool Kit
ImprovementPlan Tool Kit
For this assessment, you will develop a Word document or an online resource repository of at least 12 annotated professional or scholarly resources that you consider critical for the audience of your safety improvement plan to understand or implement to ensure the success of the plan.
Collapse All
Introduction
Communication in the health care environment consists of an information-sharing experience, whether through oral or written messages (Chard & Makary, 2015). As health care organizations and nurses strive to create a culture of safety and quality care, the importance of interprofessional collaboration, the development of tool kits, and the use of wikis becomes more relevant and vital. In addition to the dissemination of information and evidence-based findings and the development of tool kits, continuous support for and availability of such resources are critical. Among the most popular methods to promote ongoing dialogue and information sharing are blogs, wikis, websites, and social media. Nurses know how to support people in times of need or crisis and how to support one another in the workplace; wikis in particular enable nurses to continue that support beyond the work environment. Here, they can be free to share their unique perspectives, educate others, and promote health care wellness at local and global levels (Kaminski, 2016).
You are encouraged to complete the Determining the Relevance and Usefulness of Resources activity prior to developing the repository. This activity will help you determine which resources or research will be most relevant to address a particular need. This may be useful as you consider how to explain the purpose and relevance of the resources you are assembling for your toolkit. The activity is for your own practice and self-assessment, and demonstrates course engagement.
References
Chard, R., & Makary, M. A. (2015). Transfer-of-care communication: Nursing best practices. AORN Journal, 102(4), 329–342.
Kaminski, J. (2016). Why should all nurses/be authors? Canadian Journal of Nursing Informatics, 11(4), 1–7.
Professional Context
Nurses are often asked to implement processes, concepts, or practices—sometimes with little preparatory communication or education. One way to encourage the sustainability of quality and process improvements is to assemble an accessible, user-friendly toolkit for knowledge and process documentation. Creating a resource repository or tool kit is also an excellent way to follow up on an educational or in-service session, as it can help to reinforce attendees’ new knowledge as well as the understanding of its value. By practicing creating a simple online tool kit, you can develop valuable technology skills to improve your competence and efficacy. This technology is easy to use, and resources are available to guide you.
Scenario
For this assessment, build on the work done in your first three assessments and create an online tool kit or resource repository that will help the audience of your in-service understand the research behind your safety improvement plan about a specific patient safety issue and put the plan into action.
Preparation
Google Sites is recommended for this assessment; the tools are free to use and should offer you a blend of flexibility and simplicity as you create your online tool kit. Please note that this requires a Google account; use your Gmail or Google Docs login, or create an account following the directions under the “Create Account” menu.
Refer to the resources on the following list to help you get started with Google Sites:
- Assessment 4: Google Sites reading list.
Instructions
Using Google Sites, assemble an online resource tool kit containing at least 12 annotated resources that you consider critical to the success of your safety improvement initiative. These resources should enable nurses and others to implement and maintain the safety improvement you have developed.
It is recommended that you focus on the 3 or 4 most critical categories or themes with respect to your safety improvement initiative. For example, for an initiative that concerns improving workplace safety for practitioners, you might choose broad themes such as general organizational safety and quality best practices; environmental safety and quality risks; individual strategies to improve personal and team safety; and process best practices for reporting and improving environmental safety issues.
Following the recommended scheme, you would collect 3 resources on average for each of the 4 categories, focusing on a specific patient safety issue. Each resource listing should include the following:
- An APA-formatted citation of the resource with a working link.
- A description of the information, skills, or tools provided by the resource.
- A brief explanation of how the resource can help nurses better understand or implement the safety improvement initiative regarding a specific patient safety issue.
- A description of how nurses can use this resource and when its use may be appropriate.
Remember that you must make your site “public” so that your faculty can access it. Check out the Google Sites resources for more information.
Here is an example entry:
- Merret, A., Thomas, P., Stephens, A., Moghabghab, R., & Gruneir, M. (2011). A collaborative approach to fall prevention. Canadian Nurse, 107(8), 24–29.
- This article presents the Geriatric Emergency Management-Falls Intervention Team (GEM-FIT) project. It shows how a collaborative nurse-led project can be implemented and used to improve collaboration and interdisciplinary teamwork, as well as improve the delivery of health care services. This resource is likely more useful to nurses as a resource for strategies and models for assembling and participating in an interdisciplinary team than for specific fall-prevention strategies. It is suggested that this resource be reviewed prior to creating an interdisciplinary team for a collaborative project in a health care setting.
Additionally, be sure that your plan addresses the following, which corresponds to the grading criteria in the scoring guide. Please study the scoring guide carefully so you understand what is needed for a distinguished score.
- Identify necessary resources to support the implementation and continued sustainability of a safety improvement initiative pertaining to a specific patient safety issue.
- Analyze the usefulness of resources to the role group responsible for implementing quality and safety improvements, focusing on a specific patient safety issue.
- Analyze the value of resources to reduce patient safety risk related to a specific patient safety issue.
- Present reasons and relevant situations for the use of the resource tool kit by its target audience.
- Communicate in a clear, logically structured, and professional manner that applies current APA style and formatting.
Example Assessment: You may use the following example to give you an idea of what a Proficient or higher rating on the scoring guide would look like, but keep in mind that your toolkit will focus on promoting safety with the quality issue you selected in Assessment 1. Note that you do not have to submit your bibliography in addition to the Google Site; the example bibliography is merely for your reference.
- Assessment 4 Example [PDF] Download Assessment 4 Example [PDF].
To submit your online tool kit assessment, paste the link to your Google Site in the assessment submission box.
Example Google Site: You may use the example found on the Assessment 4: Google Sites reading list, Resources for Improved Heparin Infusion Safety, to give you an idea of what a Proficient or higher rating on the scoring guide would look like for this assessment but keep in mind that your tool kit will focus on promoting safety with the quality issue you selected in Assessment 1
Note: If you experience technical or other challenges in completing this assessment, please contact your faculty member.
Competencies Measured
By completing this assessment, you will demonstrate your proficiency in the course competencies through the following assessment scoring guide criteria:
- Competency 1: Analyze the elements of a successful quality improvement initiative.
- Analyze the usefulness of resources to the role group responsible for implementing quality and safety improvements, focusing on a specific patient safety issue.
- Competency 2: Analyze factors that lead to patient safety risks.
- Analyze the value of resources to reduce patient safety risk related to a specific patient safety issue.
- Competency 3: Identify organizational interventions to promote patient safety.
- Identify necessary resources to support the implementation and continued sustainability of a safety improvement initiative pertaining to a specific patient safety issue.
- Competency 5: Apply professional, scholarly, evidence-based strategies to communicate in a manner that supports safe and effective patient care.
- Present reasons and relevant situations for the resource tool kit to be used by its target audience.
- Communicate the resource tool kit in a clear, logically structured, and professional manner that applies current APA style and formatting.
Resources
Use the resources linked below to help complete this assessment.
Collapse All
Collaborationand Teamwork
The following readings may help you in completing this assessment’s activities:
- Assessment 4: Collaboration and Teamwork reading list.
Wikis, Blogs, and Google Sites
The following readings may help you in completing this assessment’s activities:
Wikis
- Assessment 4: Wikis reading list.
Blogs
- Assessment 4:Blogs.
Google Sites
Refer to the resources on this list to help you build your tool kit:
- Assessment 4: Google Sites reading list.
Building Professional Efficacy and Visibility
The following readings may help you in completing this assessment’s activities:
- Assessment 4:Building Professional Efficacy and Visibility reading list.
Evaluating Resources
- Assessment 4: Evaluating Resources.
- This reading may help you in completing this assessment’s activities:
- Think Critically About Source Quality.
- This Capella University Library guide offers a method to help you determine which resources to include in your tool kit.
Program Resources
Capella Writing Center
- Writing Center.
- Access the various resources in the Capella Writing Center to help you better understand and improve your writing.
APA Style and Format
- Capella University follows the style and formatting guidelines in the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association, known informally as the APA manual. Refer to the Writing Center’s APA Module for tips on proper use of APA style and format.
Capella University Library
- BSN Program Library Research Guide.
- The library research guide will be useful in guiding you through the Capella University Library, offering tips for searching the literature and other references for your assessments.
Activity
Click the linked title below, Determining the Relevance and Usefulness of Resources to complete this formative activity, which will help you determine which resources or research will be most relevant to address a particular need. This may be useful as you consider how to explain the purpose and relevance of the resources you are assembling for your toolkit.
This is for your own practice and self-assessment.
This tool needs to be loaded in a new browser window
Introduction to NURS 4020 Assessment Four
In NURS-FPX 4020 Assessment Four: Improvement Plan Tool Kit, you will develop a comprehensive resource repository to support a safety improvement plan. This How-To NURS-FPX 4020 Guide will provide structured steps to create a Word document or an online repository of at least 12 annotated professional or scholarly resources. These resources are crucial for understanding and implementing your safety improvement initiative effectively. This task emphasizes the importance of communication, collaboration, and continuous support within healthcare environments to foster a culture of safety and quality care.
An APA-formatted citation of the resource with a working link. A description of the resource’s information, skills, or tools. A brief explanation of how the resource can help nurses better understand or implement the safety improvement initiative regarding a specific patient safety issue. A description of how nurses can use this resource and when its use may be appropriate.
Identifying Critical Categories/Themes
We will identify critical categories or themes to start the NURS-FPX 4020 Assessment Four: Improvement Plan Tool Kit.
- Focus on 3 or 4 critical categories related to your safety improvement initiative.
- Examples of categories might include organizational safety and quality best practices, environmental safety risks, individual personal and team safety strategies, and process best practices for reporting safety issues.
- Ensure these categories are broad enough to encompass various aspects of the safety issue but specific enough to provide targeted resources.
- Reflect on the primary goals of your safety improvement initiative.
- Identify key themes that are central to achieving these goals.
- Write down these categories and ensure they align with your objective.
Selecting and Annotating Resources
Next, we will select and create annotated resources for the categories or themes.
- Each resource must be cited in APA format and include a working link.
- Use reliable citation tools or guides to format your citations correctly.
- Double-check the links to ensure they are functional.
- Provide a summary of the resource’s information, skills, or tools.
- Explain how the resource can help nurses understand or implement the safety improvement initiative.
- Describe how and when nurses can use this resource effectively.
Example
Massey, D., Chaboyer, W., & Anderson, V. (2016). What factors influence ward nurses’ recognition of and response to patient deterioration? An integrative review of the literature. Nursing Open, 4(1), 6–23. https://doi.org/10.1002/nop2.53
The integrative analysis of ward nurses’ awareness and response to patient deterioration provides valuable insights into utilizing resources for those responsible for quality and safety improvements. The essential components of the resource toolkit include highlighted issues such as patient assessment, patient knowledge, access to support, environmental factors, non-technical skills, education, and emotional responses. The analysis indicates that these areas are crucial for enhancing nurses’ abilities and reactions to patient deterioration. This resource is vital due to the complex issues associated with early detection and response to clinical deterioration. Nurses can use the toolkit to enhance their non-technical skills, access necessary support, and manage emotional reactions during patient deterioration cases. The resource toolkit is vital for reducing patient safety concerns, offering a structured approach for nurses to recognize and respond to deterioration. Nurses should utilize these resources daily to improve patient safety through prompt evaluations and actions.
NOTE: I will provide an annotated bibliography for one resource and three resources in the sample solution. By following the guidelines, write an annotated bibliography for the necessary resources.
Demonstration of Proficiency
Competency 1: Analyze the elements of a successful quality improvement initiative.
Competency 2: Analyze factors that lead to patient safety risks.
Competency 3: Identify organizational interventions to promote patient safety.
Competency 5: Apply professional, scholarly, evidence-based strategies to communicate in a manner that supports safe and effective patient care.
These competencies guide you to systematically approach and solve the assignment, ensuring a thorough and professional outcome.
Closing
Completing the NURS-FPX 4020 Assessment Four: Improvement Plan Tool Kit will equip you to create a valuable resource repository that can significantly enhance patient safety and quality care in healthcare settings. The key takeaways include understanding the importance of structured communication, the relevance of annotated resources, and the impact of accessible, well-organized information on the success of safety improvement initiatives. NURS-FPX 4020 Assessment Four: Improvement Plan Tool Kit How-To Owlisdom Guide provides a detailed, step-by-step approach to developing a resource repository for a safety improvement plan. By adhering to these guidelines, you can ensure that your repository is comprehensive, relevant, and accessible, supporting the ongoing efforts to enhance patient safety and quality care in healthcare settings.




