MGMT-415 – Global Operations Management: Key Concepts, Course Insights, and Study Support
Published: 2025-10-06
Modified: 2025-10-06
Samples Solutions
- MGMT 415 Module 1 Discussion: Personal Experiences with the Six Aims
- MGMT 415 Module 1 assignment: Personal Experiences with the Six Aims
- MGMT 415 Module 2 Discussion: Patient-Centered Care Discussion
- MGMT 415 Module 2 Assignment: To Err is Human
- MGMT 415 Module 3 Assignment: Evidence-Based Practice Assignment
- MGMT 415 Module 5 DISCUSSION: Quality Improvement Tools
- MGMT 415 Module 6 Discussion: Just Culture
- MGMT 415 Module 7 discussion: Healthcare Accreditors
- MGMT 415 Module 7 assignment: Purpose of Accreditation
- MGMT 415 Module 7-3 discussion: PDSA Project Sharing
- MGMT 415 Module Eight discussion: PDSA Healthcare Applications
- MGMT 415 Module Eight assignment: Healthcare Quality Orientation
Introduction
MGMT-415 – Global Operations Management introduces students to the principles of coordinating business activities across international markets. The course explores supply chain efficiency, global logistics, and production management. For help with assignments or case studies, visit Owlisdom’s MBA Assignment Help to get expert academic support.
MGMT 415 Module 1 Discussion: Personal Experiences with the Six Aims
Instructions for MGMT 415 Module 1 Discussion
Personal Experiences with the Six Aims Discussion
3535 unread replies.4949 replies.
In this discussion, you will consider an experience that you, a family member, or a friend has had with healthcare in light of the six aims of healthcare quality.
Discussion Directions
In your initial post,
- Briefly describe the healthcare encounter. (Comply with HIPAA privacy laws by not revealing personally identifiable information.)
- Compare the experience with each of the six aims of healthcare.
- Explain how care quality could have been improved based on what you have learned about the six aims of healthcare.
Your initial post is due by the discussion due date.
Peer Responses
Respond to two peers before the discussion closing date (see the Canvas calendar). Peer responses must further the discussion. For example, you may think of additional ways that their experience could relate to the six aims of healthcare. You could also discuss the merits of their ideas for improvement or offer ideas they may not have considered.
To view the rubric for a discussion in Canvas, click the dropdown menu (three vertical dots near the discussion title) and select “Show Rubric.”
Introduction to MGTM 415 Module One Discussion
This How-To MGMT 415 guide provides a step-by-step approach to analyzing a healthcare experience in light of the six aims of healthcare quality: safety, effectiveness, patient-centeredness, timeliness, efficiency, and equity. You will learn how to describe a healthcare encounter while maintaining privacy, compare the experience against the six aims, suggest improvements, and engage in peer discussions to deepen the analysis.
Briefly describe the healthcare encounter. (Comply with HIPAA privacy laws by not revealing personally identifiable information.)
Describing the Healthcare Encounter
To start the MGMT 415 Module 1 Discussion: Personal Experiences with the Six Aims, we will discuss describing the healthcare encounter.
- Avoid using names, specific dates, or locations.
- Generalize details that might identify individuals (e.g., “a relative” instead of “my grandmother”).
- Begin with the context: briefly explain the situation and the type of care received.
- Highlight key aspects of the encounter: what happened, the interactions with healthcare professionals, and the outcome.
Compare the experience with each of the six aims of healthcare.
Comparing the Experience with the Six Aims of Healthcare
For this section of the MGMT 415 Module 1 Discussion: Personal Experiences with the Six Aims, we will, for each aim, provide a brief comparison of how the healthcare experience is measured.
Safety
- Assess whether the care provided avoided harm to the patient.
- Consider if there were any safety protocols in place and if they were followed.
Effectiveness
- Evaluate if the care delivered was based on scientific knowledge and evidence.
- Reflect on the outcomes: did the treatment achieve its intended results?
Patient-centeredness
- Determine if the care respected the patient’s preferences, needs, and values.
- Note any efforts made to involve the patient in decision-making.
Timeliness
- Assess if the care was provided promptly.
- Identify any delays in treatment or long waiting times.
Efficiency
- Consider how well resources were used in providing care.
- Look for signs of waste or duplication of services.
Equity
- Evaluate if the care was provided fairly and without bias.
- Reflect on whether all individuals had equal access to the care needed.
Explain how care quality could have been improved based on what you have learned about the six aims of healthcare.
Explaining Improvements Based on Six Aims
Here, we will explain the improvements based on the Six Aims.
- Compare your experience against each aim to identify areas where the care fell short.
- Provide practical recommendations for how care could have been better aligned with the six aims.
- Use evidence from your learning to support your suggestions.
Respond to two peers before the discussion closing date (see the Canvas calendar). Peer responses must further the discussion. For example, you may think of additional ways that their experience could relate to the six aims of healthcare. You could also discuss the merits of their ideas for improvement or offer ideas they may not have considered.
Peer Responses
According to the instructions of MGMT 415 Module 1 Discussion: Personal Experiences with the Six Aims, we are supposed to write two peer responses. I have addressed the given instructions in one response. Following these instructions, you can write your peer responses to Module 1 Discussion without a hassle.
- Read your peers’ descriptions and analyses carefully.
- Think critically about how their experiences relate to the six aims.
- Assess the merits of their improvement ideas.
- Offer constructive feedback on their analyses.
- Suggest additional ways their healthcare experiences could be improved.
Response 01
Your detailed analysis of the healthcare encounter is insightful. To further improve patient-centeredness, consider implementing post-visit patient feedback surveys to tailor future care. Additionally, enhancing timeliness by adopting telemedicine for initial consultations can reduce ER wait times. Your suggestion for continuous training on medical advancements is crucial for maintaining effectiveness.
Response 02
Responding to peers is one of the vital parts of the MGMT 415 1-1 Discussion posts. We need to provide at least two peer responses. I will provide one example post. You can write your peer responses by keeping the above points in mind.
Closing
By following this How-To Owlisdom Guide, you will be able to critically analyze healthcare experiences and provide well-supported recommendations for improving care quality based on the six aims of healthcare. Engaging in peer discussions will further enhance your understanding and contribute to a richer learning experience.
MGMT 415 Module 1 assignment: Personal Experiences with the Six Aims
Instructions for MGMT 415 Module 1 Assignment
Six Aims of Healthcare Quality Assignment
The purpose of this assignment is for students to familiarize themselves with a healthcare quality framework, which will form the foundation for the course.
Assignment Directions
Review the readings and videos for Module 1 related to the six domains of healthcare quality. Then, create a six-slide PowerPoint presentation. Your presentation should have one slide for each of the domains of healthcare quality, also known as the six aims for improvement.
On each slide:
- List the name of the aim in the title of the slide
- Describe the aim
- Give an example of how the aim can be measured
- Give an example of how the improvement can happen with regard to the aim
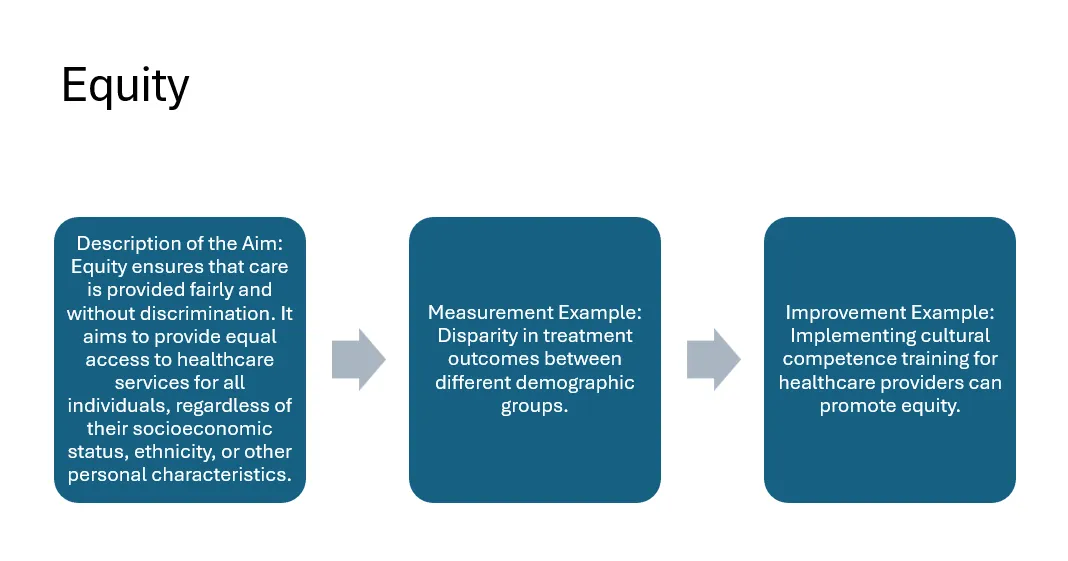
Example
Here is an example of a slide on the TimelyLinks to an external site. aim.
Readings and Videos for Module 1
Use the readings and videos to help you prepare for the assignments in this module. This week’s lesson material will help you illustrate how healthcare quality indicators are demonstrated in a healthcare setting and develop quality recommendations based on healthcare quality indicators.
Read
Healthcare Quality Book: Vision, Strategy, and ToolsTextbookLinks
to an external site. pp. 5-13
Institute of Medicine (IOM) The Six Aims of Healthcare QualityLinks to
an external site.
View
6 Dimensions of Healthcare Quality – 7 min
Introduction to MGTM 415 Module One Assignment
Each slide of the MGMT 415 Module 1 assignment, Personal Experiences with the Six Aims, will focus on one of the six aims for improvement, providing a clear description, an example of how it can be measured, and a practical example of how improvements can be made. This exercise is designed to help students understand and apply these foundational concepts in healthcare quality. This How-To MGMT 415 Guide provides a structured approach for students to create a PowerPoint presentation on the six domains of healthcare quality.
Review the readings and videos for Module 1 related to the six domains of healthcare quality. Then, create a six-slide PowerPoint presentation. Your presentation should have one slide for each of the domains of healthcare quality, also known as the six aims for improvement.
On each slide:
- List the name of the aim in the title of the slide
- Describe the aim
- Give an example of how the aim can be measured
- Give an example of how the improvement can happen towards the aim
Presentation on Healthcare Quality
For the MGMT 415 Module 1 assignment: Personal Experiences with the Six Aims, we need to make a PowerPoint Presentation on the topic of Healthcare Quality.
- Write the name of each aim (Safety, Effectiveness, Patient-Centeredness, Timeliness, Efficiency, Equity) in the title of its respective slide.
- Provide a brief description of what each aim entails (e.g., Safety aims to avoid harm to patients).
- Include an example of how the aim can be measured (e.g., infection rates for Safety).
- Provide an example of how improvements can be made related to each aim (e.g., hand hygiene protocols for Safety).
- Ensure that the readings and videos from Module 1 inform your descriptions, measurements, and improvement examples.
- Use concise text and visuals to make each slide clear and engaging, highlighting the key points for each aim.
Example Presentation





Closing
By following this How-To Owlisdom Guide, you will be able to critically analyze healthcare experiences and provide well-supported recommendations for improving care quality based on the six aims of healthcare. In the next module of MGMT 415, we will discuss Patient-Centered Care.
MGMT 415 Module 2 Assignment: To Err is Human
Instructions for MGMT 415 Module 2 Assignment
To Err is Human Assignment
As explained in the Module 2 readings and videos, the Institute of Medicine’s “To Err is Human” report (1999) was a catalyst for a renewed emphasis on bolstering healthcare quality by improving patient safety. A key conclusion of the report was that system-wide changes need to be made in order to prevent deaths and injuries from medical errors (Donaldson, 2008).
Source Guidelines
- Locate information from a credible source about a preventable error that has occurred in a healthcare process and resulted in patient harm. (Credible sources include healthcare industry publications, journal articles, or information available from a healthcare organization such as a hospital’s website.)
- Cite the source of your information whenever you reference it in the assignment.
Assignment Directions
- Describe the error.
- Identify possible causes for the error, explaining the connections between the error and its possible causes.
- Propose one or more quality improvement strategies that would accomplish both of the following objectives:
- detect the error when or before it occurs
- prevent the error from resulting in patient harm
Reference
Donaldson, M. S. (2008). An overview of To Err is Human: Re-emphasizing the message of patient safety. In R. G. Hughes (ed.). Patient Safety and Quality: An Evidence-Based Handbook for Nurses. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK2673/
Introduction to MGTM 415 Module Two Assignment
In the MGMT 415 Module 2 Assignment: To Err is Human, you are tasked with analyzing a healthcare error, identifying its potential causes, and proposing quality improvement strategies to detect the error and prevent patient harm. This How-To MGMT 415 Guide will provide clear, concise instructions for each assignment section, ensuring a thorough and professional analysis.
Describe the error.
Describing the Error
To start the MGMT 415 Module 2 Assignment: To Err is Human, we will discuss the error in the Institute of Medicine’s “To Err is Human” report (1999).
- Choose a healthcare error that is well-documented and significantly impacts patient safety.
- Examples include medication errors, surgical errors, diagnostic errors, etc.
- Explain the nature of the error.
- Describe the context of the error (e.g., hospital setting, type of care, involved personnel).
- Outline the consequences of the error for the patient(s) involved.
- Include any immediate and long-term effects on health and well-being.
Example
One prominent healthcare error documented extensively in the Institute of Medicine’s (IOM) “To Err is Human” report is medication errors. These errors occur when there is a mistake in prescribing, dispensing, or administering medication, leading to harm or potential harm to patients. Medication errors are prevalent and can have significant implications for patient safety.
The nature of medication errors can vary, including incorrect dosages, wrong medication given, or medication administered at the wrong time. These errors often arise in complex hospital settings where multiple healthcare professionals interact with patients. For example, a nurse might misread a prescription, or a pharmacist might dispense the wrong drug due to similar drug names.
The consequences for patients can be severe, ranging from minor discomfort to life-threatening conditions. Immediate effects might include adverse drug reactions, while long-term effects could involve prolonged hospital stays, permanent injury, or even death. For instance, a patient receiving an incorrect dosage of insulin might suffer from hypoglycemia, leading to seizures, unconsciousness, or long-term neurological damage.
Identify possible causes for the error, explaining the connections between it and its potential causes.
Identifying Possible Causes for the Error
Next, we will discuss the possible causes of the error.
- Examine human error, system failures, communication breakdowns, and environmental influences.
- Use relevant frameworks or models (e.g., the Swiss Cheese Model) to structure your analysis.
- Link each identified cause to the error.
- Use evidence from literature and case studies to support your explanations.
- Conduct a root cause analysis to identify underlying issues.
- Focus on systemic problems rather than individual blame.
Example
Identifying the causes of medication errors involves examining multiple factors, including human error, system failures, communication breakdowns, and environmental influences. Human error is often a significant factor, stemming from fatigue, inadequate training, or cognitive overload. For instance, a nurse working long hours might misinterpret a prescription due to exhaustion.
System failures are also critical contributors. Poorly designed healthcare systems, such as confusing medication labels or complex electronic health records, can lead to mistakes. Communication breakdowns, such as unclear doctor instructions or incomplete handovers between shifts, further exacerbate the issue. Environmental factors like inadequate lighting or high noise levels in hospitals can distract healthcare workers, increasing the likelihood of errors.
The Swiss Cheese Model is useful for understanding how these factors interconnect. This model suggests that errors occur when multiple layers of defense (like cheese slices) have holes (weaknesses) that align, allowing an error to pass through. For example, a poorly designed electronic health record system (system failure) combined with a tired nurse (human error) and a noisy environment (environmental influence) creates a perfect storm for a medication error.
Conducting a root cause analysis helps identify underlying systemic issues rather than placing blame on individuals. For example, this analysis might reveal that a hospital’s shift scheduling leads to nurse fatigue or that the electronic health record system is not user-friendly, necessitating redesigns to prevent future errors.
Propose one or more quality improvement strategies that would accomplish both of the following objectives: detect the error when or before it occurs, and prevent the error from resulting in patient harm
Proposing Quality Improvement Strategies
For this segment of Module Two Assignment, we will propose quality improvement strategies.
- Suggest methods or tools to identify the error early.
- Consider technologies (e.g., electronic health records, automated alerts) and process changes (e.g., double-checking procedures).
- Propose interventions to mitigate the impact if the error occurs.
- Strategies might include staff training, revised protocols, and safety barriers.
- Use best practice guidelines from reputable sources (e.g., Joint Commission, WHO).
- Ensure your strategies are evidence-based and feasible.
Example
To address medication errors effectively, it is crucial to implement quality improvement strategies that can detect errors early and prevent patient harm. One effective method is using advanced technologies like electronic health records (EHRs) with built-in medication verification systems. These systems can flag potential errors, such as incorrect dosages, before they reach the patient.
Automated alerts can also play a significant role. For instance, if a prescribed medication interacts adversely with another drug the patient takes, a computerized alert can notify the healthcare provider, allowing immediate correction. Process changes, such as implementing double-check procedures where two healthcare professionals verify medication orders, can further reduce the likelihood of errors.
In addition to detection, interventions to mitigate the impact of errors are essential. Staff training programs focused on medication safety can enhance awareness and competence among healthcare workers. Revised protocols, such as standardized medication administration procedures, can minimize variability and reduce errors.
Best practice guidelines from reputable sources, such as the Joint Commission and the World Health Organization (WHO), provide evidence-based strategies for improving medication safety. For instance, the Joint Commission’s “Do Not Use” list of abbreviations helps prevent misinterpretation of medication orders. They ensure these feasible strategies involve regularly monitoring and adapting them based on feedback and outcomes.
Closing
In the MGMT 415 Module 2 Assignment: To Err is Human, you have explored a healthcare error, analyzed its causes, and proposed strategies to improve patient safety. The key takeaways include understanding the multifaceted nature of healthcare errors, the importance of systemic solutions, and implementing proactive quality improvement measures. Following this How-To Owlisdom Guide, students will be well-equipped to contribute to enhancing healthcare quality and patient safety in their professional practice. The upcoming module will improve your understanding of Evidence-Based Practice and PDSA.
MGMT 415 Module 3 Assignment: Evidence-Based Practice Assignment
Instructions for MGMT 415 Module 3 Assignment
Readings and Videos for Module 3
Use the readings and videos to help you prepare for the assignments in this module. This week’s lesson material will help you illustrate how healthcare quality indicators are demonstrated in a healthcare setting, interpret recommended healthcare quality practices to determine potential implementation strategies, identify sources of healthcare errors, and describe tools and models used to improve healthcare quality.
Read:
Johns Hopkins Center for Evidence-Based Practice Evidence-Based Practice ExemplarsLinks to an external site.
Healthcare Quality Book: Vision, Strategy, and ToolsTextbookLinks to an external site. pp. 18-19 and 62-65
View:
Allied Health: Evidence-Based Practice – 3 min https://youtu.be/j5sU5H-IBSg
“Translating Evidence into Practice – The Johns Hopkins Nursing Experience” by Kathleen White for OP – 23 min https://youtu.be/_oAVz2dQAi8
These viewing
questions will help you pay attention to key concepts as you watch the video.
“PDSA Cycles: From CLABSIs to Cucumbers” – 6 min. https://youtu.be/8Q7qnNpTWxM
Evidence-Based Practice Assignment
Start Assignment
- Due Friday by 11:59pm
- Points 35
- Submitting a file upload
Watch the video entitled “Translating Evidence into Practice – The Johns Hopkins Nursing Experience” by Kathleen White. (There are viewing questions to help you follow along with the video. The questions are for your own benefit, you do not need to submit your answers.) After you have watched the video, do your own exploration of the evidence-based projects that have resulted from this initiative.
Assignment Directions
Go to the Johns Hopkins Evidence-Based Practice websiteLinks to an external site.. Select a project and respond to the following prompts:
- List the title of the project.
- Summarize what the project team learned from examining the evidence.
- Explain how the findings relate to one or more of the six aims of healthcare quality improvement (we learned about the six aims in Module 1).
- Restate the project team’s practice recommendations in your own words.
- Propose additional ideas for how the evidence could be put into practice, supporting your ideas with logical reasoning.
Rubric
Evidence Based Practice Assignment Rubric
|
Evidence Based Practice Assignment Rubric |
||||||
|
Criteria |
Ratings |
Pts |
||||
|
This criterion is linked to a Learning OutcomeMGMT415_01.00 Illustrate how healthcare quality indicators are demonstrated in a healthcare setting threshold: 8.5 pts |
|
10 pts |
||||
|
This criterion is linked to a Learning OutcomeMGMT415_7.00 Interpret recommended healthcare quality practices to propose implementation strategies threshold: 8.5 pts |
|
10 pts |
||||
|
This criterion is linked to a Learning OutcomeSkill: Written Quality threshold: 8.5 pts |
|
10 pts |
||||
|
This criterion is linked to a Learning OutcomeSkill: Timeliness threshold: 5.0 pts |
|
5 pts |
||||
PDSA Proposal
Start Assignment
- Due Friday by 11:59 pm
- Points 45
- Submitting a file upload
In the “PDSA Cycles: From CLABSIs to Cucumbers” video for this module, Dr. Goldmann gives the example of using a Plan – Do – Study – Act (PDSA) cycle to improve his vegetable garden. He recommends trying PDSA in your personal life so that the process feels familiar when you need to apply the model in healthcare.
We are going to take Dr. Goldmann’s advice! First, you will propose a PDSA project in this module. Then, you will carry out the PDSA cycle over the course of the next few modules. Finally, you will report your results at the end of the course.
Directions
Students will be using a Google Template to complete this assignment. The steps have linked guides for students to use as needed.
- Authorize Google Access to Canvas if you haven’t already done so for another course (see the guide for authorizing Google).
- Access the Google Drive account associated with your Bryan College of Health Sciences e-mail account.
- Make a copy of the PDSA TemplateLinks to an external site., making note of where you saved the file in your Google Drive (see the guide for Google Automatic Copy Links)
- Stop after completing the “Plan” section of the document.
- Submit your work (see the guide for Google Drive Direct to Canvas Submissions)
- If you encounter any errors, try sharing the file publicly or downloading the file and uploading (see the guide for resolving submission errorsLinks to an external site.)
Criteria
Complete all items in the assigned section of the template. See the rubric for the grading criteria.
Rubric
PDSA Proposal Assignment Rubric
|
PDSA Proposal Assignment Rubric |
||||||
|
Criteria |
Ratings |
Pts |
||||
|
This criterion is linked to a Learning OutcomeMGMT415_01.00 Illustrate how healthcare quality indicators are demonstrated in a healthcare setting threshold: 8.5 pts |
|
10 pts |
||||
|
This criterion is linked to a Learning OutcomeMGMT415_3.00 Identify sources of errors threshold: 8.5 pts |
|
10 pts |
||||
|
This criterion is linked to a Learning OutcomeMGMT415_4.00 Describe tools and models used to improve healthcare quality threshold: 8.5 pts |
|
10 pts |
||||
|
This criterion is linked to a Learning OutcomeSkill: Written Quality threshold: 8.5 pts |
|
10 pts |
||||
|
This criterion is linked to a Learning OutcomeSkill: Timeliness threshold: 5.0 pts |
|
5 pts |
||||
|
Total Points: 45 |
||||||
Introduction to MGTM 415 Module Three Assignment
The MGMT 415 Module 3 Assignment: Evidence-Based Practice Assignment involves critically analyzing a project from the Johns Hopkins Evidence-Based Practice initiative. You will explore a selected project, summarize its findings, relate those findings to healthcare quality improvement aims, restate practice recommendations, and propose additional ideas for evidence implementation. This How-To MGMT 415 Guide provides a step-by-step approach to completing each part of the assignment successfully.
List the title of the project.
Selecting and Listing the Project
We will select and list the project title to start the MGMT 415 Module 3 Assignment: Evidence-Based Practice Assignment.
- Visit the Johns Hopkins Evidence-Based Practice website.
- Navigate the available projects and select one that interests you or aligns with your academic focus.
- list the title of the selected project.
- Ensure the title is accurately represented as it appears on the website.
Example
Title: “Reducing Hospital-Acquired Infections Through Hand Hygiene Compliance”
The project “Reducing Hospital-Acquired Infections Through Hand Hygiene Compliance” aimed to address the persistent issue of hospital-acquired infections (HAIs), significantly impacting patient safety and healthcare costs. The project team focused on improving hand hygiene compliance among healthcare workers as a primary strategy to reduce HAIs.
Through a comprehensive review of the evidence, the project team found that enhancing hand hygiene practices could dramatically decrease the incidence of HAIs. They conducted an extensive literature review, analyzed data from multiple healthcare settings, and utilized observational studies to understand the factors influencing hand hygiene compliance. The key findings indicated that consistent hand hygiene practices led to a substantial reduction in infection rates.
Moreover, the team discovered that education and regular training sessions were crucial in maintaining high compliance rates. They noted that visual reminders and easy access to hand-sanitizing stations played significant roles. The project underscored the importance of creating a safety culture where all healthcare workers adhere to hand hygiene protocols.
Summarize what the project team learned from examining the evidence.
Summarizing the Project Team’s Learnings
Next, we will summarize the project team learning.
- Thoroughly read the project description, objectives, methodology, and results.
- Focus on key findings and insights gained by the project team.
- Provide a concise summary of what the project team learned from examining the evidence.
- Highlight significant outcomes, patterns, and conclusions drawn from the project.
Please explain how the findings relate to one or more of the six aims of healthcare quality improvement (we learned about the six aims in Module 1).
Explaining the Findings of the Six Aims of Healthcare Quality Improvement
For this section of MGMT 415 Module 3 Assignment: Evidence-Based Practice Assignment, we will explain the findings of the Six Aims of Healthcare Quality Improvement that we explored in Module One of this course.
- Recall the six aims of healthcare quality improvement: safe, effective, patient-centered, timely, efficient, and equitable care.
- Reflect on how these aims guide overall healthcare quality.
- Identify the six aims addressed by the project’s findings.
- Explain how the evidence supports or advances these aims, providing specific examples from the project.
Example
Explaining the Findings of the Six Aims of Healthcare Quality Improvement
The findings from the hand hygiene project align with several of the six aims of healthcare quality improvement.
Safe Care
The primary aim of reducing HAIs is to enhance patient safety directly. The evidence shows that improved hand hygiene practices significantly lower the risk of infections, thereby protecting patients from preventable harm.
Effective Care
Adequate care is achieved by implementing evidence-based practices. The project’s reliance on proven strategies for hand hygiene ensures that the interventions are based on solid scientific evidence, leading to better health outcomes.
Patient-Centered Care
Patient-centered care is reflected in the project’s emphasis on reducing HAIs that directly affect patient well-being and satisfaction. By prioritizing patient safety and comfort, the project aligns with this aim.
Timely Care
The project contributes to timely care by reducing the incidence of HAIs. Patients experience fewer complications, shorter hospital stays, and faster recovery times, enhancing the overall efficiency of healthcare delivery.
Efficient Care
Reducing HAIs improves efficiency, reducing healthcare costs and resource utilization. Preventing infections minimizes the need for additional treatments, medications, and extended hospital stays.
Equitable Care
The project ensures equitable care by implementing standardized hand hygiene practices across all healthcare settings, benefiting all patients regardless of their background or condition.
Restate the project team’s practice recommendations in your own words.
Restating Practice Recommendations
Here, we will discuss the team’s practice recommendations in our own words.
- Carefully review the practice recommendations made by the project team.
- Note the core elements and intended outcomes of these recommendations.
- Paraphrase the recommendations clearly and succinctly.
- Ensure you capture the essence of the recommendations while using your language.
Example
Restating Practice Recommendations
The project team recommended several vital practices to improve hand hygiene compliance:
Regular Training and Education
Healthcare workers should undergo continuous education and training sessions to stay updated on hand hygiene protocols and the importance of compliance.
Visual Reminders and Signage
Placing visual reminders, such as posters and signs, in strategic locations within healthcare facilities can reinforce the importance of hand hygiene and prompt compliance.
Access to Hand Hygiene Supplies
Ensuring that hand sanitizing stations and soap dispensers are easily accessible and adequately stocked is crucial for maintaining high compliance rates.
Monitoring and Feedback
Implementing a system for monitoring hand hygiene practices and providing regular feedback to healthcare workers can help sustain compliance and address any lapses promptly.
Propose additional ideas for implementing the evidence, supporting your ideas logically.
Proposing Additional Ideas for Implementing Evidence
Next, we will propose additional ideas for implementing evidence.
- Evaluate the current strategies for putting evidence into practice as outlined in the project.
- Identify any gaps or areas for improvement.
- Suggest additional methods or tools that could enhance evidence implementation.
- Support your ideas with logical reasoning, considering feasibility, potential impact, and alignment with healthcare quality aims.
Example
Proposing Additional Ideas for Implementing Evidence
The following additional strategies can be considered further to enhance the implementation of evidence-based hand hygiene practices.
Technological Solutions
Integrating technology, such as electronic monitoring systems, can provide real-time feedback on hand hygiene compliance. These systems can track when healthcare workers sanitize their hands and offer reminders for missed compliance.
Incentive Programs
Introducing incentive programs that reward healthcare workers for consistent hand hygiene compliance can motivate adherence. Recognizing and rewarding departments or individuals with high compliance rates can foster a culture of safety.
Engaging Patients and Families
Educating patients and their families about the importance of hand hygiene and encouraging them to remind healthcare workers can create an additional layer of accountability and support.
Leadership Commitment
Strong leadership commitment to hand hygiene practices can set the tone for the organization. Leaders should model proper hand hygiene and promote its importance through policies and communication.
By implementing these strategies, healthcare facilities can further improve hand hygiene compliance, thereby reducing the incidence of hospital-acquired infections and enhancing overall patient safety and care quality.
Closing
In completing the MGMT 415 Module 3 Assignment: Evidence-Based Practice Assignment, you will gain a deeper understanding of evidence-based practice and its application in healthcare quality improvement. Key takeaways include the ability to analyze evidence critically, relate findings to established quality aims, and propose innovative strategies for practice improvement. By following this How-To Owlisdom Guide, you will effectively contribute to the ongoing efforts to enhance healthcare outcomes through evidence-based initiatives.
MGMT 415 Module 5 DISCUSSION: Quality Improvement Tools
Instructions for MGMT 415 Module 5 Discussion
Readings and Videos for Module 5
Use the readings to help you prepare for the assignments in this module. This week’s lesson material will help you describe tools and models used to improve healthcare quality and interpret recommended healthcare quality practices to propose implementation strategies.
Read:
Healthcare Quality Book: Vision, Strategy, and ToolsTextbookLinks to an external site. pp. 22-33
Quality Tools A to Z Links to an external site.(Choose one tool no one else has chosen for the discussion post)
Quality Tools Discussion
No unread replies.11 replies.
In this discussion, we will learn about and apply a variety of quality tools. These tools help understand and manage healthcare processes. They can also help decision-makers collect data for process improvement.
Directions
Start by visiting the Quality Tools A to Z websiteLinks to an external site. and choosing a tool to research. Please pick a tool no one else has chosen. You can “claim” a tool early by starting a discussion post with the name of the tool. Then, you can come back and edit or reply to your post to complete it before the due date.
In your initial post, explain the basics of your chosen tool by:
- Identifying the tool’s purpose.
- Discussing the components or elements of the tool.
- Describing (in general terms) appropriate situations for the tool’s use.
Although a certain number of citations are not required, be sure to reference the textbook and any other professional websites or scholarly resources you find on your own (cited in APA-style). You should reference sources as needed to provide an overview for your peers.
Your initial post is due by the discussion due date.
Peer Responses
Read through all posts and choose one for your reply that hasn’t received responses already (if all posts have received responses, select the post with the fewest responses). In the response,
- Describe a specific healthcare situation in which it would be appropriate to use the tool explained by your peer.
- Interpret how the tool should be implemented in the situation to improve quality, justifying why the tool is a good match for the situation.
Respond by the discussion closing date (see the Canvas calendar).
To view the rubric for a discussion in Canvas, click the dropdown menu (three vertical dots near the discussion title) and select “Show Rubric.”
PDSA Status Update 2: Study
Start Assignment
- Due Jun 7 by 11:59pm
- Points 25
- Submitting a file upload
This assignment is designed as a continuation of the PDSA project.
Directions
Students will continue using a Google Template to complete this assignment.
- Access the Google Drive account associated with your Bryan College of Health Sciences e-mail account.
- Find the PDSA Template document that you began in the PDSA Proposal Assignment (Hint: Search your Google Drive for PDSA)
- Check for instructor feedback on the “Do” section (aka the PDSA Status Update 1: Do) and modify the plan as needed.
- Continue working and stop after completing the “Study” section of the document.
- Submit your work (see the guide for Google Drive Direct to Canvas Submissions)
- If you encounter any errors, try sharing the file publicly or downloading the file and uploading (see the guide for resolving submission errors)
Criteria
Complete all items in the assigned section of the template. See the rubric for the grading criteria.
Rubric
PDSA Status Update Rubric
|
PDSA Status Update Rubric |
||||||
|
Criteria |
Ratings |
Pts |
||||
|
This criterion is linked to a Learning OutcomeMGMT415_4.00 Describe tools and models used to improve healthcare quality threshold: 8.5 pts |
|
10 pts |
||||
|
This criterion is linked to a Learning OutcomeSkill: Written Quality threshold: 8.5 pts |
|
10 pts |
||||
|
This criterion is linked to a Learning OutcomeSkill: Timeliness threshold: 5.0 pts |
|
5 pts |
||||
|
Total Points: 25 |
||||||
Introduction to MGTM 415 Module Five Discussion
In the MGMT 415 Module 5 Discussion: Quality Improvement Tools, you will explore various quality tools used in healthcare to understand and manage healthcare processes effectively. This How-To MGMT 415 Guide aims to select a tool, analyze its purpose and components, and discuss suitable situations for its application. Additionally, you will engage in peer discussions to enhance your understanding of the practical use of these tools in healthcare settings.
Choose a tool to research. Please pick a tool no one else has chosen. You can “claim” a tool early by starting a discussion post with the name of the tool.
Researching and Claiming a Tool
To start the MGMT 415 Module 5 Discussion: Quality Improvement Tools, we will carry out research and select a quality tool.
- Visit the Quality Tools A to Z Website: To explore the available quality tools, visit the specified website.
- Choose a Tool: Select a tool that interests you and check the discussion posts to ensure no one else has chosen it.
- Claim the Tool: Start a discussion post with its name to claim a tool. This ensures you have exclusive rights to research and present it.
- Edit or Reply to Your Post: You can return to your post later to complete it before the due date.
Example
For this discussion, I have chosen Quality Function Deployment (QFD) as my quality tool. QFD is an effective method for transforming customer needs into engineering characteristics for a product or service. This tool ensures that the voice of the customer is systematically integrated into the development process.
We are identifying the tool’s purpose.
Identifying the Tool’s Purpose
We will now identify the purposes of the selected tool.
- Understand the Tool’s Function: Research the tool’s primary purpose and determine what problems it aims to solve in healthcare settings.
- Define the Objective: Clearly articulate the tool’s primary objective. Explain why it is used and what outcomes it seeks to achieve.
Example
Identifying the Tool’s Purpose
QFD aims to align product or service characteristics with customer desires, ensuring that the final output meets or exceeds customer expectations. In healthcare, QFD is particularly valuable for designing patient-centric services and improving patient satisfaction. By translating patient needs into specific service features, healthcare providers can enhance service quality, streamline processes, and improve patient outcomes.
We were discussing the components or elements of the tool.
Discussing the Components or Elements of the Tool
Now, we will discuss the components of the tool that we selected.
- Break Down the Tool: Identify and describe the key components or elements of the tool.
- Explain Each Component: Briefly explain how each component functions and its role in the overall tool’s operation.
- Illustrate with Examples: Use examples to help clarify complex elements and demonstrate how they work together.
Example
Discussing the Components or Elements of the Tool
QFD consists of several key components:
House of Quality (HoQ) is the core matrix of QFD, where customer requirements are translated into technical requirements. This component visually represents the relationships between customer needs and the company’s ability to meet those needs.
Customer Requirements (CRs): These are the specific needs and desires of the customer, gathered through surveys, interviews, or focus groups. CRs might include timely appointments, friendly staff, and adequate healthcare treatment.
Technical Requirements (TRs): These specific technical characteristics must be addressed to meet the customer’s requirements. For instance, TRs could include advanced medical equipment, trained staff, and efficient administrative processes in healthcare.
Relationships Matrix: This part of the HoQ links CRs to TRs, indicating the strength of each pair’s relationship. This helps prioritize technical efforts based on customer priorities.
Competitive benchmarking involves comparing the organization’s performance with competitors regarding various customer requirements and identifying areas for improvement.
You are describing (in general terms) appropriate situations for the tool’s use.
Describing Appropriate Situations for the Tool’s Use
Here, we will describe appropriate situations for the selected tool.
- Identify Suitable Scenarios: Describe general situations in healthcare where the tool can be effectively applied.
- Highlight Benefits: Discuss the tool’s benefits in these situations, emphasizing how it can improve processes and outcomes.
- Provide Context: Explain the context in which the tool is most effective, considering factors like the type of healthcare setting, the nature of the problem, and the stakeholders involved.
Example
Describing Appropriate Situations for the Tool’s Use
QFD is particularly effective in healthcare scenarios where patient satisfaction and service quality are paramount. Suitable situations include:
Service Design: When designing a new healthcare service, QFD can ensure that the service aligns with patient needs, from ease of appointment scheduling to the quality of care provided.
Process Improvement: In existing services, QFD can help identify and address gaps between patient expectations and current service delivery, improving patient experiences and outcomes.
Product Development: QFD ensures that the end product meets the needs of healthcare providers and patients when developing new medical devices or healthcare technologies.
Benefits and Context
The benefits of using QFD in these situations are substantial. It helps healthcare organizations focus on what truly matters to patients, leading to higher satisfaction rates, better compliance with treatment plans, and improved overall health outcomes. QFD is most effective when patient feedback can be systematically gathered and used to drive improvements, such as in hospitals, clinics, and healthcare product development teams.
In the response, describe a specific healthcare situation in which it would be appropriate to use the tool explained by your peer. Interpret how the tool should be implemented to improve quality, justifying why the tool is a good match for the situation.
Peer Responses
According to MGMT 415 Module 5 Discussion: Quality Improvement Tools instructions, we are supposed to write two peer responses. I have addressed the given instructions in one response. Following these instructions, you can write your peer responses to the Week 5 Discussion without a hassle.
- Read All Posts: Review all discussion posts to understand the tools chosen by your peers.
- Choose a Post to Respond To: Select a post that hasn’t received responses yet. If all posts have responses, choose the one with the fewest replies.
- Identify a Relevant Situation: Think of a specific healthcare situation that aligns well with the tool discussed by your peer.
- Provide Details: Describe this situation in detail, explaining the context and the issues that need addressing.
- Explain Implementation: Discuss how the tool should be implemented in the described situation. Provide a step-by-step approach if necessary.
- Justify the Tool’s Use: Explain why the tool is appropriate for the situation and highlight its potential impact on improving quality and outcomes.
Response 01
Hey Sam, nice post! An ideal healthcare situation for QFD would be redesigning a hospital’s outpatient services to improve patient satisfaction. Implementing QFD involves gathering patient feedback on waiting times, staff interactions, and treatment effectiveness. The House of Quality can align these needs with technical requirements like staff training and scheduling systems. By prioritizing these changes based on patient feedback, QFD ensures targeted and practical improvements, leading to better patient experiences and outcomes.
Response 02
Responding to peers is vital to the MGMT 410 Module Five discussion posts. We need to provide at least two peer responses. I have provided one example post. You can write your peer responses keeping the above points in mind.
Closing
The MGMT 415 Module 5 Discussion: Quality Improvement Tools aims to enhance your understanding of quality tools in healthcare and their practical applications. By selecting, analyzing, and discussing these tools, you will gain valuable insights into process improvement techniques. Engaging in peer responses further enriches this learning experience, providing real-world context and fostering collaborative learning. The key takeaway of this How-To Owlisdom Guide is the importance of selecting the right tools for the right situations to achieve optimal healthcare outcomes. In the upcoming module of MGMT 415, we will explore Just Culture.
MGMT 415 Module 6 Discussion: Just Culture
Instructions of MGMT 415 Module 6 Discussion
Readings and Videos for Module 6
Use the readings and videos to help you prepare for the assignments in this module. This week’s lesson material related to the Just Culture Discussion will help you analyze healthcare scenarios to determine healthcare quality impacts and develop healthcare quality improvement recommendations. The material related to the Wrong Site Surgery Assignment will help you identify sources of errors and interpret recommended healthcare quality practices to propose implementation solutions.
Read for the Discussion:
Healthcare Quality Book: Vision, Strategy, and ToolsTextbookLinks to an external site. 253-276
“The 4Es of a reporting culture” Links to an external site.
View for the Discussion:
CUSP: Understand “Just Culture” – 5.5 mins. https://youtu.be/P2a69klu37k
Annie’s Story: How a System’s Approach Can Change Safety Culture – 5.5 mins. https://youtu.be/zeldVu-3DpM
Read for the Wrong Site Surgery Assignment:
“Patient safety workshop: Wrong site surgery example”Links to an external site.
The Joint Commission “The universal protocol for preventing wrong site, wrong procedure, and wrong person surgery”Links to an external site.
“5 traits of high reliability organizations: How to hardwire each in your organization”Links to an external site. (note: hardwiring means putting systems in place to make sure a particular value or process is performed consistently)-Once you click on the link, you will need to register your email address. It is a free site and does not cost to register.
View for the Wrong Site Surgery Assignment:
What is a High Reliability Organization? – 12.53 mins. https://youtu.be/INWJytX27uw
Identifying error Swiss Cheese Model – 3 mins. https://youtu.be/JRCMxfBULB4
Just Culture Discussion
No unread replies.No replies.
Begin this discussion after reviewing the readings and videos for Module 6, especially Just Culture, 4Es of Reporting Culture, and Annie’s Story. In this discussion, students will contrast a just culture, which seeks to address issues by focusing on the system from a blame culture, which blames individuals when mistakes occur.
Discussion Directions
- Discuss how healthcare leaders can distinguish between legitimate mistakes and at-risk or reckless behavior.
- Compare the impacts of a blame culture versus the impacts of a just culture on healthcare quality.
- Give practical advice for healthcare organizations that are interested in adopting a just culture. (Start with resources from the module, but then expand the discussion with your own ideas about how to implement these resources in practice).
Your initial post is due by the discussion due date.
Peer Responses
Respond to two peers before the discussion closing date (see the Canvas calendar). Peer responses must further the discussion. Some ideas for advancing this discussion include probing further with regard to mistakes, reacting to your peers’ conceptualization of blame vs. just culture, adding to your peers’ recommendations (without duplicating advice from your original post), etc.
To view the rubric for a discussion in Canvas, click the dropdown menu (three vertical dots near the discussion title) and select “Show Rubric.”
Wrong Site Surgery Case Study
Start Assignment
- Due Jun 14 by 11:59pm
- Points 35
- Submitting a file upload
This module’s videos highlight two contrasting concepts:
- The Swiss Cheese Model explains how safety systems can fail.
- High Reliability Organizations have excellent safety outcomes, despite operating in complex, high risk environments with the potential for error.
In this activity, students will study system failures that aligned like swiss cheese and led to a patient error. Then you will generate ideas for how to put practices in place that create a reliable organization in which errors are prevented.
You will also be using a new tool that can help improve quality and be the basis for organizing ideas: the SBAR. The letters in SBAR stand for S=Situation, B=Background, A=Assessment, and R=Recommendation.
Assignment Directions
You will need to reference the “Patient Safety Workshop Wrong Site Surgery Example” and the Joint Commission “Universal Protocol” from the module readings for this assignment. Your submission should be organized as follows:
S = Situation
Summarize what happened in the case example.
B = Background
Summarize what should have happened based on the Joint Commission protocols.
A = Assessment
- Identify 2 Joint Commission protocols that were followed in the case example*
- Identify 3 Joint Commission protocols that were not followed in the case example*
- Explain how not following the protocols resulted in the wrong site surgery error
*When identifying examples and protocols, be as exact as possible. Match precise details from the case with the specific protocol that was or was not followed.
R = Recommendation
Propose at least 2 ways that the hospital could consistently implement the protocols in order to improve quality, helping to prevent errors in the future. In other words, how can they become a more reliable organization? Be sure to explain why your ideas would work in a practice setting. [Hint: You might find the reading “5 traits of high reliability organizations” to be helpful in generating ideas.]
Rubric
Wrong Site Surgery Case Study Rubric
|
Wrong Site Surgery Case Study Rubric |
||||||
|
Criteria |
Ratings |
Pts |
||||
|
This criterion is linked to a Learning OutcomeMGMT415_3.00 Identify sources of errors threshold: 8.5 pts |
|
10 pts |
||||
|
This criterion is linked to a Learning OutcomeMGMT415_7.00 Interpret recommended healthcare quality practices to propose implementation strategies threshold: 8.5 pts |
|
10 pts |
||||
|
This criterion is linked to a Learning OutcomeSkill: Written Quality threshold: 8.5 pts |
|
10 pts |
||||
|
This criterion is linked to a Learning OutcomeSkill: Timeliness threshold: 5.0 pts |
|
5 pts |
||||
|
Total Points: 35 |
||||||
PDSA Status Update 3: Act
Start Assignment
- Due Jun 14 by 11:59pm
- Points 25
- Submitting a file upload
This assignment is designed as a continuation of the PDSA project.
Directions
Students will continue using a Google Template to complete this assignment.
- Access the Google Drive account associated with your Bryan College of Health Sciences e-mail account.
- Find the PDSA Template document that you began in the PDSA Proposal Assignment (Hint: Search your Google Drive for PDSA)
- Check for instructor feedback on the “Study” section (aka the PDSA Status Update 2: Study) and modify the plan as needed.
- Complete the “Act” section of the document.
- Take out any remaining instructions or stop sign images.
- Submit your work (see the guide for Google Drive Direct to Canvas Submissions)
- If you encounter any errors, try sharing the file publicly or downloading the file and uploading (see the guide for resolving submission errors)
Criteria
Complete all items in the assigned section of the template. See the rubric for the grading criteria.
Rubric
PDSA Status Update Rubric
|
PDSA Status Update Rubric |
||||||
|
Criteria |
Ratings |
Pts |
||||
|
This criterion is linked to a Learning OutcomeMGMT415_4.00 Describe tools and models used to improve healthcare quality threshold: 8.5 pts |
|
10 pts |
||||
|
This criterion is linked to a Learning OutcomeSkill: Written Quality threshold: 8.5 pts |
|
10 pts |
||||
|
This criterion is linked to a Learning OutcomeSkill: Timeliness threshold: 5.0 pts |
|
5 pts |
||||
|
Total Points: 25 |
||||||
Introduction to MGTM 415 Module Six Discussion
The MGMT 415 Module 6 Discussion: Just Culture. aims to help students explore how healthcare leaders can differentiate between legitimate mistakes and at-risk or reckless behaviour, compare the impacts of these cultures on healthcare quality, and offer practical advice for adopting a Just Culture in healthcare organizations. This Owlisdom How-To Guide provides a structured approach for students to understand and discuss key concepts related to healthcare quality, mainly focusing on Just Culture versus Blame Culture.
Understanding Just Culture vs. Blame Culture
To start the MGMT 415 Module 6 Discussion: Just Culture. , we will briefly discuss the culture vs. blame culture.
- Defining Just Culture: Start by summarizing the concept of Just Culture. Use the module readings and videos to explain how Just Culture emphasizes learning and system improvement over individual blame.
- Defining Blame Culture: Contrast this with Blame Culture, which focuses on punishing individuals for mistakes. Highlight the key differences and the focus on systemic issues in Just Culture.
Example
Just Culture is a framework in healthcare that emphasizes learning and continuous improvement over individual blame. It seeks to create an environment where staff feel safe reporting errors and near misses, understanding that most mistakes result from flawed systems rather than individual negligence. According to the module readings, Just Culture focuses on identifying and rectifying systemic issues, promoting transparency, and encouraging open communication. It prioritizes understanding the root causes of errors and implementing changes to prevent recurrence, enhancing overall safety and quality of care.
In contrast, Blame Culture centers on assigning fault to individuals when mistakes occur. This punitive approach discourages reporting errors due to fear of punishment, leading to a culture of secrecy and blame. Blame Culture fails to address the underlying systemic issues, resulting in repeated mistakes and diminished morale among healthcare staff. The focus remains on punishing the individual rather than understanding and rectifying the factors contributing to the error.
Discuss how healthcare leaders can distinguish between legitimate mistakes and at-risk or reckless behaviour.
Distinguishing Between Legitimate Mistakes and At-Risk or Reckless Behavior
Here in MGMT 415 Module 6 Discussion: Just Culture, we will distinguish between legitimate mistakes and at-risk mistakes.
- Criteria for Identifying Legitimate Mistakes: Discuss the characteristics of legitimate mistakes, such as human error that occurs despite following procedures. Refer to module resources to define these clearly.
- Criteria for Identifying At-Risk Behavior: Explain at-risk behavior as actions that increase risk, often unknowingly, due to flawed processes or lack of awareness. Use examples from the readings to illustrate.
- Criteria for Identifying Reckless Behavior: Describe reckless behavior as conscious disregard for substantial risks. Provide examples from healthcare settings to clarify.
Example
Healthcare leaders must differentiate between legitimate mistakes, at-risk behavior, and reckless behavior to foster a Just Culture.
Legitimate Mistakes are unintentional errors that occur despite following procedures. For instance, a nurse may administer the wrong medication dosage due to a calculation error. These mistakes highlight the need for better training and support systems.
At-risk behavior involves actions that increase risk, often unknowingly, due to flawed processes or a lack of awareness. An example is a doctor bypassing a safety protocol to save time, not realizing the potential for harm. Addressing at-risk behavior involves educating staff and improving system processes to reduce risk.
Reckless Behavior is a conscious disregard for substantial risks. An example is a surgeon operating under the influence of alcohol. Such behavior requires disciplinary action due to the deliberate nature of the risk.
Compare the impacts of a blame culture versus a just culture on healthcare quality.
Impacts of Just Culture and Blame Culture on Healthcare Quality
This section of the MGMT 415 Module 6 Discussion: Just Culture. revolves around the impacts of blame culture on healthcare quality.
- Negative Outcomes of Blame Culture: Explain how blame culture can lead to fear, decreased reporting of errors, and poor morale. Use case studies from the module to support your points.
- Case Studies and Examples: Include specific examples from the readings or personal experiences highlighting blame culture’s detrimental effects.
- Positive Outcomes of Just Culture: Discuss how Just Culture fosters a safe environment for reporting errors, continuous learning, and system improvements. Cite specific examples from the module.
- Case Studies and Examples: Use case studies provided in the module to illustrate the benefits of Just Culture.
Example
Blame Culture leads to adverse outcomes such as fear, decreased error reporting, and poor morale. Case studies from the module illustrate that in environments where staff fear punishment, errors are hidden, preventing opportunities for learning and improvement. For example, a study showed that hospitals with a blame culture had higher rates of adverse events because staff were reluctant to report errors.
On the other hand, Just Culture fosters a safe environment for reporting errors, leading to continuous learning and system improvements. For instance, a hospital that implemented Just Culture saw a significant increase in error reporting and a subsequent reduction in adverse events. Staff felt empowered to speak up about safety concerns, leading to proactive changes and enhanced patient safety.
Give practical advice for healthcare organizations interested in adopting a just culture. (Start with resources from the module, but then expand the discussion with your ideas about implementing these resources in practice.)
Practical Advice for Adopting a Just Culture
Now in this section MGMT 415 Module 6 Discussion: Just Culture., we will discuss the practical advice for adopting a just culture.
- Initial Steps and Resources: Suggest steps healthcare organizations can take to adopt Just Culture, such as training programs and policy changes. Refer to the module resources for initial guidance.
- Strategies for Implementation: Provide detailed strategies for implementing Just Culture, including leadership commitment, employee engagement, and regular feedback mechanisms.
- Continuous Improvement and Monitoring: Emphasize the importance of ongoing monitoring and improvement, using data and feedback to refine processes.
Example.
To adopt a Just Culture, healthcare organizations can follow several initial steps:
- Initial Steps and Resources: Begin with comprehensive training programs to educate staff about Just Culture principles. Implement policy changes that support non-punitive error reporting. Use module resources as a starting point for developing these initiatives.
- Strategies for Implementation: Leadership commitment is crucial. Leaders should model Just Culture behaviors and ensure that all levels of the organization are engaged. Encourage employee involvement in identifying and addressing safety issues. Regular feedback mechanisms like safety huddles and anonymous reporting systems can support ongoing communication.
- Continuous Improvement and Monitoring: Establish systems for continuous monitoring and improvement. Use data from error reports to identify trends and implement changes. Regularly review and refine processes based on feedback and outcomes to ensure sustained improvements in safety and quality.
By following these steps, healthcare organizations can create an environment prioritizing safety, learning, and continuous improvement, ultimately enhancing patient care quality.
Respond to two peers before the discussion closing date (see the Canvas calendar). Peer responses must further the discussion. Some ideas for advancing this discussion include probing further about mistakes, reacting to your peers’ conceptualization of blame vs. just culture, adding to your peers’ recommendations (without duplicating advice from your original post), etc.
Peer Responses
According to MGMT 415 Module 6 Discussion: Just Culture., we are supposed to write two peer responses. I have addressed the given instructions in one response. Following these instructions, you can write your peer responses to Module 6 Discussion without a hassle.
- Effective Engagement Strategies: Guide students on engaging effectively with peers, focusing on respectful, constructive feedback.
- Adding Value to Discussions: Encourage students to build on their peers’ posts by providing additional insights, questions, and alternative perspectives without repeating the content of their original posts.
Response 01
Hey Max, great post! Your explanation of distinguishing between legitimate mistakes and reckless behavior is insightful. Implementing regular training sessions can significantly reduce at-risk behaviors by continuously educating staff on safety protocols. Additionally, your suggestion to enhance transparency through anonymous reporting systems can build trust among staff, fostering a more open and proactive environment. Your practical strategies are crucial for promoting a Just Culture in healthcare.
Response 02
Responding to peers is vital to the MGMT 415 Module 6 Discussion: Just Culture. posts. We need to provide at least two peer responses. I have provided one example post. You can write your peer responses keeping the above points in mind.
Closing
In MGMT-415 Module 6 Discussion: Just Culture is understanding organizational culture’s significant impact on healthcare quality. By differentiating between types of behaviors and adopting a Just Culture, healthcare leaders can foster an environment that prioritizes safety, learning, and continuous improvement. Engaging in thoughtful discussions with peers will further enhance your understanding and application of these critical concepts in real-world settings. In the next module of MGMT 415 Module 7 Guide. We will explore the 8-1 Discussion: Making Connections.
MGMT 415 Module 7 discussion: Healthcare Accreditors
Instructions for MGMT 415 Module 7 discussion
Readings and Videos for Module 7
Use the readings to help you prepare for the assignments in this module. This week’s lesson material will help you illustrate how healthcare quality indicators are demonstrated in a healthcare setting and discuss the relationship between regulating bodies and healthcare organizations.
Read:
Healthcare Quality Book: Vision, Strategy, and ToolsHealthcare Quality-Ch19.pdf Download Healthcare Quality-Ch19.pdfpp. 495-512 (this is from the 3rd edition). Use the reading guide to focus your study.
CMS-Approved Accrediting Organizations ListLinks to an external site. (select one accrediting organization that no one else has chosen for the discussion post)
Healthcare Accreditors Discussion
No unread replies replies.
There are many accreditors in the healthcare industry. Each accreditor has a purpose and scope for its work. Some accreditors focus on hospital- or facility-wide accreditation, while others focus on a specific part of the organization, such as dialysis or ambulatory care services. In this discussion, students will become familiar with the work of accrediting agencies.
Discussion Directions
Choose one Healthcare Accrediting Organization (AO) approved by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services from the following listLinks to an external site.. Select an accreditor that no one else has chosen.
Visit the website listed for the AO and answer the following questions:
- What is the name of the AO you chose?
- What types of programs/organizations do they accredit?
- What are some of the standards or criteria that they require member organizations to meet?
- Which one of the six aims of healthcare quality does the AO emphasize the most in its standards or criteria?
- What are the pros and cons of being accredited by the AO?
Your initial post is due by the discussion due date.
Peer Responses
Respond to two peers before the discussion closing date (see the Canvas calendar). Peer responses must further the discussion. Some ideas for advancing this discussion include: Comparing and contrasting your peer’s chosen AO with your chosen AO or providing reasons why a healthcare organization should or should not try to obtain accreditation from the peer’s AO.
To view the rubric for a discussion in Canvas, click the dropdown menu (three vertical dots near the discussion title) and select “Show Rubric.”
Introduction to MGTM 415 Module Seven Discussion
Accreditation is vital in ensuring quality and safety in the complex healthcare landscape. The MGMT 415 Module 7 discussion: Healthcare Accreditors requires you to explore and understand the role of various accrediting organizations (AOs) approved by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Through this How-To MGMT 415 Guide, you will gain insights into the standards and criteria that drive healthcare quality and the accreditation implications for healthcare organizations.
Choose one Healthcare Accrediting Organization (AO) approved by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services from the following list.
Selecting a Healthcare Accrediting Organization (AO)
To start the MGMT 415 Module 7 discussion: Healthcare Accreditors, we will choose a healthcare accrediting organization (AO) from the list provided.
I am choosing The Joint Commission (TJC).
- Choose one AO from the list provided by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS).
- Ensure the AO you select interests you or aligns with your future career aspirations in healthcare.
Example
For this discussion, I have selected The Joint Commission (TJC), a leading healthcare accrediting organization approved by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS). TJC’s comprehensive approach to accreditation aligns with my career aspirations in healthcare administration, particularly in ensuring high patient care and safety standards.
What is the name of the AO you chose?
Researching the Selected AO
Next, we will research the AO we choose to explore and answer the below points:
Name of the AO
- Visit the official website of the chosen AO.
- Identify and note down the full name of the organization.
Example
The full name of the AO I chose is The Joint Commission (TJC). Founded in 1951, TJC is a non-profit organization that accredits and certifies healthcare organizations and programs in the United States. Their mission is to continuously improve healthcare for the public by evaluating healthcare organizations and inspiring them to excel in providing safe and effective care of the highest quality and value.
What types of programs/organizations do they accredit?
Types of Programs/Organizations Accredited
- Explore the AO’s website to determine the range of programs or organizations they accredit.
- Note whether they focus on hospitals, outpatient facilities, specialized services (e.g., dialysis), etc.
Example
The Joint Commission accredits many healthcare organizations, including hospitals, outpatient facilities, behavioral healthcare organizations, home care services, nursing homes, long-term care facilities, ambulatory care providers, laboratory services, office-based surgeries, and specialty services such as dialysis centers and critical access hospitals.
What are some of the standards or criteria that they require member organizations to meet?
Standards or Criteria Required
- Investigate the accreditation standards or criteria that member organizations must meet.
- Look for documents, manuals, or web pages that outline these requirements and summarize key points.
Example
TJC’s accreditation standards are comprehensive and cover several critical areas of healthcare operations. Essential standards include patient safety goals (e.g., preventing surgical errors and infections), effective communication among healthcare providers, proper medication management practices, infection control measures, patient rights, leadership and staff qualifications, and emergency management protocols. These standards are detailed in their accreditation manuals, which serve as a roadmap for healthcare organizations aiming to achieve and maintain high-quality care.
Which one of the six aims of healthcare quality does the AO emphasize the most in its standards or criteria?
Emphasis on Healthcare Quality Aims
- Review the AO’s standards to identify which of the six aims of healthcare quality (safe, effective, patient-centered, timely, efficient, equitable) they emphasize the most.
- Provide examples or direct quotes from their materials to support your analysis.
Example
The Joint Commission places significant emphasis on all six aims of healthcare quality: safe, effective, patient-centered, timely, efficient, and equitable care. However, their standards mainly highlight patient safety and effectiveness. For instance, TJC’s National Patient Safety Goals (NPSGs) focus on critical areas such as preventing infections, ensuring correct surgical procedures, and improving communication among caregivers. These goals are designed to address specific safety concerns and improve patient outcomes.
What are the pros and cons of being accredited by the AO?
Pros and Cons of Accreditation
- Evaluate the benefits and drawbacks of being accredited by the AO.
- Consider aspects such as reputation, operational changes, costs, and potential for quality improvement.
Example
Accreditation by The Joint Commission offers several advantages, including enhanced reputation and credibility, improved operational efficiency and patient safety, access to TJC’s extensive resources and best practices, and increased eligibility for CMS reimbursements and federal funding. However, some drawbacks exist, such as high costs associated with the accreditation process, the potential for significant operational changes to meet TJC standards, and continuous pressure to maintain compliance and undergo periodic reviews.
Respond to two peers before the discussion closing date (see the Canvas calendar). Peer responses must further the discussion. Some ideas for advancing this discussion include comparing and contrasting your peer’s chosen AO with your chosen AO or providing reasons why a healthcare organization should or should not try to obtain accreditation from the peer’s AO.
Peer Responses
According to MGMT 415 Module 7 discussion: Healthcare Accreditors instructions, we are supposed to write two peer responses. I have addressed the given instructions in one response. Following these instructions, you can write your peer responses to the Module 7 Discussion without a hassle.
- Read your peers’ posts thoroughly.
- Respond to at least two peers before the discussion closing date.
- Aim to further the discussion by comparing and contrasting their chosen AO with yours or by debating the pros and cons they mentioned.
- Be respectful and constructive in your responses.
Response 01
Hey Sam, great post! Your analysis of The Joint Commission (TJC) is thorough and insightful. Comparing TJC with my chosen AO, the Accreditation Association for Ambulatory Health Care (AAAHC) reveals that both emphasize patient safety and quality care. However, TJC’s extensive reach across various healthcare settings contrasts with AAAHC’s focus on ambulatory care. The detailed standards and rigorous accreditation process of TJC offer significant credibility and operational benefits despite the high costs and compliance demands, making it a valuable endeavor for comprehensive healthcare facilities.
Response 02
Responding to peers is vital to the MGMT 415 Module Seven discussion posts. We need to provide at least two peer responses. I have provided one example post. You can write your peer responses keeping the above points in mind.
Closing
In completing the MGMT 415 Module 7 discussion: Healthcare Accreditors, you will deepen your understanding of the various accrediting organizations in the healthcare sector and the significance of their standards. They will develop critical thinking and analytical skills by engaging with peers to evaluate healthcare organizations’ quality and efficacy.
This How-To Owlisdom Guide offers a comprehensive look into healthcare accreditation, highlighting the importance of standards in ensuring high-quality care. Through research and peer engagement, you will learn about specific AOs and appreciate the broader implications of accreditation on healthcare practices and patient outcomes.
MGMT 415 Module 7 assignment: Purpose of Accreditation
Instructions for MGMT 415 Module 7 Assignment
Purpose of Accreditation Assignment
Start Assignment
- Due Jun 21 by 11:59 pm
- Points 35
- Submitting a file upload
Before doing this assignment, please read the textbook reading assigned for this module with the reading guide (the guide to focus your reading; you do not need to submit your answers to the reading guide questions).
Assignment Directions
In your submission, respond to the following prompts:
- Describe at least two reasons accreditation is necessary for health care organizations.
- Explain how the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) regulates accrediting organizations.
- Analyze how accreditation can help organizations achieve the six aims of healthcare quality.
- Discuss the benefits and challenges of accreditation for healthcare organizations.
Rubric
Purpose of Accreditation Assignment Rubric
|
Purpose of Accreditation Assignment Rubric |
||||||
|
Criteria |
Ratings |
Pts |
||||
|
This criterion is linked to a Learning OutcomeMGMT415_01.00 Illustrate how healthcare quality indicators are demonstrated in a healthcare setting threshold: 8.5 pts |
|
10 pts |
||||
|
This criterion is linked to a Learning OutcomeMGMT415_5.00 Discuss the relationship between regulating bodies and healthcare organizations threshold: 8.5 pts |
|
10 pts |
||||
|
This criterion is linked to a Learning OutcomeSkill: Written Quality threshold: 8.5 pts |
|
10 pts |
||||
|
This criterion is linked to a Learning OutcomeSkill: Timeliness threshold: 5.0 pts |
|
5 pts |
||||
|
Total Points: 35 |
||||||
Introduction to MGTM 415 Module Seven Assignment
The MGMT 415 Module 7 Assignment: Purpose of Accreditation focuses on the significance of accreditation in healthcare organizations. You will explore why accreditation is crucial, how the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) regulates accrediting organizations, and how accreditation helps achieve the six aims of healthcare quality. The insights gained from this How-To MGMT 415 Guide will enhance your understanding of the role and impact of certification in healthcare.
Describe at least two reasons accreditation is necessary for healthcare organizations.
Importance of Accreditation
To start the MGMT 415 Module 7 assignment: Purpose of Accreditation, we will first discuss the importance of accreditation.
- Begin by identifying and describing at least two reasons why accreditation is essential for healthcare organizations.
- Consider aspects such as improving patient safety, enhancing quality of care, building public trust, and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards.
- Use evidence from the textbook and other credible sources to support your explanations.
Example
Importance of Accreditation
Accreditation is vital for healthcare organizations for several compelling reasons. Firstly, it significantly enhances patient safety. Accredited organizations must adhere to stringent standards that mitigate risks and promote best practices (Hussein et al., 2021). For instance, The Joint Commission (TJC) has National Patient Safety Goals that target specific safety concerns, such as preventing infections and surgical errors, thereby fostering a safer healthcare environment. Evidence from multiple studies indicates that accredited hospitals generally report lower incidences of adverse events and medical errors, underscoring the critical role of accreditation in patient safety.
Secondly, accreditation builds public trust. When a healthcare organization is accredited, it signals to patients and the community that it meets high standards of care and operational excellence. This trust is essential for patient satisfaction and loyalty. An article in the Journal of Healthcare Management highlights that accredited facilities are more likely to be perceived as trustworthy and reliable by the public, which can enhance the institution’s reputation and patient influx.
Explain how the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) regulates accrediting organizations.
Role of the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS)
Next, we will explore the role of the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services.
- Explain the role of CMS in regulating accrediting organizations.
- Discuss how CMS grants “deeming authority” to accrediting bodies, allowing them to certify healthcare organizations for participation in Medicare and Medicaid programs.
- Reference CMS guidelines and regulations to provide a clear understanding of their oversight and regulatory functions.
Example
Role of the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS)
The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) are pivotal in regulating accrediting organizations (LaPelusa & Bohlen, 2023). CMS grants “deeming authority” to certain accrediting bodies, which allows these entities to certify healthcare organizations for participation in Medicare and Medicaid programs. This authority means that if an organization meets the accrediting body’s standards, it is also deemed to meet CMS’s requirements.
CMS’s oversight is extensive and rigorous. It involves evaluating accrediting organizations to ensure their standards are equivalent to or exceed CMS’s requirements. For instance, CMS reviews and approves accrediting organizations through a comprehensive process examining their survey processes, standards, and enforcement actions (Friedlander, 2024). This regulation ensures accredited healthcare providers maintain high quality and safety, aligning with federal guidelines. According to CMS guidelines, this oversight system helps maintain consistency and reliability across different accrediting organizations, ensuring that all accredited entities provide a comparable standard of care.
Analyze how accreditation can help organizations achieve the six aims of healthcare quality.
Accreditation and Healthcare Quality
We will discuss the accreditation and healthcare quality for this section of the MGMT 415 Module 7 assignment: Purpose of Accreditation.
- Analyze how accreditation helps healthcare organizations achieve the six aims of healthcare quality: safe, effective, patient-centered, timely, efficient, and equitable care.
- Provide specific examples of accreditation standards or practices contributing to these aims.
- Support your analysis with evidence from accreditation manuals, standards, or case studies.
Example
Accreditation and Healthcare Quality
Accreditation is instrumental in helping healthcare organizations achieve the six aims of healthcare quality, as defined by the Institute of Medicine: safe, effective, patient-centered, timely, efficient, and equitable care (Hussein et al., 2021).
Safe: Accreditation standards prioritize patient safety by implementing rigorous protocols and procedures. For example, TJC’s National Patient Safety Goals include measures to prevent infections and surgical errors, directly contributing to safer healthcare environments.
Effective: Accredited organizations must use evidence-based practices to ensure that the care provided is adequate. For instance, accreditation bodies often mandate clinical guidelines and pathways proven to improve patient outcomes.
Patient-Centered: Accreditation emphasizes patient-centered care by including standards that require organizations to respect patients’ preferences, needs, and values. The Joint Commission, for example, has standards that focus on effective communication, cultural competence, and patient rights.
Timely: Accreditation helps reduce care delays by enforcing standards that streamline operations and enhance efficiency. For instance, accredited emergency departments must meet specific criteria for timely triage and treatment, reducing wait times and improving patient outcomes.
Efficient: Accreditation encourages the elimination of waste and optimization of resources. Standards often include guidelines for efficient use of personnel, equipment, and facilities, which can lead to cost savings and improved care delivery.
Equitable: Accreditation bodies require organizations to provide care that does not vary in quality due to personal characteristics such as gender, ethnicity, or socioeconomic status. For example, standards might mandate equitable access to services and culturally competent care, ensuring all patients receive high-quality care.
Accreditation standards and practices, such as those implemented by TJC, include specific guidelines and case studies demonstrating these improvements (Friedlander, 2024). For instance, a case study might show how implementing TJC’s infection control standards significantly reduced hospital-acquired infections, illustrating the tangible benefits of accreditation.
Closing
The MGMT 415 Module 7 assignment, Purpose of Accreditation, emphasizes the critical role of accreditation in enhancing healthcare quality and safety. By understanding the reasons for certification, CMS’s regulatory role, and alignment with the six aims of healthcare quality, you will gain a comprehensive perspective on the importance of maintaining high standards in healthcare organizations. In the upcoming module of MGMT 414, we will discuss PDSA Project Sharing.
References
Friedlander, M. (2024). Regulations and Accreditation. In C. McKay & K. S. Nehal (Eds.), Laboratory Manual for Mohs Micrographic Surgery: Frozen Tissue Processing (pp. 193–212). Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-52434-9_16
Hussein, M., Pavlova, M., Ghalwash, M., & Groot, W. (2021). The impact of hospital accreditation on healthcare quality: A systematic literature review. BMC Health Services Research, 21(1), 1057. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-021-07097-6
LaPelusa, A., & Bohlen, J. (2023). Medicare and Medicaid Accreditation and Deemed Status. StatPearls. https://www.statpearls.com/point-of-care/155642/
MGMT 415 Module 7-3 discussion: PDSA Project Sharing
Instructions of MGMT 415 Module 7-3 discussion
PDSA Project Sharing Discussion
No unread replies.No replies.
Students have all learned a lot in the PDSA project, and it only makes sense to share the learning with others! The purpose of this discussion is to summarize what was learned and respond to others so that all can benefit from the knowledge gains.
This is a discussion, rather than a formal presentation, because a discussion is a good way to share thoughts about what has been learned along the way. Students may remember the video that started this project in which Dr. Goldmann conversationally described the cycle he used to improve his vegetable garden. He summarized the highlights and main steps of the process improvements with his cucumbers. We will be using a similar style in this discussion. Students will share the main steps and events that happened during the PDSA cycle (we don’t need all of the details, just the main points). Then there will be opportunities to reflect on the learning that occurred. Dr. Goldmann’s video is in Module 3 and it’s called “From CLABSIs to Cucumbers.”
Directions
- State the process that the PDSA cycle was intended to improve.
- Summarize your PDSA cycle. (Keep this brief at about 1-2 paragraphs focused on the main steps and events in the cycle.)
- Explain the results. Did the cycle work? If so, what impact will the new cycle have? If not, what should be tried next?
- Describe what you learned about PDSA cycles from this project.
Peer Responses
Respond to two peers before the discussion closing date (see the Canvas calendar). Peer responses must further the discussion. Some ideas for advancing this discussion include reacting to the usefulness of your peers’ project, suggesting additional improvements that the peer may not have considered, or adding to your peers’ reflection on learning.
To view the rubric for a discussion in Canvas, click the dropdown menu (three vertical dots near the discussion title) and select “Show Rubric.
Step-By-Step Guide MGMT 415 Module 7-3 discussion: PDSA Project Sharing
Introduction to MGTM 415 Module 7-3 Discussion
The MGMT 415 Module 7-3 discussion: PDSA Project Sharing summarizes and discusses the Plan-Do-Study-Act (PDSA) project. The goal is to share the main steps and outcomes of your PDSA cycle, reflect on the learning that occurred, and engage in a meaningful discussion with peers. This Owlisdom guide will help you structure your discussion post effectively, ensuring you cover all necessary points concisely and clearly.
State the process that the PDSA cycle was intended to improve.
Stating the Process
To start the MGMT 415 Module 7-3 discussion: PDSA Project Sharing, we will begin by discussing the process.
- Begin by clearly stating the process your PDSA cycle aims to improve.
- Be specific about the area of focus, such as reducing infection rates, improving patient flow, or enhancing medication administration.
Example
The PDSA (Plan-Do-Study-Act) cycle aimed to improve the medication administration process in our healthcare facility. Specifically, the focus was on reducing medication errors during the evening shift, where a higher incidence of errors was observed. The goal was to enhance patient safety by ensuring accurate and timely medication administration.
Summarizing the PDSA Cycle
Summarize your PDSA cycle. (Keep this brief at about 1-2 paragraphs focused on the main steps and events in the cycle.)
Summarizing the PDSA Cycle
Next, we will summarize the PDSA Cycle.
- Provide a summary of your PDSA cycle, focusing on the main steps and events.
- Describe the Plan phase: What was the objective? What plan did you create to address the problem?
- Outline the Do phase: What actions did you take? How did you implement the plan?
- Discuss the Study phase: What data did you collect? How did you analyze the results?
- Summarize the Act phase: What changes did you make based on the findings? What were the next steps?
Example
In the Plan phase, the objective was to identify the root causes of medication errors and develop a strategy to mitigate these issues. We conducted a root cause analysis, which revealed that distractions, inadequate staffing, and incomplete patient information were primary factors. The plan involved implementing a standardized medication administration protocol, increasing staffing levels during peak times, and enhancing communication tools for accurate patient information.
We implemented the new protocol and communication tools over four weeks during the Do phase. Staff received training on the latest procedures, and additional nurses were scheduled for the evening shift to ensure adequate coverage. We also introduced a quiet zone around medication carts to minimize distractions.
In the Study phase, data on medication errors were collected before and after implementing the new protocol. We analyzed the frequency and types of errors using statistical tools to determine the impact of the changes. The data indicated a significant reduction in medication errors, particularly those related to distractions and incomplete information.
In the Act phase, based on our findings, we made the new protocol a permanent practice. We also developed ongoing training sessions for new staff and scheduled periodic reviews to ensure continued adherence to the protocol. The following steps included exploring additional technological solutions to further streamline the medication administration process.
Explain the results. Did the cycle work? If so, what impact will the new cycle have? If not, what should be tried next?
Explaining the Results
Here, we will explain the results of the PDSA cycle.
- Explain the outcomes of your PDSA cycle.
- Did the cycle achieve its objectives? Provide specific results or data points.
- Discuss the impact of the new cycle if it worked. How did it improve the process?
- If the cycle did not work, suggest what should be tried next. What adjustments or new strategies could be implemented?
Example
The results of the PDSA cycle were promising. The cycle achieved its objective by reducing medication errors by 40% during the evening shift. This improvement significantly enhanced patient safety and staff confidence in the medication administration process. The impact of the new cycle included better patient outcomes, increased staff satisfaction, and a more efficient workflow. If the cycle had not worked, the following steps would have involved further refining the protocol, increasing staff engagement in identifying barriers, and testing additional interventions such as electronic medication administration records (eMARs).
Describe what you learned about PDSA cycles from this project.
Describing Learning Outcomes
This section of the MGMT 415 Module 7-3 Discussion: PDSA Project Sharing describes the learning outcomes of the PDSA cycle.
- Reflect on what you learned about the PDSA cycles from this project.
- Consider the practical insights gained, such as the importance of thorough planning, flexibility, and the value of data-driven decision-making.
- Discuss any challenges faced and how they were addressed.
Example
This PDSA cycle provided several valuable insights. Thorough planning is crucial for identifying root causes and developing effective interventions. Flexibility is essential, as unexpected challenges may arise that require adjustments to the plan. Finally, data-driven decision-making is vital for evaluating the impact of changes and ensuring sustained improvements. One challenge was initial staff resistance to the new protocol, addressed through continuous education and involving staff in the improvement process.
Respond to two peers before the discussion closing date (see the Canvas calendar). Peer responses must further the discussion. Some ideas for advancing this discussion include reacting to the usefulness of your peers’ projects, suggesting additional improvements that the peer may not have considered, or adding to your peers’ reflections on learning.
Peer Responses
According to MGMT 415 Module 7-3 discussion: PDSA Project Sharing instructions, we are supposed to write two peer responses. I have addressed the given instructions in one response. Following these instructions, you can write your peer responses to the Module 7 Discussion without a hassle.
- Read your peers’ posts thoroughly before responding.
- Respond to at least two peers before the discussion closing date.
- Aim to further the discussion by reacting to your peers’ project’s usefulness, suggesting additional improvements, or adding to their reflections on learning.
- Be respectful and constructive in your responses.
Response 01
Hey Beck, nice post! Your impressive and well-structured analysis of the PDSA cycle to reduce medication errors during the evening shift highlights the effectiveness of your interventions. For additional improvement, consider implementing electronic medication administration records (eMARs) to streamline the process further and reduce manual entry errors. Your emphasis on flexibility and data-driven decision-making provides valuable insights into the PDSA cycle’s adaptability and effectiveness.
Response 02
Responding to peers is vital to the MGMT 415 Module Seven discussion posts. We need to provide at least two peer responses. I have provided one example post. You can write your peer responses keeping the above points in mind.
Closing
In conclusion, this discussion assignment is an opportunity to share the key learnings from your PDSA project, reflect on the process, and engage with peers to deepen your understanding. Following the guidelines, you can create a comprehensive and insightful discussion post that effectively communicates your experience and insights.
MGMT 415 Module Eight discussion: PDSA Healthcare Applications
Instructions for MGMT 415 Module Eight discussion
Plan for Module 8
Introduction
Welcome to the last module in the course! During this module, we will put together the healthcare quality concepts we have learned. We will first use the PDSA model in real healthcare scenarios by providing best possible solutions to the issue at hand (I can’t wait to hear what your recommended plan will be). Next, we will have the opportunity to teach a “future employee” all of the healthcare quality concepts we learned throughout the course. I have enjoyed having all of you my class!
Course Outcome Focus for the Module:
- Illustrate how healthcare quality indicators are demonstrated in a healthcare setting
- Analyze healthcare scenarios to determine healthcare quality impacts
- Identify sources of errors
- Describe tools and models used to improve healthcare quality
- Discuss the relationship between regulating bodies and healthcare organizations
- Develop healthcare quality improvement recommendations
- Interpret recommended healthcare quality practices to propose implementation strategies
Learning Objectives:
- Identify a healthcare process that needs quality improvement
- Outline a plan for applying the PDSA quality approach to a healthcare process
- Integrate healthcare quality concepts into quality improvement planning
- Synthesize healthcare quality knowledge and skills in a culminating presentation
Assignments:
PDSA Healthcare Applications Discussion
Healthcare Quality Orientation Presentation
PDSA Healthcare Applications Discussion
No unread replies.No replies.
Now that you have enacted a PDSA cycle in your personal lives, we will discuss healthcare situations in which it would be appropriate to use PDSA.
Discussion Directions
- Give specifics about a healthcare situation involving quality issues that need to be improved.
- In your discussion, explain why PDSA is an appropriate approach to the problem.
- Offer ideas for an initial “plan” for the PDSA cycle in the situation you have described.
- Incorporate quality improvement concepts (e.g., six aims, quality improvement tools, etc.) into your recommended plan.
Your initial post is due by the discussion due date.
Peer Responses
Respond to two peers before the discussion closing date (see the Canvas calendar). Peer responses must further the discussion. Some ideas for advancing this discussion include: Giving your peer additional ideas for how to approach the problem or set up the “plan” stage in the PDSA or uncovering some of the barriers your peer may encounter in trying to enact process changes.
To view the rubric for a discussion in Canvas, click the dropdown menu (three vertical dots near the discussion title) and select “Show Rubric.”
Introduction to MGTM 415 Module 8 Discussion
The MGMT 415 Module Eight discussion: PDSA Healthcare Applications discusses a healthcare situation requiring quality improvement and explains why the PDSA (Plan-Do-Study-Act) cycle is appropriate. You will describe the specific quality issues, propose an initial plan for the PDSA cycle, and incorporate relevant quality improvement concepts. This How-To MGMT 415 Guide aims to apply theoretical knowledge to practical scenarios, enhancing your understanding of quality improvement in healthcare.
Give specifics about a healthcare situation involving quality issues that need to be improved.
Describing a Healthcare Situation
To start the MGMT 415 Module Eight discussion: PDSA Healthcare Applications, we will describe a healthcare situation first.
- Identify a specific healthcare situation where quality issues are evident.
- Be detailed in describing the problem, such as high patient readmission rates, medication errors, or long waiting times.
- Provide context to help readers understand the significance and impact of the issue.
Example
Describing a Healthcare Situation
In our healthcare facility, we have identified a significant issue with high patient readmission rates, particularly among patients with chronic heart failure. This problem affects patient outcomes, increases the financial burden on the healthcare system, and diminishes the quality of care provided. Patients are frequently readmitted within 30 days of discharge due to complications or inadequate post-discharge care. This situation underscores a critical gap in our patient management processes, indicating a need for improved care coordination, patient education, and follow-up practices.
Justifying the Use of PDSA
The Plan-Do-Study-Act (PDSA) cycle is an ideal approach to addressing this quality issue. Its iterative nature allows for testing changes on a small scale, which helps identify effective strategies before broader implementation. This approach reduces risks associated with large-scale changes and ensures that modifications are evidence-based. Additionally, PDSA supports continuous monitoring and refinement, crucial for complex healthcare environments where ongoing adjustments are necessary to meet dynamic patient needs and improve care processes.
Proposing an Initial Plan
Objective: The initial plan aims to reduce patient readmission rates for chronic heart failure by 20% within six months.
Actions in the Plan Phase:
- Data Collection: Gather baseline data on readmission rates, reasons for readmissions, and patient demographics.
- Resource Allocation: Allocate resources for a multidisciplinary team, including cardiologists, nurses, case managers, and patient educators.
- Develop Interventions: Create standardized discharge protocols, including detailed patient education on disease management, medication adherence, and lifestyle changes. Implement a follow-up schedule involving telehealth consultations and home visits within the first 30 days post-discharge.
- Roles and Responsibilities: Assign specific roles to team members for patient education, follow-up calls, and home visits. Ensure clear communication channels among team members to facilitate coordinated care.
Incorporating Quality Improvement Concepts
Our plan integrates vital quality improvement concepts to address the six aims of healthcare quality:
- Safe: The standardized discharge protocols and follow-up care aim to prevent complications and reduce the risk of readmission.
- Effective: Evidence-based interventions, such as medication management and patient education, ensure that the care provided is practical and based on best practices.
- Patient-Centered: The plan focuses on individualized care plans and patient education, ensuring that care is tailored to each patient’s needs and preferences.
- Timely: Telehealth consultations and home visits are scheduled promptly post-discharge to address any emerging issues quickly.
- Efficient: Coordinated care and clear communication among team members optimize resource use and reduce redundancy.
- Equitable: The plan ensures all patients receive the same level of care regardless of their socioeconomic status or background.
Quality Improvement Tools:
- Flowcharts: These map out the discharge and follow-up process to ensure clarity and efficiency.
- Root Cause Analysis: Identified vital factors contributing to readmissions, guiding the development of targeted interventions.
- Control Charts: Monitor readmission rates over time to assess the effectiveness of the interventions and make necessary adjustments.
In conclusion, by applying the PDSA cycle and incorporating quality improvement concepts, we aim to significantly reduce readmission rates for chronic heart failure patients, enhancing patient outcomes and overall quality of care.
Explain why PDSA is an appropriate approach to the problem in your discussion.
Justifying the Use of PDSA
Next, we will justify the use of PDSA.
- Explain why the PDSA cycle suits the identified quality issue.
- Discuss the iterative nature of PDSA and effectiveness in testing changes on a small scale before full implementation.
- Highlight how PDSA allows continuous monitoring and refinement, making it ideal for complex healthcare environments.
Offer ideas for an initial “plan” for the PDSA cycle in your described situation.
Proposing an Initial Plan
Here, we will discuss proposing an initial plan.
- Outline a detailed initial plan for the PDSA cycle.
- Specify the objective of the plan and the expected outcomes.
- Describe the actions to be taken in the Plan phase, including data collection methods, resources needed, and roles and responsibilities.
Incorporate quality improvement concepts (e.g., six aims, quality improvement tools, etc.) into your recommended plan.
Incorporating Quality Improvement Concepts
We will incorporate quality improvement concepts for this section of the MGMT 415 Module Eight discussion: PDSA Healthcare Applications.
- Integrate relevant quality improvement concepts into your plan.
- Discuss how your plan addresses the six aims of healthcare quality: safe, effective, patient-centered, timely, efficient, and equitable care.
- Support your plan using quality improvement tools like flowcharts, root cause analysis, or control charts.
Peer Responses
According to MGMT 415 Module Eight discussion: PDSA Healthcare Applications instructions, we are supposed to write two peer responses. I have addressed the given instructions in one response. Following these instructions, you can write your peer responses to Module 8 Discussion without a hassle.
- Read your peers’ posts thoroughly before responding.
- Provide constructive feedback by offering additional ideas for approaching the problem or enhancing the Plan phase.
- Identify potential barriers your peer might encounter and suggest ways to overcome them.
- Ensure your responses are respectful and aim to further the discussion.
Response 01
Responding to peers is vital to the PHIL 210 Module Eight discussion posts. We need to provide at least two peer responses. I have provided one example post. You can write your peer responses keeping the above points in mind.
Closing
The MGMT 415 Discussion Module 8 provides an opportunity to apply the PDSA cycle to real-world healthcare quality issues. You will gain practical insights into continuous improvement processes by describing a specific situation, justifying the use of PDSA, proposing a detailed plan, and incorporating quality improvement concepts. Engaging with peers through thoughtful responses will enrich everyone’s learning experience.
MGMT 415 Module Eight assignment: Healthcare Quality Orientation
Instructions of MGMT 415 Module Eight assignment
Healthcare Quality Orientation Presentation
Start Assignment
- Due Jun 28 by 11:59pm
- Points 85
- Submitting a file upload
Congratulations! You’ve made it to the last module of the course! In this assignment, you also get to pretend that you have been given a special assignment at work. You will have the opportunity to bring together everything you have learned in the course in this culminating activity.
Assignment Directions
Imagine that you are a healthcare manager and you have been given the task of creating a presentation about healthcare quality for new employee orientation. The purpose of this presentation is to familiarize new employees with healthcare quality concepts. Using all of the lessons from this course, please create a PowerPoint presentation addressing these prompts:
- Outline the 6 aims of healthcare quality, providing the rationale for why each aim should be practiced in healthcare settings.
- Highlight examples that illustrate at least 2 common healthcare quality issues and use those examples to teach new employees about the consequences of high- and low-quality practices in healthcare (cite sources for your examples).
- Provide at least 2 strategies for how employees can identify the causes of healthcare errors, explaining how the strategies can either reduce the impact of errors or prevent errors from occurring.
- Explain at least 3 tools or models that can be used to improve healthcare quality (in your explanation, be sure to explain the elements that make up the tools or models).
- Create 2 recommendations of how new employees can contribute to improving healthcare quality at the organization.
- Research at least 1 evidence-based practice recommendation that should be implemented in a healthcare organization to enhance quality and provide guidance to the new employees for how to implement this evidence-based practice into their work (provide citations for your research).
- Identify at least 1 healthcare accrediting body that will be regulating the organization and describe the benefits and challenges of complying with the accreditor’s quality requirements.
There is no minimum or maximum number of slides, use what is needed to convey the preceding information. You may reuse any materials you have created for prior assignments in this course, re-purposing the materials as needed to fit this assignment. Please cite sources with both in-text citations on the slide where the information is presented and full references at the end of the presentation.
Rubric
Healthcare Quality Orientation Presentation Rubric
|
Healthcare Quality Orientation Presentation Rubric |
||||||
|
Criteria |
Ratings |
Pts |
||||
|
This criterion is linked to a Learning OutcomeMGMT415_01.00 Illustrate how healthcare quality indicators are demonstrated in a healthcare setting threshold: 8.5 pts |
|
10 pts |
||||
|
This criterion is linked to a Learning OutcomeMGMT415_2.00 Analyze healthcare scenarios to determine healthcare quality impacts threshold: 8.5 pts |
|
10 pts |
||||
|
This criterion is linked to a Learning OutcomeMGMT415_3.00 Identify sources of errors threshold: 8.5 pts |
|
10 pts |
||||
|
This criterion is linked to a Learning OutcomeMGMT415_4.00 Describe tools and models used to improve healthcare quality threshold: 8.5 pts |
|
10 pts |
||||
|
This criterion is linked to a Learning OutcomeMGMT415_5.00 Discuss the relationship between regulating bodies and healthcare organizations threshold: 8.5 pts |
|
10 pts |
||||
|
This criterion is linked to a Learning OutcomeMGMT415_6.00 Develop healthcare quality improvement recommendations threshold: 8.5 pts |
|
10 pts |
||||
|
This criterion is linked to a Learning OutcomeMGMT415_7.00 Interpret recommended healthcare quality practices to propose implementation strategies threshold: 8.5 pts |
|
10 pts |
||||
|
This criterion is linked to a Learning OutcomeSkill: Written Quality threshold: 8.5 pts |
|
10 pts |
||||
|
This criterion is linked to a Learning OutcomeSkill: Timeliness threshold: 5.0 pts |
|
5 pts |
||||
|
Total Points: 85 |
||||||
Step-By-Step Guide MGMT 415 Module Eight assignment: Introduction to MGTM 415 Module 8 Assignment
MGMT 415 Module Eight assignment: Healthcare Quality Orientation. Understanding the fundamentals of healthcare quality is crucial. This How-To MGMT 415 Guide will help you create a PowerPoint presentation to familiarize new employees with essential healthcare quality concepts. Your task is to convey the importance of these concepts clearly and compellingly, drawing from lessons learned throughout your course.
Outline the six aims of healthcare quality, explaining why each objective should be practiced in healthcare settings.
The Six Aims of Healthcare Quality
To start the MGMT 415 Module Eight Assignment: Healthcare Quality Orientation, we will discuss healthcare quality and its six aims.
Example

Safe
- Explain the importance of minimizing risks and harm to patients.
- Discuss practices such as proper hand hygiene and infection control protocols.

Effective
- Highlight the need for evidence-based practice and adherence to clinical guidelines to ensure that care improves patient health outcomes.

Patient-Centered
- Emphasize respecting patients’ preferences, needs, and values.
- Use examples like personalized care plans to illustrate this point.

Timely
- Stress the need to reduce wait times and harmful delays for patients and providers.
- Discuss strategies like streamlined appointment scheduling.

Efficient
- Address the elimination of waste in healthcare processes.
- Examples include optimizing resource use and improving workflow efficiency.

Equitable
- Highlight the necessity of providing care that does not vary in quality based on personal characteristics such as ethnicity, gender, geographic location, or socioeconomic status.

Highlight examples that illustrate at least two common healthcare quality issues and use those examples to teach new employees about the consequences of high- and low-quality practices in healthcare (cite sources for your examples).
Examples of Healthcare Quality Issues
Next, we will discuss the examples of healthcare quality.
- Provide an example where high-quality care led to positive patient outcomes. Cite sources to support your example.
- Describe a scenario where low-quality care resulted in negative consequences. Explain the impact on patient safety and cite sources for reference.
Example

Provide at least two strategies for how employees can identify the causes of healthcare errors, explaining how the strategy can either reduce the impact of errors or prevent mistakes from occurring.
Strategies to Identify Causes of Healthcare Errors
Here, we will explore the strategies to identify the causes of healthcare errors.
- Explain how RCA helps identify underlying issues that contribute to errors. Detail the steps involved in conducting an RCA.
- Describe how FMEA anticipates potential failures and their effects. Guide on implementing FMEA in clinical settings.
Example

Explain at least three tools or models that can be used to improve healthcare quality (in your explanation, be sure to explain the elements that make up the tools or models).
Tools and Models for Improving Healthcare Quality
For this section of MGMT 415 Module Eight assignment: Healthcare Quality Orientation, we will explore the tools and models for improving healthcare quality.
- Detail the four phases of the PDSA cycle and its iterative nature. Please provide examples of its application in quality improvement projects.
- Explain the principles of Lean Six Sigma, focusing on reducing waste and improving processes. Discuss tools like DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control).
- Describe how the Balanced Scorecard aligns business activities with the vision and strategy of the organization. Outline its four perspectives: financial, customer, internal process, and learning and growth.
Example
Create two recommendations for how new employees can improve healthcare quality at the organization.
Recommendations for New Employees
Now, we will discuss recommendations for the new employees.
- Encourage ongoing professional development through workshops, courses, and certifications.
- Advise new employees to engage in quality improvement projects and committees to foster a culture of excellence.
Research at least one evidence-based practice recommendation that should be implemented in a healthcare organization to enhance quality and provide guidance to the new employees on how to implement this evidence-based practice into their work (provide citations for your research).
Evidence-Based Practice Recommendation
Here, we will discuss evidence-based practice recommendations.
- Choose a relevant evidence-based practice, such as infection control protocols or patient safety measures.
- Provide a step-by-step approach to integrating this practice into daily operations. Cite relevant research to support your recommendations.
Identify at least one healthcare accrediting body regulating the organization and describe the benefits and challenges of complying with the accreditor’s quality requirements.
Healthcare Accrediting Bodies
We will discuss the healthcare accrediting bodies for this MGMT 415 Module 8 Assignment segment.
- Select a well-known accrediting body, such as The Joint Commission.
- Discuss how compliance enhances quality of care, increases patient trust, and meets regulatory requirements.
- Address potential challenges such as resource allocation and the need for continuous updates to meet evolving standards.
Closing
p>Understanding and implementing healthcare quality concepts are vital for delivering exceptional patient care. By following this How-To Owlisdom Guide, you will be equipped to create an informative and engaging presentation that will empower new employees to contribute positively to our organization’s quality improvement efforts. Remember, high-quality care improves patient outcomes and fosters a culture of excellence and safety within the healthcare environment.




