SCMG-501 – UAV Technologies in Supply Chain Management: Revolutionizing Logistics Through Automation and Aerial Innovation
Published: 2025-10-14
Modified: 2025-10-14
Samples Solutions
- SCMG 501 Week 1 Discussion: Self-Driving Technology
- SCMG 501 Week 1 Assignment: Self-Driving Technology
- SCMG 501 Week 2 Discussion: Drone Technology in Supply Chain Management
- SCMG 501 Week 2 Assignment: Integrating Self-Driving Technology into Supply Chain Management
- SCMG 501 Week 3 Discussion: Visibility in Supply Chains
- SCMG 501 Week 4 Discussion: Artificial Intelligence in Supply Chain Management
- SCMG 501 Week 4 Assignment: Artificial Intelligence in Supply Chain Management
- SCMG 501 Week 5 Discussion: Blockchain Technology in Supply Chain Management
- SCMG 501 Week 6 Discussion: Cyber Vulnerabilities of Supply Chains
- SCMG 501 Week 6 Assignment: Cyber Vulnerabilities of Supply Chains
- SCMG 501 Week 7 Discussion: App-Based Technology in Supply Chain Management
- SCMG 501 Week 8 Discussion: Most Important Concept of the Class
- SCMG 501 Week 8 Assignment: Final Paper
Introduction:
SCMG-501 – UAV Technologies in Supply Chain Management focuses on how unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) transform logistics operations, from warehouse monitoring to last-mile delivery. The course highlights automation, efficiency, and sustainability in modern supply chain systems. For expert help with logistics or supply chain management projects, visit Owlisdom’s MBA Assignment Help.
SCMG 501 Week 1 Discussion: Introduction
Instructions for CMG 501 Week 1 Discussion
Week 1 Discussion: Introduction
Discussion Prompt:
For the Introductory post, introduce yourself to the class in 250 words or more. Tell us about your goals, interests, and what you want to accomplish in learning throughout the next eight weeks. Be sure to submit your introduction and discussion posting by Sunday midnight.
Failure to complete the introduction discussion post by midnight on Sunday will automatically drop you from this course.
Discussion Instructions:
For the Introductory post, introduce yourself to the class in 250 words or more. Tell us about your goals, interests, and what you want to accomplish in learning throughout the next eight weeks. Be sure to submit your introduction discussion posting by Thursday midnight. This discussion submission serves as your official entry into the course.
Your Introduction must be submitted during the first week of the course to maintain your registration for the course. Students who do not post to this discussion by 11:59 p.m., ET, Sunday will be automatically dropped from the course.
Initial Post Due: Sunday, by 11:59 p.m., ET
Responses Due: Sunday, by 11:59 p.m., ET
Note, that your Introductory Discussion is both graded and serves as notice that you are in attendance for this course. If you fail to post an Introduction by Sunday (end of Week 1) you may be automatically withdrawn from the course.
Attached is a copy of the Discussion Help Sheet and Rubric, please download, save, and then read it carefully. Discussions are an important and integral part of this course and, as such, are taken very seriously.
Plagiarism
Please pay close attention to the APUS Plagiarism policy. This course uses Turnitin to scan all papers turned in by students during this class. As such, Turnitin will find and note any areas of a paper that have been copied from another source without giving credit. Just don’t do it. Plagiarism is one “sin” that can get a student an F in a course.
This is a graded discussion; please return a short note stating that you have read the policy on plagiarism and will adhere to the APUS standards. The policy can be found at the following hyperlink: https://www.apu.apus.edu/student-handbook/university-policies-and-code-of-conduct/apus-student-code-of-conduct/prohibited-student-conduct/
Introduction to SCMG 501 Week 1 Discussion
The SCMG 501 Week 1 Discussion: Introduction is more than just saying hello; it is an opportunity to share your background, objectives, and what you are excited about learning in the SCMG 501 course. I will provide brief and descriptive guidelines to solve the Week 1 Discussion post and a dummy solution for each section. By following this How-To SCMG 501 Guide, you will be able to solve this discussion without any hassle.
Structuring Your Introduction
- Begin with a brief background about yourself.
- This might include your current role, academic journey, or any relevant experience in supply chain management or technology.
Example
Hello everyone! I am pursuing a supply chain management degree and am keenly interested in how technology optimizes our field. Before joining this course, I completed internships at logistics companies, where I was fascinated by the integration of AI and data analytics in streamlining operations. My academic journey has been driven by a desire to blend technical insights with supply chain strategies, aiming to innovate and improve efficiency in supply chains. I am excited to learn more and share insights with all of you!
Detailing Your Goals for the SCMG Course
- Clearly articulate why you chose the SCMG course.
- Discuss your goals, such as acquiring new skills, understanding particular technologies, or applying supply chain management theories to real-world scenarios.
Example
I chose the SCMG course to deepen my understanding of how cutting-edge technologies, like blockchain and IoT, can revolutionize supply chains. My goal is to acquire practical skills in these technologies and learn to apply theoretical concepts in real-world settings, ultimately enhancing efficiency and sustainability in supply chain operations.
Sharing Your Interests Related to Supply Chain Management and Technology
- Highlight areas within supply chain management and technology that particularly interest you. This could be anything from data analytics, logistics, and sustainability in supply chains to emerging technologies like blockchain or AI.
Example
My interests lie at the intersection of data analytics and sustainable practices within supply chains. I am particularly captivated by how blockchain technology and artificial intelligence can create more transparent, efficient, and sustainable supply networks. Exploring these areas further and understanding their practical applications in real-world supply chains are what I look forward to the most.
Outlining What You Want to Accomplish
- Discuss what you aim to achieve by the end of the course.
- Be specific about the knowledge and skills you hope to gain and how you plan to apply them in your professional or academic pursuits.
Example
By the end of this course, I aim to master the practical application of blockchain and AI in supply chains, from enhancing transparency to optimizing logistics. I plan to leverage these skills to propose innovative solutions in my future career, aiming for roles focusing on improving supply chain sustainability and efficiency through technology.
Closing
This How-To Owlisdom Guide helps you craft an introductory post that meets the requirements of the SCMG 501 Week 1 Discussion: Introduction and sets a positive tone for your contributions to the course discussions. Welcome aboard, and let us embark on this exciting learning journey together.
SCMG 501 WEEK 1 ASSIGNMENT: Self-Driving Technology
Instructions for SCMG 501 Week 1 Assignment
Before getting into the discussion questions for this week, please look over the requirements for these discussion postings:
- The initial discussion posting is due by midnight on Thursday.
- Initial postings that are late will receive a maximum grade of 75%. Postings after midnight will receive a grade of “0”.
- The initial discussion posting is to be a minimum of 250 words.
- Each student is to “respond” to two of their fellow students by Sunday midnight. These responses are to add personal observations regarding the position taken by the original posting.
- From time to time, the instructor will pose questions to the original posting. To receive full credit for the week’s discussion, it is recommended that the question or inquiry be answered.
- All postings emanate from your research of the topic presented–you should not be posting solely from your own opinions. Be sure to give attribution for your postings.
- Postings will be graded for (a) sentence structure, (b) grammar, (c) critical thinking content, (d) relevance to the subject matter, and (e) professional voice.
As your instructor, I look at these postings as a means to improve your knowledge of a subject, your professional communication level, and your competencies at researching a subject. Opinions are welcome (to a minor extent only). What I am looking for is your research findings and your critical thinking regarding the subject matter.
Prompt:
Investigate self-driving technologies and discuss how this technology will apply to supply chain management. As part of your research and response, consider the impact that this technology will have on the trucking and transportation industries. Consider the ethical ramifications of self-driving technology. In addition to reading your assigned resources for week 1, research online definitions for different types of self-driving technology.
Introduction to SCMG 501 Week 1 Assignment
This How-To SCMG 501 Guide helps you understand SCMG 501 Week 1 Assignment: Self-Driving Technology revolves around your understanding of self-driving technology. I will provide brief and descriptive guidelines to solve the Week 1 Assignment and a dummy solution for each section. This How-To Owlisdom Guide will equip you with guidelines to tackle all the queries related to the SCMG 501 Week 1 Assignment: Self-Driving Technology. Let us begin with the guide.
Investigate self-driving technologies and discuss how this technology will apply to supply chain management.
Self-Driving Technologies
First, we will discuss various self-driving technologies in the US market.
- Research various self-driving technologies currently in development and use.
- Understand the basic principles and functioning of self-driving vehicles.
Example
Research into self-driving technologies reveals a diverse landscape of advancements in development and use. These include LiDAR (Light et al.) systems, which utilize laser pulses to create 3D maps of surroundings, enhancing navigation accuracy (Villa et al., 2021). Additionally, radar systems are employed for object detection and tracking, complementing LiDAR’s capabilities. GPS (Global et al.) technology provides precise location data for autonomous navigation (Komjathy, 2023). Furthermore, computer vision systems enable vehicles to interpret visual information, recognize objects, and navigate complex environments. These technologies collectively allow the autonomous operation of vehicles, with ongoing advancements driving innovation in the field.
Application of Self-Driving Technology in Supply Chain Management
In this section of SCMG 501 Week 1 Assignment: Self-Driving Technology, we will explore the applications of Self-Driving Technology in Supply Chain Management.
- Explore how self-driving technologies can be integrated into different aspects of supply chain management.
- Analyze potential benefits and challenges of implementing self-driving vehicles in logistics operations.
Example
Self-driving technologies seamlessly integrate into diverse supply chain facets, optimizing transportation routes, enhancing warehouse efficiency, and expediting last-mile delivery (Gupta et al., 2021). These innovations facilitate effective fleet management and provide real-time visibility into shipment status, transforming supply chain operations. Analyzing potential benefits includes enhanced efficiency, cost savings, and increased safety. However, regulatory hurdles, technological limitations, and public perception issues must be addressed. Adapting regulations and building public trust are crucial for successful integration. Understanding these factors allows operators to maximize benefits while mitigating risks associated with self-driving vehicles.
Consider this technology’s impact on the trucking and transportation industries as part of your research and response.
Impact on Trucking and Transportation Industries
Now, we will discuss the impact of self-driving technology on the US transportation industry.
- Examine the specific implications of self-driving technology on the trucking and transportation sectors.
- Evaluate how automation may reshape job roles and workforce dynamics within these industries.
Example
When examining the impact of self-driving technology on the US transportation industry, particularly in the trucking and transportation sectors, it is essential to consider various implications:
Implications on Trucking and Transportation Sectors:
Self-driving technology promises increased efficiency, reduced labor costs, and improved safety in freight transportation (Gupta et al., 2021). However, accommodating autonomous vehicles may require substantial infrastructure investments and regulatory adjustments.
Reshaping Job Roles and Workforce Dynamics:
Automation may reshape job roles, potentially displacing traditional truck drivers (Bissell, 2021). However, new opportunities may emerge in fleet management, software development, and data analysis. Workforce training programs can prepare workers for these evolving roles.
Overall, self-driving technology offers benefits like efficiency and safety. However, carefully considering its impact on job roles is crucial to managing challenges like unemployment.
Consider the ethical ramifications of self-driving technology.
Ethical Ramifications of Self-Driving Technology
Now, let us explore the ethical ramifications of self-driving technology in SCMG.
- Consider the ethical implications surrounding adopting self-driving technologies in supply chain management.
- Reflect on issues related to safety, liability, and societal impact.
Example
When delving into the ethical ramifications of self-driving technology in Supply Chain Management (SCMG), it is imperative to consider various factors:
Ethical Implications of Adopting Self-Driving Technologies:
Adopting self-driving technologies in SCMG raises ethical concerns regarding safety, liability, and societal impact. Ensuring vehicle safety and minimizing accident risks is crucial (Ryan, 2020). Addressing liability issues and determining responsibility in accidents is essential for accountability.
Reflection on Safety, Liability, and Societal Impact:
Reflecting on safety, liability, and societal issues involves assessing risks and benefits. While self-driving vehicles reduce human error, concerns linger about reliability and complex navigation (Bissell et al., 2020). Addressing liability requires clear regulations for responsibility allocation. Societal impact assessment includes employment, urban infrastructure, and effects on transportation systems.
By considering these ethical implications, SCMG professionals can navigate the adoption of self-driving technology responsibly, ensuring that moral considerations are integrated into decision-making processes to promote safety, accountability, and societal welfare.
Conclusion
Let us conclude the SCMG 501 Week 1 Assignment: Self-Driving Technology by summarizing the key takeaways.
- Summarize key findings and insights regarding the application of self-driving technologies in supply chain management.
- Offer reflections on the broader implications and future developments in this field.
Example
Key findings reveal that self-driving technologies offer significant potential in optimizing supply chain management by enhancing efficiency, reducing costs, and improving safety. However, challenges such as regulatory hurdles and ethical considerations must be addressed. The broader implications suggest a transformative shift in transportation and logistics, with self-driving technology reshaping workforce dynamics and redefining industry standards. Future developments may focus on advancing autonomous capabilities, addressing regulatory frameworks, and fostering public acceptance to realize the full potential of self-driving technologies in supply chain management.
Closing
This How-To Owlisdom Guide allows you to understand the critical role of Self-Driving Technology in US supply chain management. Following the guidelines, you can solve SCMG 501 Week 1 Assignment: Self-Driving Technology like a pro. Good luck!
References
Bissell, D. (2021). Encountering automation: Redefining bodies through stories of technological change. Environment and Planning D: Society and Space, 39(2), 366–384. https://doi.org/10.1177/0263775820963128
Bissell, D., Birtchnell, T., Elliott, A., & Hsu, E. L. (2020). Autonomous automobiles: The social impacts of driverless vehicles. Current Sociology, 68(1), 116–134. https://doi.org/10.1177/0011392118816743
Gupta, S., Amaba, B., McMahon, M., & Gupta, K. (2021). The Evolution of Artificial Intelligence in the Automotive Industry. 2021 Annual Reliability and Maintainability Symposium (RAMS), pp. 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1109/RAMS48097.2021.9605795
Komjathy, A. (2023). Global ionospheric total electron content mapping using the Global Positioning System.
Ryan, M. (2020). The Future of Transportation: Ethical, Legal, Social and Economic Impacts of Self-driving Vehicles in the Year 2025. Science and Engineering Ethics, 26(3), 1185–1208. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11948-019-00130-2
Villa, F., Severini, F., Madonini, F., & Zappa, F. (2021). SPADs and SiPMs Arrays for Long-Range High-Speed Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR). Sensors, 21(11), Article 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21113839
SCMG 501 Week 2 Discussion: Drone Technology in Supply Chain Management
Instructions for SCMG 501 Week 2 Discussion
Course Objective:
- CO2: Explain the ramifications of the use of unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) technology in supply chain management
Prompt:
Assess and critique the use of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), also known as drones, in supply chain management. Consider the use of UAVs indoors, such as in a warehouse, and outdoors, such as being used for home delivery. In addition to reading your assigned resources for week 2, research online definitions for unmanned aerial vehicles.
Introduction to SCMG 501 Week 2 Discussion
This How-To SCMG 501 Guide is designed to assist students in exploring the implications of uncrewed aerial vehicles (UAVs), or drones, within the field of supply chain management. Focusing on indoor and outdoor applications, this assignment encourages a comprehensive understanding of UAV technology and its transformative impact on logistics and delivery systems.
Definition of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAV)
To start the SCMG 501 Week 2 Discussion, we will define the Unmanned Aerial Vehicles.
- Start by researching online for reliable definitions of UAVs. Use scholarly sources or reputable industry publications to ensure accuracy.
- Briefly explain what UAVs are and discuss their general uses in various industries, focusing on their relevance to technology and automation.
Example
Uncrewed Aerial Vehicles (UAVs), commonly known as drones, are increasingly pivotal in the evolution of supply chain management, particularly within warehouse operations and home delivery systems (Mohsan et al., 2022). The deployment of UAV technology in these domains offers an intriguing glimpse into the future of logistics, where efficiency and innovation intersect to redefine traditional practices.
Assess and critique the use of uncrewed aerial vehicles (UAV), also known as drones, in supply chain management.
Indoor Use of UAVs in Supply Chain Management
In this section of the Week 2 Discussion, we will explore the assessment of UAV Technology in Warehouses.
- Evaluate how UAVs are utilized in warehouse operations. Consider their roles in inventory management, stocking, and retrieval processes.
- Look for case studies or industry reports highlighting the efficiency improvements or logistical challenges faced when integrating UAVs indoors.
- Outline the key advantages, such as speed, reduced labor costs, and enhanced inventory tracking.
- Consider technical limitations, safety concerns, and regulatory hurdles.
Example
In warehouse settings, UAVs contribute significantly to inventory management. They enable rapid stock checks and can reach areas less accessible to human workers, thus speeding up the retrieval and stocking processes. For instance, major companies have reported that using drones for inventory tasks reduces the time spent on manual stock checking, allowing for real-time inventory updates and fewer human errors. However, integrating UAVs indoors is challenging (Mourtzis et al., 2024). Safety remains a primary concern, as drones must be operated in a manner that does not endanger human workers. Additionally, technical issues such as battery life and navigation within confined spaces pose operational challenges.
Consider using UAVs indoors, such as in a warehouse, and outdoors, such as for home delivery.
Outdoor Use of UAVs in Supply Chain Management
Now, let us discuss the assessment of UAV Technology for Home Delivery.
- Analyze the use of drones for delivering goods directly to consumers’ homes. Focus on their application during the last mile of delivery.
- Use examples from pilot projects or ongoing services by significant companies.
- Highlight efficiency, reduced delivery times, and the potential to reach remote areas.
- Address weather dependency, airspace regulation issues, and privacy concerns.
Example
Outside the confines of warehouses, UAVs are making a mark in the delivery landscape, especially in last-mile delivery to consumers’ doorsteps. This application of drone technology promises to cut down delivery times drastically and reduce carbon emissions associated with traditional delivery vehicles (Azmat & Kummer, 2020). An example is a pilot project conducted by a well-known e-commerce giant, which demonstrated that drones could deliver packages in less than thirty minutes, significantly enhancing customer satisfaction and operational efficiency. However, this innovation is accompanied by substantial hurdles, including airspace regulatory restrictions, privacy intrusion concerns, and the drones’ vulnerability to adverse weather conditions. These examples illustrate that while UAV technology harbors the potential to revolutionize supply chain management substantially, it also requires careful consideration of operational, regulatory, and ethical dimensions. As such, embracing UAV technology in supply chain management necessitates a balanced approach, weighing its extensive benefits against the practical and regulatory challenges it introduces.
Closing
In conclusion, this How-To Owlisdom Guide emphasizes UAV technology’s critical role in modernizing supply chain management. By dissecting the advantages and the obstacles associated with UAVs in indoor and outdoor settings, students gain a nuanced understanding of how emerging technologies can reshape traditional business practices. The SCMG 501 Week 2 Discussion: Drone Technology in Supply Chain Management enhances technical knowledge and fosters analytical skills necessary for future supply chain professionals.
SCMG 501 Week 2: Assignment 1
Instructions for CMG 501 Week 2: Assignment 1
Instructions
Course Objectives:
- CO1: Evaluate self-driving technology to forecast the applicability to improve supply chain management.
- CO2: Explain the ramifications of the use of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAV) technology in supply chain management.
Prompt:
Research unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), also known as drones, and consider the applications of these devices for the support of different supply chains. Consider the implications of UAVs for business-to-business (b2b) and business-to-customer (b2c) transactions. Focus on one aspect of the usefulness of UAV technology and explain where it should be applied first. Discuss the pros and cons of the deployment of UAV technology in your chosen application.
Instructions:
- Label your Word document as follows: yourlastname.docx (ex: Johnson.docx)
- Essay format; not bullet format
- Minimum 4 full pages of content (Word document) of strategic material (does not include cover page, abstract, nor reference pages)
- All charts, graphs, and pictures are to go in the appendix (not a substitute for content)
- Resources and citations are formatted according to APA (6th edition) style and formatting
- Refrain from excessive use of quotes in your response (less than 5%)
- Once you submit your document to the assignment folder, it will automatically be loaded to TURNITIN.COM within the course. Your similarity scan score must be 20% or less (the following will be excluded: headers, bibliography, etc.) prior to the instructor grading the paper—focus on the content of the scan percentage
- Plagiarism will result in an automatic zero for this assignment.
- There are no late assignments accepted after the last day of the course.
Introduction to SCMG 501 Week 2 Assignment
This How-To SCMG 501 Guide serves as a framework to critically evaluate the role of emerging technologies, specifically self-driving vehicles and uncrewed aerial vehicles (UAVs), in enhancing supply chain management. Examining these technologies’ applicability and implications will give you insights into their potential to streamline operations and improve efficiencies in both B2B and B2C contexts.
Evaluate self-driving technology to forecast the applicability to improve supply chain management.
Overview of Self-Driving Technology in Supply Chain Management
To start the SCMG 501 Week 2: Assignment 1, we will explore self-driving technology in supply chain management.
- Forecasting Applicability: Assess how self-driving technology can be integrated into supply chain logistics, focusing on transportation and delivery processes.
- Potential Improvements: Identify and explain potential enhancements in efficiency, cost reduction, and safety.
Example
Integrating self-driving technology into supply chain management represents a transformative shift, promising to enhance logistical efficiency while reducing operational costs and improving safety (Tripathi & Gupta, 2020). This technology, primarily through autonomous vehicles (AVs), offers a compelling solution to some of the most persistent challenges in transportation and delivery processes. Self-driving vehicles can be seamlessly integrated into supply chain logistics, especially when automating the transportation of goods across extensive networks. Autonomous trucks, for example, are already being tested on public roads, with companies like Tesla and Waymo at the forefront (Simons, 2020). These vehicles can operate without human intervention, potentially reducing the need for drivers and minimizing human error. The primary applicability of AVs in supply chains lies in their ability to maintain consistent speeds, adhere strictly to routes, and operate in a wide range of conditions, day or night, which optimizes delivery times and improves route efficiency.
Understanding UAV Technology
Next, we will discuss the understanding of UAV Technology. General Applications in Supply Chains: Research the roles of UAVs in supply chains, emphasizing how they support various logistical tasks.
- Specific Focus on B2B and B2C Transactions: Analyze how UAVs can improve operational efficiencies in both business models.
Example
Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs), commonly known as drones, are increasingly utilized in various aspects of supply chain management, providing agile responses to complex logistical challenges. Drones are not just for surveillance or photography; their roles in supply chain management are growing. In warehouses, drones perform inventory checks faster than human workers. For transportation, they deliver small packages over short distances, bypassing ground traffic and reducing delivery times dramatically. In B2B environments, drones can expedite the transport of goods between facilities by overcoming geographical and infrastructural constraints, which is crucial for industries like manufacturing, where time and precision are paramount (Mohsan et al., 2022). In B2C scenarios, drones revolutionize last-mile delivery, directly delivering goods to consumers’ doorsteps. This method is faster and reduces the carbon footprint compared to traditional delivery vans. Integrating Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) into supply chain management marks a significant technological advancement poised to revolutionize the logistics sector. This analysis delves into the utilization of UAVs, specifically exploring their role in transforming last-mile delivery, a critical segment of the supply chain known for its complexity and cost implications. Last-mile delivery is the final step in the supply chain, involving transporting goods from a distribution center to the end customer’s location. It is often the most challenging and expensive part of the logistics process due to traffic congestion in urban areas, the small quantity of goods being delivered per stop, and customer availability issues (Mourtzis et al., 2024). UAVs, or drones, emerge as a promising solution to these challenges, offering a quicker, more efficient method of package delivery. Companies like Amazon have been at the forefront of testing UAV systems for delivery. Their Amazon Prime Air program aims to safely deliver packages to customers within 30 minutes of order placement using drones. This initiative showcases the feasibility and potential efficiency gains of using UAV technology in operational settings.
Explain the ramifications of using unmanned aerial vehicles (UAV) technology in supply chain management.
Detailed Analysis of UAV Technology
In this section of SCMG 501 Week 2: Assignment 1, we will explore the analysis of UAV technology.
- Selection of a Specific Application: Choose one key area (e.g., last-mile delivery, inventory management) where UAVs could be significantly impactful.
- Pros and Cons of UAV Deployment: Discuss advantages such as increased speed, reduced operational costs, and challenges like regulatory issues and privacy concerns.
Example
As UAV technology continues to evolve, its application in last-mile delivery is expected to expand, driven by continuous improvements in drone endurance, reliability, and automation. Future developments might include advanced fleet management systems, enhanced battery life, and improved navigation technologies, which will further increase the operational viability of drones in the supply chain. Drones excel in enhancing delivery speeds, significantly reducing the time it takes for packages to reach their destinations. This is particularly advantageous in urban areas where traffic congestion often delays traditional delivery methods. By flying directly to delivery points, drones bypass ground obstacles, ensuring rapid delivery that is faster and more predictable, thereby improving customer satisfaction and service reliability. Deploying drones for delivery tasks can lead to considerable cost savings over traditional methods involving manned vehicles. Drones are particularly cost-effective for transporting small, lightweight items over short distances, as they require less energy and no direct human operation during transit. This reduction in labor and fuel expenses makes drones an economically attractive option for companies aiming to optimize their delivery operations. They provide a critical advantage in reaching remote or difficult-to-access areas where traditional delivery vehicles may struggle to operate (Simons, 2020). This capability is invaluable in rural or geographically challenging regions, ensuring that essential goods and services can be delivered where they are most needed. Drones’ ability to overcome physical barriers opens up new possibilities for service expansion, enhancing the reach and impact of various businesses and humanitarian efforts. Drones are subject to strict regulations that can hinder widespread adoption, particularly concerning airspace and usage in urban areas. These regulations, often varying significantly by region, aim to ensure safety and privacy but can restrict operational flexibility. Navigating this complex regulatory landscape requires constant vigilance and adaptation by companies looking to integrate UAV technology into their logistics strategies.
Instructional Tips
- Document Labeling: Label your Word document with your last name (e.g., Johnson.docx).
- Format: Use essay format; avoid bullet points for the main text.
- Length Requirement: Minimum of 4 total pages of strategic content, excluding cover page, abstract, and reference pages.
- Appendices: Include all charts, graphs, and pictures in the appendix, not as content substitutes.
- APA Formatting: Adhere to APA (6th edition) style for resources and citations.
- Quotation Use: Limit quotations to less than 5% of your content.
- TURNITIN.COM Submission: Ensure a similarity scan score of 20% or less, focusing on content rather than headers or bibliography.
- Plagiarism Policy: Be aware that plagiarism results in an automatic zero for this assignment.
- Late Submissions: No assignments are accepted after the last day of the course.
Closing
This How-To Owlisdom Guide equips students to critically assess the integration of self-driving and UAV technologies within supply chain management. By evaluating these technologies’ applicability and implications, you will enhance their understanding of technological advancements and develop a strategic perspective on how these innovations can transform supply chain operations.
References
Mohsan, S. A. H., Khan, M. A., Noor, F., Ullah, I., & Alsharif, M. H. (2022). Towards the Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs): A Comprehensive Review. Drones, 6(6), Article 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones6060147 Mourtzis, D., Angelopoulos, J., & Panopoulos, N. (2024). Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) path planning and control assisted by Augmented Reality (AR): The case of indoor drones. International Journal of Production Research, 62(9), 3361–3382. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207543.2023.2232470 Simons, R. A. (2020). Identification of major vehicle-related hardware and technological trends. In Driverless Cars, Urban Parking and Land Use. Routledge.
Tripathi, S., & Gupta, M. (2020). Transforming towards a smarter supply chain. International Journal of Logistics Systems and Management, 36(3), 319–342. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJLSM.2020.108694
SCMG 501 WEEK 3 DISCUSSION: Visibility in Supply Chains
Instructions for SCMG 501 Week 3 Discussion
Course Objective
- CO3: Evaluate technologies that will disrupt the visibility of customer-driven supply chains.
Prompt:
Evaluate the supply chain implications of visible customer supply chains with disruptive technology such as Uber, Lyft, Zipcar, Lime, Bird, and Amazon Key. Consider other supply chain technologies that are disrupting the understanding of visible supply chains. In addition to reading your assigned resources for week 3, research online definitions for ride-sharing.
Peregrine Assessment
Instructions
Peregrine Assessment Due in Week 3
During week 2, a sample of students enrolled in this course will be selected to complete an academic programmatic assessment through Peregrine Academic Services.
Please check your university email via your Office 365 email account during week 2 to find an email that will either provide you with detailed instructions on how to complete the Peregrine assessment or a waiver stating that you were not selected to complete the assessment.
If selected to complete the assessment, please do your best, but please keep in mind that this is only an initial measurement of your graduate-level business and supply chain subject knowledge. During the final requirement course for the MA Supply Chain Management program, students in that program will complete this assessment again to measure the knowledge gained throughout the program. APUS uses the results from this assessment to aid in our continuous improvement process.
The assessment will include approximately 60 multiple-choice questions. You can exit and resume the exam, but you will only be able to do so three times over a 48-hour period.
The Peregrine assessment is a required, graded assignment for all, however, you get full credit for simply completing the assessment or with your waiver email. The assignment grade is not based on your test score. To get credit for the assignment, attach and submit the score results you get from Peregrine or the waiver email you get from LOA@apus.edu in the Submit Assignment section below.
For Technical Assistance regarding registration and completion of the Peregrine assessment, please contact Peregrine Academic Services directly.
Completion of the Peregrine Assessment and submission of results or waiver is due by the end of Week 3.
NOTE: If you have already completed the Inbound Peregrine Programmatic Assessment in SCMG501, DO NOT take the exam again. Your previous Inbound Peregrine Test score for this course can be submitted. Use this link if you need assistance retrieving your completion certificate.
Introduction to SCMG 501 Week 3 Discussion
The SCMG 501 Week 3 Discussion: Visibility in Supply Chains focuses on evaluating the impact of disruptive technologies on the visibility of customer-driven supply chains. With the advent of services like Uber, Lyft, and Amazon Key, the traditional supply chain management landscape is evolving rapidly. This SCMG 501 guide will help you understand and analyze how these technologies reshape supply chain visibility and operations.
Disruptive Technologies in Supply Chain
To start the SCMG 501 Week 3 Discussion: Visibility in Supply Chains, we will discuss the disruptive technologies in Supply Chain Management.
- Briefly describe the role of technology in modern supply chains.
- Mention examples like Uber and Amazon Key to set the context.
- Define ‘supply chain visibility’ as tracking products and services from origin to consumption.
- Explain ‘disruptive technology‘ as innovations that significantly alter how businesses operate.
- Research and define ‘ridesharing’ and its relevance to supply chains.
Example
Supply chain visibility is crucial as it allows businesses to track products and services from origin to consumption. This transparency is vital for optimizing processes and ensuring customer satisfaction. Disruptive technologies enhance this visibility by integrating advanced tracking systems, real-time data analytics, and customer feedback mechanisms directly into the supply chain network. For instance, Amazon Key, which allows deliveries inside a customer’s home or vehicle, leverages real-time tracking and verification technologies to ensure security and improve delivery efficiency. This system increases customer trust and provides Amazon with valuable data on delivery logistics and customer preferences. Ridesharing platforms like Uber and Lyft have also transformed supply chain dynamics, particularly regarding last-mile delivery. This supply chain segment moves goods from a transportation hub to the final delivery destination. By employing freelance drivers who use their own vehicles, these companies reduce the need for dedicated delivery fleets, thus lowering operational costs and enhancing scalability. Furthermore, the data collected from these ridesharing services help predict demand patterns and optimize routes, significantly reducing delivery times and improving service reliability.
Evaluating Disruptive Technologies
Next, we will evaluate the Disruptive Technologies in detail.
- Select one or two technologies (e.g., Uber, Amazon Key) and detail their effects on supply chain visibility.
- Establish efficiency, cost reduction, and customer satisfaction criteria to evaluate these technologies.
- Discuss the operational and economic impacts using examples.
- Discuss immediate impacts (e.g., improved delivery times) and long-term strategic implications (e.g., need for infrastructure changes).
- Use examples to illustrate how companies might need to adapt.
Example
Evaluating the impact of such technologies requires a clear set of criteria: efficiency, cost reduction, and customer satisfaction. For example, Uber’s foray into the food delivery service with Uber Eats uses its existing network of drivers to deliver food, thus repurposing its logistical framework for a new market segment. This expands the service offering and increases operational efficiency by maximizing the utility of its assets. The long-term strategic implications of these technologies cannot be underestimated. Companies must consider infrastructure changes to accommodate these new technologies. They might need to invest in more sophisticated IT systems or develop partnerships with technology providers to maintain competitiveness in a digitally evolving market. In conclusion, disruptive technologies are reshaping the supply chain management landscape by enhancing visibility and improving efficiency. As these technologies continue to evolve, they present both opportunities and challenges. Companies that can effectively integrate these technologies into their operations will likely achieve significant competitive advantages in terms of operational efficiency, cost reduction, and enhanced customer satisfaction. The ongoing evaluation and adaptation to these disruptive technologies will be crucial for businesses aiming to thrive in the dynamic market of the future.
Closing
By following this How-To Owlisdom Guide, you can anticipate changes in the supply chain landscape and adapt strategies accordingly. The SCMG 501 Week 3 Discussion: Visibility in Supply Chains enhances your understanding and equips you with the analytical tools to assess the real-world impact of technological advancements on supply chains.
Peregrine Assessment Precap
Congratulations and good luck to those who got selected for the Peregrine Assessment. To ace the assessment, keep in mind the following points:
- This is an initial assessment to gauge your graduate-level business and supply chain knowledge for the MA Supply Chain Management program; a final assessment will be taken at the program’s end to measure acquired knowledge.
- The assessment consists of approximately 60 multiple-choice questions and can be exited and resumed thrice within 48 hours.
- APUS utilizes results from this assessment for continuous improvement purposes.
- Although the Peregrine assessment is mandatory and graded, full credit is awarded for completing the evaluation or submitting a waiver email.
- To receive credit for this assignment, submit your score results from Peregrine or your waiver email from LOA@apus.edu in the designated “Submit Assignment” section.
SCMG 501 Week 4 Elevator Pitch: Artificial Intelligence in Supply Chain Management
Instructions of SCMG 501 Week 4 Elevator Pitch
Course Objective:
- CO 4: Explain the use of artificial intelligence in supply chain management systems and processes.
Prompt:
Research and devise a plan to utilize artificial intelligence in supply chain management. Covert your plan into a short ‘elevator pitch’ and submit your pitch as your posting for the week. Feel free to use video or sound to supplement your pitch to use artificial intelligence in supply chain management. Below are some tools that might be helpful in creating video or sound:
- PowerPoint
- YouTube
- Powtoon
- Microsoft Sway
- Prezi
- Google Slides
In addition to reading your assigned resources for week 4, research online definitions for artificial intelligence.
Introduction to SCMG 501 Week 4 Elevator Pitch
This How-To SCMG 501 Guide is designed to walk you through understanding and implementing Artificial Intelligence (AI) in supply chain management. AI technologies offer transformative potential for enhancing efficiency, predicting market dynamics, and optimizing logistics. By the end of the SCMG 501 Week 4 Elevator Pitch: Artificial Intelligence in Supply Chain Management, you will know how to research AI applications, devise a strategic implementation plan, and succinctly communicate your proposal through an effective elevator pitch.
Understanding Artificial Intelligence in Supply Chains
- Define AI and discuss its relevance in modern supply chains, emphasizing predictive analytics, automation, and decision-making enhancements.
- Provide examples like AI-driven demand forecasting or autonomous delivery vehicles to illustrate the integration of AI in supply chains.
Researching AI Innovations
- Investigate recent advancements in AI technology relevant to supply chains, such as machine learning models for inventory management.
- Study case studies where AI implementation has led to significant improvements in supply chain efficiency and include insights gained.
Devising an AI Implementation Plan
- Clearly state the objectives of your AI implementation, focusing on specific areas like reducing lead times or improving product quality.
- Detail the technology stack needed, including any software and hardware requirements.
- Address potential challenges like data privacy concerns or high initial costs and propose practical solutions.
Crafting an Elevator Pitch
- Enumerate the key elements to cover in your pitch: the problem, your AI solution, and the expected impact.
- Structure your pitch to be concise and compelling, ideally lasting no more than 30-60 seconds.
- Practice your pitch to ensure clarity and confidence in delivery.
Presentation Tools
- Discuss the features of each tool (PowerPoint for slideshows, YouTube for video hosting, etc.) and their best uses.
- Select a tool that suits the nature of your pitch and audience. Sophisticated tools like Prezi or Powtoon may be appropriate for a tech-savvy audience.
- Provide tips for practical use, such as keeping slides uncluttered in PowerPoint or making engaging visuals in Powtoon.
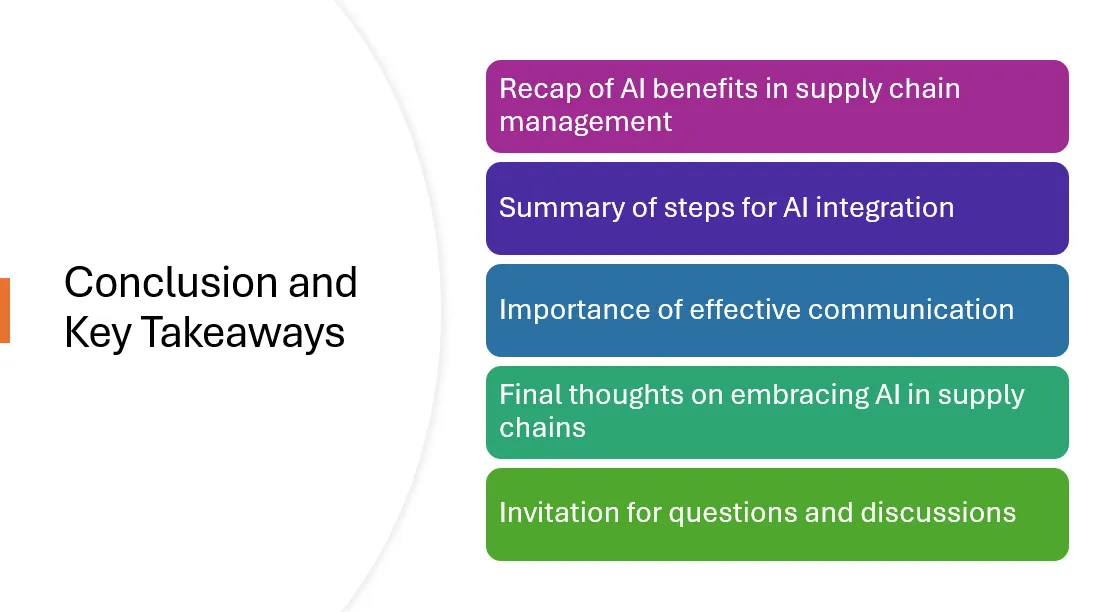
Conclusion and Final Considerations
- Summarize the steps to integrate AI into supply chain operations successfully.
- Highlight the importance of clear communication in your elevator pitch to garner stakeholder support.
Closing
Integrating AI into supply chain management can significantly enhance operational efficiencies and competitive advantages. The SCMG 501 Week 4 Elevator Pitch: Artificial Intelligence in Supply Chain Management helps you understand the practical steps involved and equips you with the skills to propose your ideas effectively. Remember, the key to successful implementation is as much about technological integration as it is about clear and persuasive communication of the benefits to stakeholders.
Elevator Pitch Example (PowerPoint)
Speaker’s Notes
Slide 1: Title Slide
Welcome everyone. Today, we’ll explore how artificial intelligence is transforming supply chain management. We’ll cover the steps to implement AI effectively and communicate these strategies succinctly.

Slide 2: Introduction to AI in Supply Chains
Artificial Intelligence is reshaping supply chains, making processes more predictive and efficient. Today’s focus is on understanding these changes and their benefits.
Slide 3: Understanding AI’s Role
AI enhances decision-making, automates tasks, and optimizes logistics. Let’s look at how AI improves forecasting and inventory management through real-world applications.
Slide 4: Researching AI Innovations
Identifying and adopting the right AI technologies is crucial. We’ll discuss leveraging case studies and staying updated on AI trends relevant to supply chains.
Slide 5: AI Implementation Plan
Developing a clear AI implementation plan is essential. We’ll outline the steps, from selecting technologies to addressing potential challenges.
Slide 6: Crafting an Elevator Pitch
An effective elevator pitch communicates your AI strategy succinctly. We’ll review a persuasive pitch’s components and practice delivery strategy.

Slide 7: Choosing Presentation Tools
Selecting the right tools can enhance how you present your AI strategies. We’ll compare popular tools like PowerPoint and Powtoon, focusing on their strengths.

Slide 8: Implementing Your Plan
Notes: Implementation involves rolling out AI, monitoring progress, and adjusting. We’ll discuss measuring success and training your team on new tools.

Slide 9: Long-Term Strategic Implications
Adopting AI affects long-term strategies. We’ll discuss future implications, potential benefits, and the importance of adaptability.

Slide 10: Conclusion and Key Takeaways
To conclude, integrating AI in supply chains is transformative. Remember, clear communication and strategic planning are essential to successful implementation. Let’s open the floor for questions.
SCMG 501 WEEK 4 ASSIGNMENT TWO
Instructions for SCMG 501 Week 4 Assignment Two
Instructions
Course Objectives:
- CO3: Evaluate technologies that will disrupt the visibility of customer-driven supply chains.
- CO4: Explain the use of artificial intelligence in supply chain management systems and processes.
Prompt:
Research artificial intelligence and consider how it is currently being applied to support supply chains and how it can be used in the future. Consider how organizations are already harvesting data in order to better target new purchases to individuals leveraging artificial intelligence. Remain within the current technological constraints, but you can combine multiple related technologies to support why and how artificial intelligence will be instrumental in the supply chains of the future.
Instructions:
- Label your Word document as follows: yourlastname.docx (ex: Johnson.docx).
- Essay format; not bullet format
- Minimum 4 full pages of content (Word Document) of strategic material (does not include cover page, abstract, nor reference pages)
- All charts, graphs, and pictures are to go in the appendix (not a substitute for content).
- Resources and citations are formatted according to APA (6th edition) style and formatting.
- Refrain from excessive use of quotes in your response (less than 5%).
- Once you submit your document to the assignment folder it will automatically be loaded to TURNITIN.COM within the course. Your similarity scan score must be 20% or less (the following will be excluded: headers, bibliography, etc.) prior to the instructor grading the paper—focus on the content of the scan percentage
- Plagiarism will result in an automatic zero for this assignment.
- There are no late assignments accepted after the last day of the course.
Introduction to SCMG 501 Week 4 Assignment Two
The SCMG 501 Week 4 Assignment Two explores Artificial Intelligence (AI) ‘s disruptive role in enhancing customer-driven supply chain visibility. It delves into how AI is utilized, its potential for future applications, and the strategic integration of related technologies to optimize supply chain operations.
Research artificial intelligence and consider how it is currently being applied to support supply chains and how it can be used in the future.
AI in Supply Chain Management
We will discuss AI in supply chain management to start the SCMG 501 Week 4 Assignment Two.
- Define AI and its significance in modern supply chains.
- Discuss the concept of supply chain visibility and why it is critical.
- Research and present case studies where AI has improved supply chain visibility.
- Analyze how AI contributes to operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Example
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a tool and a transformative force in supply chain management. It revolutionizes how businesses source, manufacture, and deliver products (Agrawal & Narain, 2023). AI technologies like advanced analytics and machine learning do not just optimize operations; they anticipate market demands and refine inventory levels, making businesses more agile. Predictive analytics foresee disruptions, promoting smoother operations. AI also improves manufacturing efficiency and quality by minimizing human error. Additionally, emerging technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT) and blockchain further revolutionize supply chains. IoT enhances real-time goods tracking, increasing logistical visibility and control, whereas blockchain ensures transactional security and transparency, making every supply chain transaction immutable and easily traceable.
Current Applications of AI in Supply Chains
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a technological evolution and a game-changer in supply chain management. By simulating human cognitive processes to perform complex tasks such as learning from data, reasoning, and self-correction, AI profoundly enhances operational efficiency, reduces costs, and boosts customer satisfaction (Bhatt, 2021). It improves supply chain visibility, allowing businesses to monitor and track products from production to delivery, fine-tune inventory, reduce costs, and accelerate delivery, contributing to greater customer satisfaction. This is just the beginning of the benefits AI can bring to supply chains, painting a promising future for this technology.
Real-world examples of AI integration in supply chains, such as those by IBM and Amazon, inspire us with the potential of this technology. IBM uses AI to track goods in real-time and predict disruptions, improving decision-making and reducing downtime. Amazon utilizes machine learning to forecast demand, adjust prices, and optimize delivery routes, aligning inventory with consumer demand and minimizing shipping delays. This strategic application of AI enhances efficiency and customer experiences, showing us the tangible benefits of AI in supply chain management.
Furthermore, AI-driven automation in warehousing, such as robotic systems performing storage and retrieval tasks, reduces labor costs and human error, increasing operational capabilities (Sodiya et al., 2024). As AI technology evolves, its deeper integration into supply chain management is anticipated, promising enhanced automation and system-wide integration that could revolutionize the field further. This ongoing development signifies a shift towards more agile, responsive, and customer-centric business practices, driving efficiency and fostering a robust, adaptive business environment.
Future Potential of AI in Supply Chains
Next, we will discuss AI’s potential in the future supply chain.
- Explore advanced AI applications like predictive analytics for forecasting demand.
- Discuss the role of AI in automating supply chain processes and real-time data usage.
- Outline AI-driven techniques for data collection that enhance customer profiling.
- Evaluate how AI supports targeted marketing strategies to boost sales.
Example
The role of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in enhancing supply chain operations is poised for significant expansion. AI’s predictive analytics are crucial for forecasting demand by analyzing historical data and discerning patterns (Bhatt, 2021). This allows companies to optimize inventory and align production with market needs efficiently. Additionally, AI-driven automation, mainly through Robotic Process Automation (RPA), revolutionizes warehouse operations by automating repetitive tasks such as packing and sorting, reducing labor costs and minimizing human error. This automation enhances supply chain processes’ precision, speed, and reliability.
Real-time data analytics transform supply chains by enabling continuous monitoring and proactive adjustments. This capability ensures that companies can quickly adapt to changes, maintaining operational continuity and avoiding disruptions in today’s fast-paced markets. Moreover, AI’s role extends to strategic customer engagement and profiling. By analyzing extensive customer data, AI identifies buying behaviors and preferences, allowing companies to tailor their marketing strategies effectively. This targeted approach improves customer engagement and increases sales efficiency by aligning products with consumer expectations.
AI also fosters a more integrated supply chain management approach, synchronizing data across various points to create a responsive, cohesive system. This integration is vital for optimizing logistics, reducing waste, and enhancing supply chain responsiveness. As AI technology evolves, its integration into supply chain management is set to deepen, promising more sophisticated solutions to contemporary logistical challenges and marking a new era of efficiency in global commerce.
Consider how organizations are already harvesting data to better target new purchases to individuals leveraging artificial intelligence.
Combining Technologies to Enhance AI Utility
For this section of the Week 4 Assignment, we will explore combining technologies to enhance the AI utility in SCM.
- Explain the integration of AI with the Internet of Things (IoT) and its benefits.
- Discuss the role of cloud computing and big data in supporting AI functionalities.
- List the steps to implement AI technologies in supply chains effectively.
- Address potential technological and ethical challenges and propose solutions.
Example
To fully leverage AI in supply chain management, integrating it with other technologies like the Internet of Things (IoT) and cloud computing is essential. The IoT, for instance, provides a network of connected devices that collect and exchange data in real time. Combined with AI, this data can be analyzed instantly to enhance decision-making processes (Azmat & Kummer, 2020). For example, IoT devices in a fleet of delivery trucks can send real-time location and status data to an AI system, which can then optimize routes based on traffic conditions or vehicle performance issues.
Cloud computing and big data are also critical in supporting AI functionalities. Cloud platforms can store vast amounts of data and provide the computational power needed for AI algorithms to process this data effectively. This synergy allows for scalable, flexible, and more efficient data handling and AI processing capabilities.
Implementing AI in Supply Chains
To effectively leverage Artificial Intelligence (AI) in supply chain management, define your objectives, such as improving efficiency, reducing costs, or boosting customer service. Next, select appropriate AI technologies and tools that best meet these goals (Sodiya et al., 2024). Integration of these tools with existing systems is crucial, followed by comprehensive testing to confirm they operate as expected. Equally important is the training and development of staff to proficiently use the new AI technologies. Establish and disseminate guidelines for best practices to ensure consistent application across your operations. Finally, continuous monitoring and adaptability should be implemented to respond to feedback and evolving conditions, allowing for ongoing optimization of AI system performance. This structured approach ensures that AI tools are implemented efficiently, sustainably, and effectively to enhance supply chain operations.
Addressing Challenges
Implementing Artificial Intelligence (AI) offers numerous advantages but presents several challenges. Technologically, integrating AI systems into existing infrastructures can be intricate and expensive, requiring significant investment. Ethically, the implementation raises issues such as data privacy and the potential displacement of jobs, which companies must carefully consider. Ensuring strong cybersecurity measures is crucial to protect sensitive information from breaches. Additionally, businesses need to address the societal impact of replacing jobs traditionally performed by humans with automated processes, balancing technological advancement with responsible and ethical decision-making. These considerations are essential for a successful and conscientious AI integration.
Conclusion
We will conclude our SCMG 501 Week 4 Assignment Two by summarizing all the key takeaways we learned.
- Summarize the transformative potential of AI in supply chains.
- Highlight the importance of strategic planning and ethical considerations in AI implementation.
Instructional Tips
- Label your document as yourlastname.docx (e.g., Johnson.docx).
- Use essay format, not bullet format.
- Ensure at least four total pages of strategic content, excluding cover page, abstract, and references.
- Include all charts, graphs, and pictures in the appendix, not as content substitutes.
- Follow the APA (6th edition) style for formatting and citations.
- Limit quotes to less than 5% of your response.
- Aim for a similarity scan score of 20% or less, excluding headers and bibliography.
- Understand that plagiarism will result in a zero for this assignment.
Closing
By following this How-To SCMG 501 Guide, you will be equipped to manage and evaluate AI technologies, understand their current and future roles in supply chain management, and develop a strategic plan for their implementation.
References
Agrawal, P., & Narain, R. (2023). Analyse enablers for the supply chain digitalization using an interpretive structural modeling approach. International Journal of Productivity and Performance Management, 72(2), 410–439.
Azmat, M., & Kummer, S. (2020). Potential applications of unmanned ground and aerial vehicles to mitigate challenges of transport and logistics-related critical success factors in the humanitarian supply chain. Asian Journal of Sustainability and Social Responsibility, 5(1), 3. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41180-020-0033-7
Bhatt, A. (2021). Artificial intelligence in managing clinical trial design and conduct: Man and Machine still on the Learning curve? In Perspectives in clinical research (Vol. 12, Issue 1, pp. 1–3). Medknow.
Sodiya, E. O., Umoga, U. J., Amoo, O. O., & Atadoga, A. (2024). AI-driven warehouse automation: A comprehensive review of systems. GSC Advanced Research and Reviews, 18(2), 272–282.
SCMG 501 WEEK 5 DISCUSSION: Blockchain Technology and Supply Chains
Instructions for SCMG 501 Week 5 Discussion
Course Objective:
- CO5: Evaluate the feasibility of applying blockchain technology to an organization’s supply chain.
Prompt:
Research and assess blockchain technology and its applicability to supply chain management. Consider how blockchain technology can be used and offer a supportive argument for its adoption by a company. Justify your position with an explanation of how blockchain will be able to reduce supply chain costs and complexity. In addition to reading your assigned resources for week 5, research online definitions for blockchain.
Introduction to SCMG 501 Week 5 Discussion
This How-To SCMG 501 Guide is designed to assist students in understanding how to evaluate the feasibility and applicability of integrating blockchain technology into an organization’s supply chain management. As blockchain technology offers transformative potential for enhancing transparency and efficiency, this assignment will delve into its implementation’s theoretical and practical aspects.
Blockchain and Supply Chain
To start the SCMG 501 Week 5 Discussion: Blockchain Technology and Supply Chains, we will introduce the blockchain concept and its relevance to supply chains. We will determine if blockchain is a viable solution for the organization.
- Begin with a definition of blockchain.
- Briefly explain how it differs from traditional data management technologies and its specific advantages for supply chains.
- Analyze the organization’s current supply chain workflow and identify areas where blockchain could improve.
- Discuss any potential barriers to implementation.
Example
In exploring the transformative potential of blockchain technology within supply chain management (SCM), we must first understand its foundational concept and advantages over traditional data management systems. Blockchain is a distributed ledger technology that stores transaction data across multiple nodes, making it immutable and transparent. Unlike centralized systems, blockchain offers enhanced security and traceability, which is critical in SCM. These features address common challenges such as counterfeiting, product theft, and the inefficiency of paper-based tracking systems. The next step involves analyzing the current workflow of an organization’s supply chain to identify potential enhancements through blockchain. For instance, in industries like pharmaceuticals, where compliance and product authenticity are paramount, blockchain can significantly streamline processes and strengthen the integrity of the supply chain. However, potential barriers such as technological integration with existing systems, initial setup costs, and a lack of expertise in blockchain technology might impede implementation.
Research and assess blockchain technology and its applicability to supply chain management. Consider how blockchain technology can be used and offer a supportive argument for its adoption by a company.
Researching Blockchain Technology
Next, we will gather contemporary insights on blockchain in supply chain management. Also, evaluate how blockchain can be applied explicitly to the chosen organization’s supply chain.
- Utilize academic journals, industry reports, and case studies to understand blockchain’s current trends and real-world applications in similar organizations.
- Map out the supply chain process and pinpoint where blockchain could integrate to enhance visibility, accuracy, and efficiency.
Example
A detailed examination of contemporary insights and real-world applications is necessary to justify the blockchain application further. By reviewing academic journals and industry reports, we observe that organizations with integrated blockchain technology often achieve remarkable improvements in efficiency and accuracy. For example, a case study involving a major retail company showed that blockchain implementation reduced the time needed for inventory tracking and verification processes by over 30%, highlighting substantial operational efficiency. By mapping an organization’s specific supply chain processes with potential blockchain integration points, we can uncover areas for immediate improvement. For instance, integrating blockchain to manage supplier agreements and certifications can significantly enhance visibility and compliance across the supply chain. This practical application is particularly beneficial in sectors with complex supplier networks, like the electronics and automotive industries, providing tangible benefits that can be readily understood and appreciated.
Justify your position with an explanation of how blockchain will be able to reduce supply chain costs and complexity.
Supportive Argument for Adoption
For this section of the SCMG 501 Week 5 Discussion: Blockchain Technology and Supply Chains, we will argue in favor of adopting blockchain technology by justifying blockchain’s adoption based on cost and complexity considerations.
- Highlight the specific benefits observed in other case studies, focusing on improvements in operational efficiency and data integrity.
- Conduct a cost-benefit analysis detailing expected cost savings and reductions in supply chain complexities. Use quantitative data from similar case studies where possible.
Example
Supporting the adoption of blockchain in supply chains involves a balanced analysis of the costs and benefits. A cost-benefit analysis based on similar organizational implementations suggests that while initial investments in blockchain technology are substantial, the long-term savings and improvements in efficiency justify the expenditure. Reduced instances of fraud, faster transaction times, and lower compliance and monitoring costs all contribute to a strong case for blockchain adoption.
Conclusion
We will summarize the essential findings and recommend a course of action.
- Recap the potential benefits and challenges discussed.
- Offer a balanced viewpoint on whether the organization should implement blockchain technology.
Example
In conclusion, our exploration into blockchain technology within SCM underscores its potential to revolutionize traditional practices, enhancing transparency and operational efficiencies. While the benefits are clear, the challenges, such as technological integration and initial costs, require careful consideration. Organizations must weigh these factors and decide if the long-term benefits of blockchain technology align with their strategic goals. This balanced approach, grounded in a thorough understanding of blockchain’s potential to transform the supply chain, ensures that the adoption of blockchain technology is both strategic and beneficial, instilling confidence in the decision-making process.
Closing
Upon completing the SCMG 501 Week 5 Discussion: Blockchain Technology and Supply Chains, you should clearly understand how blockchain technology can be pragmatically and strategically implemented in a supply chain context. The key takeaway is that while blockchain presents substantial benefits for supply chain management, its adoption should be evaluated against organizational goals and capabilities to ensure alignment and feasibility.
SCMG 501 WEEK 6 DISCUSSION: Cyber Vulnerabilities of Supply Chains
Instructions of SCMG 501 Week 6 Discussion
Course Objective:
- CO6: Diagnose the cyber vulnerabilities of systems that support an organization’s supply chain.
Prompt:
Assess and critique the potential cyber vulnerabilities in supply chain management. Your initial posting should propose a few different cyber risks, and the posting should also explain potential solutions to combat these cyber risks. Explain the global factors and implications regarding these cyber risks. In addition to reading your assigned resources for week 6, research online definitions for cyber and cyber vulnerabilities.
Introduction to SCMG 501 Week 6 Discussion
This How-To SCMG 501 Guide provides a structured approach for you, as students and professionals, to diagnose and assess cyber vulnerabilities within an organization’s supply chain systems. Given the increasing interconnectivity and reliance on digital platforms, your understanding and efforts in mitigating cyber risks are crucial for maintaining the integrity and efficiency of supply chain operations.
Diagnose cyber vulnerabilities of systems that support an organization’s supply chain. Assess and critique the potential cyber vulnerabilities in supply chain management.
Cybersecurity in Supply Chain Management.
To start the SCMG 501 Week 6 Discussion: Cyber Vulnerabilities of Supply Chains, we will introduce the context for the importance of cybersecurity in supply chain management. We will define cyber vulnerabilities and the types that affect supply chains.
- Briefly introduce the concept of supply chain management and the role of digital technologies.
- Highlight why cybersecurity is a critical aspect.
- Explain the term ‘cyber vulnerability’ and classify the common types, such as malware, ransomware, data breaches, etc., particularly focusing on those that impact supply chains.
Example
In the realm of supply chain management, the adoption of digital technologies has significantly optimized processes but also introduced substantial cybersecurity vulnerabilities. As professionals and students in this field, you must understand the landscape of these vulnerabilities. This knowledge is essential for safeguarding the integrity and continuity of supply chain operations and keeping you informed and aware of your roles. Supply chain management involves coordinating the production, shipment, and delivery of goods from origin to consumer. The reliance on digital systems introduces various cyber threats, making cybersecurity not just important, but pivotal for data protection and ensuring operational continuity and trust in supply chain networks. Cyber vulnerabilities refer to weaknesses in information systems that can be exploited to gain unauthorized access or cause damage. In supply chains, these vulnerabilities can have severe consequences. Critical vulnerabilities include malware, which disrupts operations through malicious software; ransomware, which locks access to systems demanding ransom; and data breaches, where sensitive information is exposed or stolen. These disruptive vulnerabilities can lead to halted operations, significant financial loss, and compromised business relationships. It’s crucial to understand the urgency of addressing these issues.
Your initial posting should propose a few different cyber risks, and the posting should also explain potential solutions to combat these cyber risks.
Assessing Cyber Vulnerabilities
Next, we will outline how to assess these vulnerabilities in a supply chain context. Also, identify and propose potential cyber risks in supply chains.
- Discuss various tools and techniques for vulnerability assessment, including cybersecurity audits, penetration testing, and the use of vulnerability scanners tailored explicitly for supply chain components.
- List common cyber risks in supply chains, using case studies or hypothetical scenarios to illustrate how these risks can manifest in real life.
Example
Organizations should employ various tools and techniques to assess these cyber vulnerabilities effectively. Cybersecurity audits evaluate the thoroughness of security policies and controls. Penetration testing simulates cyber attacks to test system robustness. Vulnerability scanners, tailored for supply chain components, detect real-time vulnerabilities, providing ongoing risk assessment. Identifying potential cyber risks involves understanding vulnerabilities and analyzing how these might affect the supply chain. For instance, a data breach in a supplier’s database can expose proprietary information, and ransomware can disrupt logistics software, halting goods delivery.
Explain the global factors and implications regarding these cyber risks.
Solutions to Cyber Risks
This section of SCMG 501 Week 6 Discussion: Cyber Vulnerabilities of Supply Chains will explain potential solutions and preventative measures. We will also discuss the global factors influencing cyber risks and their management.
- Outline strategies to combat identified risks, such as implementing robust encryption, regular employee security training, and adopting advanced cybersecurity technologies.
- Evaluate how international regulations like GDPR and cross-border data flow challenges affect cybersecurity strategies in global supply chains.
Example
Addressing these risks involves implementing robust cybersecurity measures like solid encryption to protect data integrity, regular security training for employees to prevent phishing attacks, and adopting advanced technologies like blockchain to enhance transaction security across the supply chain. Global factors also significantly influence cybersecurity strategies. International regulations like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) mandate stringent data protection standards, affecting data handling across borders. These regulations are not just rules; they directly impact how we manage cybersecurity in our supply chains. Cross-border data flow challenges, such as differing national cybersecurity protocols, complicate the implementation of uniform security measures across supply chain nodes. It is essential to consider this global context in our discussions and strategies. In conclusion, the interconnected nature of modern supply chains makes them susceptible to cyber threats. Understanding these risks and employing strategic measures can mitigate potential impacts and maintain robust supply chain operations. Comprehensive cybersecurity strategies and adherence to international regulations are essential to effectively managing and mitigating cyber risks globally.
Closing
In completing the SCMG 501 Week 6 Discussion: Cyber Vulnerabilities of Supply Chains, you will have developed a comprehensive understanding of the cyber vulnerabilities affecting supply chains and how to effectively assess and address these issues. The integration of robust cybersecurity measures is not merely a technical requirement but a strategic imperative that underpins the reliability and efficiency of global supply chain operations.
SCMG 501 WEEK 6 ASSIGNMENT THREE PAPER
Instructions for SCMG 501 Week 6 Assignment Three Papers
Course Objective:
- CO6: Diagnose cyber vulnerabilities of systems that support an organization’s supply chain.
Prompt:
Research recent cyber breaches that have occurred with different companies. Select a company that had a cyber breach and consider what happened and what could have been done differently (examples include Sony, Maersk, Saks, Lord & Taylor, Sacramento Bee, TicketFly, Panera, Facebook, Target, Under Armour, and Equifax). Given that cyber breaches are more common, write about the importance of cyber defenses and organizational hardening for an organization’s supply chain. In your paper, consider the government requirements that are currently in place and how these might apply to commercial organizations. Consider using the outline below to better focus your paper on this complex topic:
- Introduction
- Review and discuss the organization that had a cyber breach.
III. Explain the importance of cyber defenses as it relates to the cyber breach under discussion.
- Discuss the applicable government requirements.
- Conclusion
Instructions:
- Label your Word document as follows: yourlastname.docx (ex: Johnson.docx).
- Essay format; not bullet format
- Minimum 4 full pages of content (Word Document) of strategic material (does not include cover page, abstract, nor reference pages)
- All charts, graphs, and pictures are to go in the appendix (not a substitute for content).
- Resources and citations are formatted according to APA (6th edition) style and formatting.
- Refrain from excessive use of quotes in your response (less than 5%).
- Once you submit your document to the assignment folder it will automatically be loaded to TURNITIN.COM within the course. Your similarity scan score must be 20% or less (the following will be excluded: headers, bibliography, etc.) prior to the instructor grading the paper—focus on the content of the scan percentage
- Plagiarism will result in an automatic zero for this assignment.
Introduction to SCMG 501 Week 6 Assignment Three
This How-To SCMG 501 Guide is designed to assist you in understanding and analyzing the cyber vulnerabilities that can affect supply chain management systems. Through a focused examination of a past cyber breach, you will explore the vital role of cyber defenses and the implications of government regulations. The SCMG 501 Week 6 Assignment Three Paper is crucial for developing robust strategies to protect organizations against future cyber threats.
Cybersecurity and Supply Chain Management
To solve the SCMG 501 Week 6 Assignment Three Paper, we will establish the paper’s context and highlight cybersecurity’s relevance in supply chain management.
- Start with a general statement about the critical nature of cybersecurity in today’s interconnected world.
- Briefly mention a few high-profile breaches to set the stage for the detailed case study.
Example
In the modern global economy, the susceptibility of supply chains to cyber threats has become an urgent concern. As enterprises increasingly integrate their operations through digital platforms, the risk of cyber-attacks grows substantially. The infamous cyber breaches at major corporations such as Equifax, Target, and Sony illustrate that no organization is safe from such threats. These incidents highlight the severe consequences of cyber-attacks, which not only lead to the loss of sensitive information but also disrupt operations and the flow of goods along supply chains. This situation underscores the critical need for companies to implement stringent and effective cybersecurity measures to protect their assets and ensure continuous business operations.
Research recent cyber breaches that have occurred with different companies. Select a company that had a cyber breach and consider what happened and what could have been done differently (examples include Sony, Maersk, Saks, Lord & Taylor, Sacramento Bee, TicketFly, Panera, Facebook, Target, Under Armour, and Equifax).
Review and Discuss the Organization That Had a Cyber Breach
Here, we will provide a detailed case study of an organization that experienced a cyber breach.
I am choosing the SONY Cybersecurity Breach, April 2011.
- Choose an organization from the provided list based on its impact or the uniqueness of its breach.
- Summarize the incident, focusing on how it affected the organization’s operations.
Example
In the current digital landscape, cybersecurity emerges as a crucial priority for every organization, a fact starkly underscored by numerous high-profile cyberattacks, including the significant breach suffered by Sony in 2011 (Twingate, 2011). This incident had devastating effects, with around 77 million user accounts compromised, leading to the exposure of personal and financial information. The repercussions of this breach were severe, not only in terms of operational disruptions but also through extensive reputational damage and economic losses estimated in the millions (Quinn & Arthur, 2011).
Sony undertook a series of measures to strengthen their security framework in response to the crisis. The company revamped its cybersecurity protocols to seal the exploited vulnerabilities and took steps to mitigate the damage to its customers by offering free identity theft protection and credit monitoring services (Lee, 2014). These actions were essential in restoring customer trust and stabilizing the company’s standing in the market.
This incident highlights the critical need for organizations to maintain rigorous cybersecurity practices. It serves as a stark reminder of the potential consequences of security lapses and the importance of being prepared for and responsive to cyber threats. Effective cybersecurity is not a one-time setup but a continuous process of adaptation and improvement.
Organizations must implement comprehensive security strategies, including advanced technological defenses and thorough training programs for employees to recognize and respond to security threats. Regular audits, updates, and the implementation of stringent security policies are essential to safeguard sensitive data (REUTERS, 2011). Additionally, staying informed about the latest cybersecurity trends and threat vectors plays a crucial role in defending against evolving cyber threats.
The Sony breach teaches a valuable lesson on the necessity of proactive security measures and constant vigilance in monitoring security systems to prevent similar incidents. It also emphasizes that cybersecurity is a critical aspect of strategic management, vital for protecting not just the operational capabilities of a company but also its public image and relationships with stakeholders. In an increasingly digital world, the integrity of cybersecurity measures is fundamental to maintaining trust and confidence among consumers and partners.
Since cyber breaches are more common, write about the importance of cyber defenses and organizational hardening for an organization’s supply chain.
Importance of Cyber Defenses Concerning the Cyber Breach
For this section of the SCMG 501 Week 6 Assignment Three Paper, we will analyze the cyber defenses in place during the breach and propose enhancements.
- Discuss the pre-breach cyber defense measures and identify their shortcomings.
- Suggest realistic improvements or strategies that could have mitigated the breach.
Example
The Sony cyberattack highlights the urgent necessity for robust and preemptive cybersecurity measures. Before this breach, Sony’s cybersecurity protocols faced criticism for several glaring deficiencies, notably the lack of data encryption and the inadequate segmentation of network areas. These weaknesses allowed attackers to infiltrate critical segments of Sony’s infrastructure and access sensitive information.
To counteract such vulnerabilities, organizations must implement a multi-layered security approach. This involves consistently applying updates and patches to all system software to close any security loopholes that cybercriminals could exploit. Moreover, integrating sophisticated threat detection systems is essential for early identification and swift response to abnormal activities within the network, potentially preventing data breaches.
Additionally, the human element of cybersecurity cannot be overlooked. Regular and comprehensive training programs for employees on cybersecurity best practices are vital. Such education helps to minimize the risk of breaches caused by human error as employees learn to recognize and avoid common cyber threats. This combination of technological updates, advanced threat detection, and employee training forms the cornerstone of a proactive cybersecurity defense strategy, aiming to safeguard sensitive data against increasingly sophisticated cyberattacks.
In your paper, consider the government requirements currently in place and how they might apply to commercial organizations.
Applicable Government Requirements
Next, we will examine how government cybersecurity regulations apply to commercial organizations.
- Research and summarize the relevant government cybersecurity laws and regulations.
- Analyze their applicability to the chosen organization and suggest how compliance might be improved or could have prevented the breach.
Example
The Sony breach has brought to light the significant influence of government regulations on shaping corporate cybersecurity strategies. In the United States, many regulations and standards are in place to direct the establishment and maintenance of cyber defenses (Lee, 2014). The Cybersecurity Framework developed by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) stands out. This set of guidelines offers a comprehensive strategy for managing and minimizing cybersecurity risks, particularly critical infrastructure.
For companies like Sony, complying with these regulatory frameworks is crucial. Not only does adherence enhance their cybersecurity measures, but it also ensures they meet legal standards that could reduce potential liabilities in the aftermath of a cyber incident. The implications of these regulations extend beyond mere compliance; they also influence the public’s perception of the company. A solid commitment to cybersecurity signaled through adherence to such standards can significantly bolster a company’s reputation in the marketplace.
Given the dynamic nature of cyber threats, corporations must continually assess and update their cybersecurity protocols. Staying aligned with evolving standards like those proposed by NIST is not just about asset protection; it is a critical component of strategic risk management (Quinn & Arthur, 2011). Companies must proactively integrate these guidelines into their security strategies to safeguard against the ever-growing spectrum of cyber threats. This continuous alignment protects the companies and assures customers and stakeholders of their commitment to maintaining high standards of security and trustworthiness.
Conclusion
- Summarize the main insights from the analysis and reinforce the importance of proactive security measures.
- Recap the key points discussed in the paper. Emphasize the need for ongoing vigilance and adaptation of cybersecurity strategies in the face of evolving threats.
Example
The Sony cyber breach analysis uncovers a complex scenario marked by insufficient defenses, advanced cyber-attack tactics, and the crucial importance of regulatory compliance. This case study underscores organizations’ need to adopt a forward-thinking approach to cybersecurity. This includes regular system updates, comprehensive employee training, and strict adherence to regulatory frameworks.
As the landscape of cyber threats continues to shift and evolve, corporate strategies must adapt continually to counter these threats. Cybersecurity must be seen not merely as a technical safeguard but as an integral component of a company’s strategic management. This proactive stance is crucial for protecting critical operations and preserving stakeholders’ trust in an environment where digital interactions are increasingly common.
Closing
This How-To Owlisdom Guide provides a structured approach to understanding the complexities of cybersecurity within supply chain management. By dissecting a real-world incident and exploring related defenses and regulations, students will gain a deeper appreciation for the necessity of comprehensive cyber defenses. Proactively managing these vulnerabilities is beneficial and essential for safeguarding modern supply chains’ operational integrity.
References
Lee, T. B. (2014, December 14). The Sony hack: How it happened, who is responsible, and what we have learned. Vox. https://www.vox.com/2014/12/14/7387945/sony-hack-explained
Quinn, B., & Arthur, C. (2011, April 26). PlayStation Network hackers accessed data of 77 million users. The Guardian. https://www.theguardian.com/technology/2011/apr/26/playstation-network-hackers-data
REUTERS. (2011, April 27). Sony PlayStation suffers a massive data breach. Reuters. https://www.reuters.com/article/idUSTRE73P6WB/
Twingate. (2011). What happened in the Sony data breach? | Twingate. https://www.twingate.com/blog/tips/sony-data-breach
SCMG 501 WEEK 7 DISCUSSION: New Technology in Supply Chain Management
Instructions for SCMG 501 Week 7 Discussion
Course Objective:
- CO7: Analyze new technology that will change the current paradigm of logistics of existing supply chains.
Prompt:
Discuss the pros and cons regarding app-based technology such as Uber Freight and how these kinds of solutions will impact and reduce cycle time within a supply chain. Offer evidence and support for your position, and consider how this will disrupt existing global business. In addition to reading your assigned resources for week 7, research online new technologies in supply chain management.
Introduction to SCMG 501 Week 7 Discussion
This How-To SCMG 501 Guide is designed to assist you in analyzing how emerging technologies, particularly app-based solutions like Uber Freight, transform the logistics of traditional supply chains. It will provide a structured approach to evaluate the advantages and disadvantages of these technologies and their potential to disrupt existing global business models.
Analyze new technology that will change the current logistics paradigm of existing supply chains.
New Technologies in Supply Chain Management
Briefly define what constitutes ‘new technology’ in the context of supply chain management.
- Highlight the relevance of innovation in logistics and its critical role in enhancing efficiency.
- Identifying Technologies: Research and list technologies that have recently altered supply chain dynamics.
- Evaluating Impact on Current Logistics: Discuss how these technologies have changed or could change logistical processes.
Example
In the context of supply chain management, ‘new technology’ refers to innovative tools and software designed to optimize supply chains’ logistics and operational efficiencies. These technologies can dramatically alter the traditional paradigms of supply chains by introducing more streamlined, real-time methods of managing the flow of goods and information.
Innovations like blockchain, artificial intelligence (AI), and advanced analytics are vital in revolutionizing supply chain dynamics. Blockchain technology, for instance, enhances transparency and security, enabling more reliable tracking of shipments and transactions. AI contributes to predictive analytics for inventory and demand forecasting, significantly reducing overstock and understock scenarios. The impact of these technologies on logistics is profound, offering enhanced accuracy in supply chain operations and facilitating quicker decision-making processes.
Discuss the pros and cons of app-based technology, such as Uber Freight and how these solutions will impact and reduce cycle time within a supply chain.
Pros and Cons of App-Based Technology in Logistics Case Study: Uber Freight
This section of the Week 7 Discussion will discuss app-based logistics technologies and how they operate. We will also provide a summary of Uber Freight and its business model.
- Assessing Benefits: Outline the key benefits, such as increased efficiency, reduced costs, and enhanced tracking capabilities.
- Identifying Drawbacks: Consider issues such as dependency on technology, privacy concerns, and potential job displacement.
- Instruct on how to find and use data to support claims about technology impacts.
- Impact on Supply Chain Cycle Time: Analyze how Uber Freight has reduced cycle times within supply chains.
- Comparative Analysis with Traditional Logistics: Compare the efficiency of Uber Freight with traditional logistics methods.
- Citing Case Studies and Research: Emphasize using credible sources and case studies to substantiate arguments.
Example
Uber Freight, an app-based logistics solution, exemplifies how digital platforms can transform traditional freight logistics. This platform connects truck drivers with shippers, allowing for real-time booking of freight services, which reduces cycle times and increases operational efficiencies.
Benefits:
Increased Efficiency: Uber Freight’s platform allows for immediate booking, reducing waiting times and speeding up the overall shipping process.
Reduced Costs: By optimizing truck routes and loads, Uber Freight minimizes empty miles driven, directly translating to fuel cost savings.
Enhanced Tracking Capabilities: Real-time GPS tracking ensures shippers can constantly monitor their freight, strengthening the security and reliability of shipments.
Drawbacks:
Dependency on Technology: Heavy reliance on digital platforms raises concerns about operational hiccups in the event of technical failures.
Privacy Concerns: The extensive data collected by these platforms pose significant privacy issues, necessitating robust cybersecurity measures.
Potential Job Displacement: Automation and platform-based logistics could reduce the need for traditional logistical roles, potentially leading to job losses.
Uber Freight has notably reduced cycle times by simplifying the connection between shippers and drivers, streamlining the shipping process. Uber Freight’s direct model offers a more efficient and less cumbersome alternative than traditional logistics methods, which often involve multiple intermediaries and manual booking processes.
Offer evidence and support for your position and consider how this will disrupt existing global business.
Disruption in Global Business
Here, we will explore the disruption in Global Business due to such technologies.
- Analyzing Market Disruption: Discuss how these technologies disrupt existing markets and business models.
- Projecting Future Trends: Speculate how these technologies might evolve and impact global supply chains.
Example
App-based technologies like Uber Freight disrupt traditional business models by introducing more agile and customer-centric solutions. These technologies democratize the logistics industry, allowing smaller shippers to compete on a larger scale. However, this disruption also forces traditional logistics companies to innovate or face obsolescence.
The evolution of these technologies might lead to more integrated global supply chains where digital platforms dominate, further reducing human error and inefficiencies. This technological progression will likely continue to disrupt existing markets, pushing companies to adapt or innovate.
Key Takeaways
This last section of the SCMG 501 Week 7 Discussion will summarize the key takeaways from this discussion post.
- Summarize the major points discussed.
- Emphasize the importance of understanding the opportunities and challenges new technologies present in supply chain management.
Example
This analysis underscores new technologies’ significant impacts and potential in transforming supply chain management. While offering numerous benefits such as efficiency and cost reduction, these technologies also introduce challenges like dependency and potential job displacement. Understanding both the opportunities and challenges of these technologies is crucial for businesses aiming to thrive in the digitized global market landscape.
Closing
In conclusion, the SCMG 501 Week 7 Discussion: New Technology in Supply Chain Management probes into the transformative potential of new technologies on supply chains, focusing on app-based solutions like Uber Freight. By understanding this How-To Owlisdom Guide, you can better anticipate and leverage changes in logistics and global business landscapes, ensuring they are well-prepared for the industry’s evolving demands.
SCMG 501 WEEK 8 DISCUSSION: Most Important Concept of the Class
Instructions for SCMG 501 Week 8 Discussion
Prompt:
Select one of the most important concepts you learned in this course and share how it impacted your perception of supply chain management. Consider how you plan to apply this new knowledge to the field of supply chain management. In addition to reading your assigned resources for week 8, research your favorite concept from the class.
Introduction to SCMG Week 8 Discussion
This How-To SCMG 501 Guide is designed to assist you in synthesizing and applying critical concepts from their study of supply chain management. By focusing on a key concept, you will reflect on how their understanding of the field has evolved and plan practical applications of their knowledge. The SCMG 501 Week 8 Discussion: The most Important Concept of the Class is crucial for bridging theoretical learning with practical industry demands.
Select one of the most important concepts you learned in this course and share how it impacted your perception of supply chain management.
Selection of a Key Concept
To start the SCMG 501 Week 8 Discussion: Most Important Concept of the Class, we will select a concept we like most in the Technology in Supply Chain Management course. I am choosing the Cybersecurity Vulnerabilities of Supply Chains.
- Criteria for Choosing a Concept: Identify concepts repeatedly emphasized throughout the course or that have had significant industry impact.
- Justification for Its Importance: Explain why this concept is critical in current supply chain challenges and opportunities.
Example
Cybersecurity vulnerabilities stand out among the various concepts covered in the course due to their increasing relevance in today’s digital and interconnected supply chain environments. This concept has been chosen because it is critical to protecting information and operational technologies across the supply chain from malicious attacks and disruptions. Cybersecurity vulnerabilities pose significant risks, including the potential for data breaches, operational disruptions, and financial losses. Given the growing reliance on digital platforms for supply chain management, understanding and mitigating these vulnerabilities is essential for ensuring the continuity and security of supply chain operations.
Impact on Perception of Supply Chain Management
Next, we will explore the impact of cybersecurity vulnerabilities on the perception of supply chain management.
- Personal Insights Gained: Describe how learning this concept has altered or enhanced your understanding of supply chain operations.
- Change in Understanding or Approach: Reflect on how this concept might influence your professional behavior or strategic thinking in supply chain roles.
Example
Learning about cybersecurity vulnerabilities has dramatically shifted my perspective on supply chain management. It highlighted the fragility of digital infrastructures and the need for robust security measures to protect these systems. This concept has instilled a proactive mindset towards security in supply chain management, emphasizing the importance of integrating cybersecurity strategies from the outset rather than as an afterthought.
Consider how you plan to apply this new knowledge to supply chain management.
Application of the Concept in Real-World Scenarios
This section of the SCMG 501 Week 8 Discussion: Most Important Concept of the Class will discuss the application of Cybersecurity Vulnerabilities in Supply Chain in real-world scenarios.
- Planning for Implementation: Outline how to incorporate this concept into your current or future job roles. Consider specific strategies or projects where this knowledge could be applied.
- Potential Challenges and Solutions: Anticipate any obstacles to implementing this concept and propose viable solutions or preventative strategies.
Example
To effectively apply this knowledge, I plan to advocate for and participate in developing comprehensive cybersecurity policies within my organization. This would include routine security assessments, implementing secure software and hardware, and creating a responsive action plan for potential cyber threats. One major challenge is the resistance to change and the allocation of resources for cybersecurity initiatives. To address this, I would demonstrate the potential financial and reputational risks of ignoring cybersecurity vulnerabilities, using recent industry examples of security breaches. Additionally, promoting a culture of security awareness through training and regular updates can help mitigate these risks.
Continual Learning and Adaptation
Next, we will discuss continual learning and adaptation.
- Keeping Updated with Industry Changes: Discuss the importance of staying informed about new technologies, methodologies, and supply chain management trends that could affect your chosen concept’s application.
- Engaging with Ongoing Professional Development: Recommend ways to continue developing your understanding and application of this concept through further education, certifications, or professional networking.
Example
Cybersecurity is a rapidly evolving field. It is crucial to stay updated with the latest security technologies, threats, and mitigation strategies. I plan to subscribe to relevant journals, attend workshops, and participate in webinars that focus on these developments.
I aim to pursue certifications such as Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP) or Certified Information Security Manager (CISM) to further my expertise. These credentials will enhance my knowledge and solidify my commitment to maintaining high-security standards in supply chain management.
The study of cybersecurity vulnerabilities in supply chains has been an enlightening experience, underscoring the critical need for integrated security measures in today’s digital-first business environment. This concept has prepared me to address security challenges within the supply chain better and advocate for comprehensive cybersecurity practices that can protect organizational assets and ensure operational continuity. Through continual learning and adaptation, I am committed to remaining at the forefront of cybersecurity advancements to manage and mitigate risks in the supply chain sector effectively.
Closing
In conclusion, selecting, analyzing, and planning the application of a critical concept in supply chain management solidifies your learning and prepares you for practical challenges in the industry. The SCMG 501 Week 8 Discussion: Most Important Concept of the Class emphasizes the importance of continual learning and adaptation in a rapidly evolving field. By following this How-To Owlisdom Guide, you will be better equipped to translate academic concepts into effective professional practices, enhancing their personal development and impact on the organizations you serve.
SCMG 501 WEEK 8 ASSIGNMENT FOUR
Instructions of SCMG 501 Week 8 Assignment Four
Course Objective:
- CO7: Analyze new technology that will change the current paradigm of logistics of existing supply chains.
Prompt:
Given all that has been covered in the class, what is the top supply chain issue for the future? Consider areas of exploration such as cybersecurity, disruptive technology, app-based solutions, or some combination of these areas. Write a minimum of a 10-page comprehensive paper (not including a cover page or reference section) that is researched and supported about technology in supply chain management. The focus can either be commercial, military, or government. The paper should address at a minimum the following topics:
- Introduce and define the focus area(s) and explain if it will focus on commercial, military, or government aspects of supply chain management.
- Explain the current uses of this technology in the military, in business, or within government.
- Explain the three best arguments that support the use of this technology(s) within your chosen area.
- Discuss possible shortcomings, limitations, or other factors that might keep a company from adopting this new solution.
- Discuss the operational, financial, and other ramifications of adopting this technology.
- Conclusion
Instructions:
- Label your Word document as follows: yourlastname.doc (ex: Johnson.docx).
- Essay format, not bullet format
- Minimum 10 full pages of content (Word Document) of strategic material (does not include a cover page, abstract, or reference pages)
- All charts, graphs, and pictures are to go in the appendix (not a substitute for content).
- Resources and citations are formatted according to APA (6th edition) style and formatting.
- Refrain from excessive use of quotes in your response (less than 5%).
- Once you submit your document to the assignment folder, it will automatically be loaded to TURNITIN.COM within the course. Your similarity scan score must be 20% or less (the following will be excluded: headers, bibliography, etc.) prior to the instructor grading the paper—focus on the content of the scan percentage
- Plagiarism will result in an automatic zero for this assignment.
- There are no late assignments accepted after the last day of the course.
Step-By-Step Guide SCMG 501 Week 8 Assignment Four
Introduction to SCMG 501 Week 8 Assignment
This How-To SCMG 501 Guide is designed to assist students in developing a well-researched and comprehensive paper that delves into the impact of new technologies on supply chain management. The paper will scrutinize how these technologies have the potential to reshape the current logistics paradigms within commercial, military, or government sectors. The SCMG 501 Week 8 Assignment Four will prompt a thorough exploration of the chosen technology’s current applications, its benefits, potential limitations, and the overall impact on the selected area of focus. The chosen technology is not just a topic of interest, but a crucial aspect of the evolving supply chain landscape.
Introduce and define the focus area(s) and explain if it will focus on commercial, military, or government aspects of supply chain management.
Supply Chain Issue For The Future
To start the SCMG 501 Week 8 Assignment Four, we will choose a focus area for this paper. I am choosing to analyze new technology that will change the current logistics paradigm of Commercial supply chains.
- Choosing the Focus Area: The first step is to decide whether the paper will concentrate on commercial, military, or government supply chains. It’s important to define the scope clearly to avoid any ambiguity in the research.
- Setting the Context: Introduce the chosen technology and explain its relevance to the selected focus area. Provide a brief overview of how it fits into the broader trends in supply chain management.
Example
The integration of new technologies has a transformative potential in supply chain management, particularly within commercial sectors. This paper will explore how emerging technologies are set to revamp the current logistics paradigms of commercial supply chains. The focus is on how these technologies align with and propel the evolution of supply chain management practices, underscoring the significance and impact of your research.
The chosen area of focus for this analysis is commercial supply chains, a sector where integrating advanced technologies can significantly enhance operational efficiency and responsiveness. As commercial enterprises increasingly rely on globalized supply networks, the need for sophisticated technological solutions to manage these complexities becomes paramount. This underscores the real-world relevance and importance of your research. (Yang et al., 2021). Technologies such as blockchain, artificial intelligence (AI), and the Internet of Things (IoT) are particularly relevant, offering new ways to optimize and secure logistics from end to end.
Explain the current uses of this technology in the military, business, or government.
Current Uses of Technology
Next, we will discuss the current uses of the technology.
- Overview of Technological Integration: Describe how the technology is currently integrated into the operations of the chosen sector.
- Specific Examples: Provide detailed examples of current uses, citing real-world applications, highlighting the technology’s role in enhancing supply chain operations.
Example
In today’s dynamic market environment, integrating advanced technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT) revolutionizes commercial supply chain operations. AI is increasingly employed to refine demand forecasting and inventory management, enabling companies to adapt swiftly and accurately to market fluctuations. This predictive capability allows businesses to anticipate demand and optimize inventory levels, reducing overstock and stockouts, thereby enhancing operational efficiency (Tiwari, 2021).
Simultaneously, IoT technology is transforming asset tracking and management within supply chains. IoT devices are deployed extensively to monitor the real-time status and condition of goods throughout transit. This technology ensures that parameters such as temperature and humidity are maintained within safe limits, safeguarding the quality of sensitive products. Major retail chains, for instance, leverage IoT to continuously track shipments, ensuring that products meet rigorous safety standards upon delivery.
Furthermore, AI enhances customer service by automating interactions and providing timely updates on orders and shipments. It also plays a crucial role in the logistical aspect of supply chains by optimizing the routing of delivery vehicles (Yang et al., 2021). This optimization is based on real-time data analysis of traffic patterns, significantly improving delivery times and reducing operational costs by minimizing delays and fuel consumption. Together, AI and IoT enhance the efficiency and transparency of supply chain operations and contribute to higher customer satisfaction and compliance with regulatory standards.
Explain the three best arguments that support using these technologies (s) within your chosen area.
Arguments Supporting the Technology
For this section of the SCMG 501 Week 8 Assignment Four, we will discuss three arguments that support our choice of focus area.
- Strongest Points in Favor: Develop three compelling arguments advocating using the technology within the selected focus area.
- Evidence and Case Studies: Support each argument with relevant research, data, and case studies demonstrating the technology’s effectiveness and benefits.
Example
The integration of advanced technologies such as AI, blockchain, and IoT presents compelling arguments for their adoption within supply chain management, primarily due to their substantial operational efficiencies (Younis et al., 2022). AI-driven analytics exemplify this through their ability to process and analyze large datasets rapidly. This capability allows businesses to optimize delivery routes, efficiently manage inventory, and accurately forecast demand trends. The result is a significant reduction in operational waste and a marked increase in the agility of supply chain responses to market changes.
In addition to AI, blockchain technology offers critical advantages in enhancing data integrity and security across complex supply networks. Blockchain’s immutable nature creates a tamper-proof ledger, essential for transparent contract management and rigorous compliance tracking. This technology fosters trust among stakeholders by ensuring that all transactions are verifiable and secure.
Furthermore, IoT technology plays a pivotal role in refining real-time decision-making processes. By enabling dynamic operations management, IoT devices provide continuous data flow, which helps make informed decisions swiftly, adapting to operational needs as they arise. For instance, Amazon’s utilization of AI for inventory and logistics optimization showcases how these technologies can dramatically boost operational efficiency and improve overall customer satisfaction. Through real-time data processing and enhanced transparency, these technological tools streamline operations and significantly elevate the customer experience in supply chain management.
Discuss possible shortcomings, limitations, or other factors that might keep a company from adopting this new solution.
Challenges and Limitations
Here, we will explore the challenges and limitations of the chosen focus area and new technologies.
- Identifying Potential Shortcomings: Discuss any known issues, limitations, or challenges that could hinder the adoption of the technology.
- Analysis of Barriers to Adoption: Explore why companies or sectors might be reluctant to adopt this technology, considering cost, complexity, or compatibility with existing systems.
Example
Despite the clear benefits, adopting cutting-edge technologies within commercial supply chains encounters notable obstacles. One of the primary challenges is the significant financial investment required to implement these advanced technologies. This high cost can be particularly prohibitive for small to medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), often deterring them from adopting innovations that could fundamentally improve their operations. The initial expenditure for technology such as AI, blockchain, or IoT includes the cost of the technology itself and the infrastructure needed to support it.
Moreover, the complexity involved in integrating these new technologies with existing systems poses another substantial challenge. This integration often necessitates extensive change management strategies and comprehensive employee training programs to ensure a smooth transition. Without proper integration, the potential benefits of these technologies can be undermined by inefficiencies or malfunctions in the workflow (Younis et al., 2022).
Furthermore, compatibility issues frequently arise when attempting to mesh advanced technologies with older, legacy systems. These issues can lead to operational disruptions, affect daily activities, and result in a steep learning curve for employees who must adapt to new interfaces and procedures. The time and resources required to resolve these compatibility issues can significantly delay the realization of benefits from new technological investments, adding another layer of complexity to the decision-making process for technology adoption in supply chains.
Discuss the operational, financial, and other ramifications of adopting this technology.
Ramifications of Adopting the Technology
We will explore the ramifications of adopting the technology in our chosen focus area for this segment.
- Operational Impacts: Analyze how introducing this technology could change operational practices.
- Financial Impacts: Consider the financial implications, including initial investment, potential savings, and ROI.
- Additional Considerations: Discuss any other impacts, such as regulatory, ethical, or social ramifications.
Example
Integrating advanced technologies like AI and IoT into commercial supply chains can dramatically streamline operational processes, minimize human error, and bolster data-driven decision-making (Younis et al., 2022). These improvements enhance the speed and accuracy of supply chain operations and significantly reduce costs associated with inefficiencies and errors. While the initial financial outlay for these technologies can be substantial, the long-term benefits—manifested in heightened efficiency and superior customer service—often result in a significant return on investment, making it financially viable over time.
However, adopting these technologies also brings a host of regulatory, ethical, and social considerations that companies must address (Tiwari, 2021).. Data privacy becomes increasingly pertinent as more data is collected and analyzed, necessitating stringent compliance with data protection laws. Additionally, the rise of automation and AI can impact employment, potentially leading to job displacement. Companies must navigate these challenges thoughtfully, balancing technological advancements with responsible practices to mitigate adverse effects on the workforce and society.
Conclusion
For this section of the SCMG 501 Week 8 Assignment Four, we will summarize all the key takeaways.
- Summary of Key Findings: Recap the main points and findings from the paper.
- Final Thoughts and Recommendations: Offer a concluding perspective on the future role of the technology in the chosen sector and provide recommendations based on the research conducted.
Example
In conclusion, adopting emerging technologies in commercial supply chains presents substantial opportunities and notable challenges. The benefits of improved efficiency, enhanced transparency, and increased security are compelling arguments for their integration. However, the challenges of high costs, complexity, and the need for compatibility with existing systems must be carefully managed. Looking ahead, companies should continue to monitor technological advancements and consider strategic investments in technology to stay competitive in the evolving market landscape. This paper recommends ongoing research and development in technological solutions alongside a strategic approach to technology adoption, ensuring that commercial supply chains can adapt to and thrive in the digital age.
Closing
The SCMG 501 Week 8 Assignment Four not only allows for an in-depth analysis of cutting-edge technology in supply chain management but also challenges students to critically evaluate its potential impacts and issues. Following this How-To Owlisdom Guide, the paper will provide valuable insights into the evolving supply chain management landscape and prepare students to think strategically about future technological integrations in their respective fields.
References
Tiwari, S. (2021). Supply chain integration and Industry 4.0: A systematic literature review. Benchmarking: An International Journal, 28(3), 990–1030.
Yang, M., Fu, M., & Zhang, Z. (2021). Adopting digital technologies in supply chains: Drivers, process and impact. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 169, 120795.
Younis, H., Sundarakani, B., & Alsharairi, M. (2022). Artificial intelligence and machine learning applications within supply chains: Systematic review and future research directions. Journal of Modelling in Management, 17(3), 916–940.




