QSO-321 – Guide to People, Planet, and Profit: Understanding Sustainability, Ethics, and Strategic Business Growth
Published: 2025-10-09
Modified: 2025-10-09
Samples Solutions
- QSO321 1‑2 Discussion Solution
- QSO‑321 1‑3 Assignment Solution
- QSO‑321 2‑2 Discussion Solution
- QSO‑321 3‑2 Discussion Solution
- QSO‑321 3‑3 Assignment Solution
- QSO‑321 4‑2 Discussion Solution
- QSO‑321 4‑3 Assignment Solution
- QSO‑321 5‑2 Discussion Solution
- QSO‑321 5‑3 Assignment Solution
- QSO‑321 6‑2 Discussion Solution
- QSO‑321 6‑3 Assignment Solution
- QSO‑321 7‑2 Project Solution
- QSO‑321 8 Solution Template
Introduction
QSO 321 – People, Planet, and Profit focuses on how businesses align social responsibility, environmental stewardship, and financial performance. The course explores sustainability models and ethical decision-making in corporate settings. For support with sustainability case studies or management projects, visit Owlisdom’s MBA Assignment Help.
QSO 321 1-2 Discussion: Is the Triple Bottom Line That Important?
Instructions of QSO 321 1-2 Discussion
1-2 Discussion: Is the Triple Bottom Line That Important?
First, introduce yourself to the class. Include your major and anything you would like to share about yourself. Then address the prompt below.
In your textbook, you learned about the triple-bottom-line (TBL) framework and its impact on people, planet,
and profit. The TBL concept was initially developed by John Elkington in 1994. In 2018, Elkington wrote an article
titled “25 Years Ago I Coined the Phrase ‘Triple Bottom Line’: Here’s Why It’s Time to
Rethink It”. He used the article as a call to strengthen how the TBL is used and to put even more focus on
sustainability and less on profit. In the article, he states:
However, success or failure in sustainability goals cannot be measured only in terms of profit and loss. It must also be measured in terms of the well-being of billions of people and the health of our planet, and the sustainability sector’s record in moving the needle on those goals has been decidedly mixed. While there have been successes, our climate, water resources, oceans, forests, soils, and biodiversity are all increasingly threatened. It is time to either step up or get out of the way.
Meanwhile, some believe that incorporating this framework into practice raises more questions than it resolves, especially around reporting, regulation, and a deviation from the financial bottom line of businesses.
In your initial post, introduce yourself and then address the following questions:
- Do you think that it is the responsibility of businesses to track and manage the social, economic, and environmental impacts of their actions? Why or why not?
- What value does using the TBL bring to a business, and is it worth the potential drawbacks of incorporating it?
- What value do businesses using the TBL bring to society, and how might society be impacted if TBL were not a common business practice?
In your replies to at least two peers, use the questions below to guide your discussion. Make sure to cite any evidence you use to support your ideas.
- Do you agree or disagree with your peer’s initial post? Why or why not?
- What examples from the textbook or outside resources (such as news articles) support or dispute your peer’s stance, and how?
- Did your peer provide any insight or information that changed your opinion about the TBL? If so, how?
To complete this assignment, review the Discussion Rubric.
Introduction to QSO 321 1-2 Discussion
Welcome to this How-To QSO 321 Guide of QSO 321 1-2 Discussion: Is the Triple Bottom Line That Important? post. This talk will discuss whether the triple bottom line is essential. I will provide brief and descriptive guidelines to solve the Discussion posts, Assignments, and Projects of QSO 321, along with a dummy solution for each task. This Owlisdom How-To Guide will equip you with strategies and insights to tackle all the queries related to the Triple Bottom Line. Let us begin with the guide.
Is it the responsibility of businesses to track and manage the social, economic, and environmental impacts of their actions? Why or why not?
Understanding TBL
For the QSO 321 1-2 Discussion: Is the Triple Bottom Line That Important? we need to give a brief introduction. Then, address the importance and history of TBL.
- TBL is the framework that encourages businesses to prioritize social, environmental, and financial responsibilities equally.
- Explain why it is essential for sustainable development.
- Provide a brief history of TBL’s development.
Example
My name is Alex, and I am thrilled to participate in this insightful journey into the People, Planet, and Profit course. My background is in environmental science, and I am deeply passionate about sustainable business practices that benefit the economy, our society, and the environment.
Businesses are responsible for tracking and managing their social, economic, and environmental impacts. In an era where sustainability is increasingly becoming a global priority, businesses have a pivotal role in fostering a sustainable future.
The Triple Bottom Line (TBL) framework, conceived by John Elkington in 1994, revolutionized how businesses approach sustainability by emphasizing social, environmental, and financial responsibilities equally (Zaharia & Zaharia, 2021). This innovative framework ensures that companies’ operations benefit the economy, society, and the environment, supporting sustainable development. Elkington’s call in his 2018 article (Tate & Bals, 2018) to revisit and reinforce the TBL framework underscores its ongoing relevance and the need for businesses to intensify their commitment to sustainability. By advocating for a balance between economic growth, ecological preservation, and social equity, TBL remains a crucial blueprint for businesses aspiring to contribute positively to our world’s future.
What value does using the TBL bring to a business, and is it worth the potential drawbacks of incorporating it?
Value of TBL to Businesses
In this section of QSO 321 1-2 Discussion: Is the Triple Bottom Line That Important? we will discuss the value of TBL concerning businesses.
- Benefits of Incorporating TBL: List the advantages businesses gain by implementing TBL, such as improved reputation, customer loyalty, and long-term sustainability.
- Potential Drawbacks: Mention TBL’s challenges and potential drawbacks, like increased costs and complexity in business operations.
Example
Utilizing the Triple Bottom Line (TBL) approach offers immense value to businesses. It encourages companies to go beyond the traditional financial metrics and incorporate social and environmental considerations into their decision-making process. This holistic approach not only aids in sustainable development but also enhances brand reputation, customer loyalty, and innovation. While incorporating TBL might present challenges, such as increased operational costs and complexity in balancing competing interests, the long-term benefits of sustainable practices outweigh these potential drawbacks.
What value do businesses using the TBL bring to society, and how might society be impacted if TBL were not a standard business practice?
TBL’s Contribution to Society
This section of QSO 321 1-2 Discussion: Is the Triple Bottom Line That Important? will explore how TBL’s contributions impact society.
- Societal Impacts: Describe how using TBL benefits society, including enhanced well-being of communities and conservation of natural resources.
- Consequences of Ignoring TBL: Discuss what might happen if businesses neglect TBL principles, focusing on environmental degradation and social inequality.
Example
Businesses that embrace the TBL contribute significantly to society by ensuring that economic growth does not come at the expense of environmental degradation and social inequality. They help build resilient communities, conserve natural resources for future generations, and create equitable opportunities for all. If TBL were not a common practice, society could face heightened environmental crises, widened social disparities, and unstable economies.
Do you agree or disagree with your peer’s initial post? Why or why not? What examples from the textbook or outside resources (such as news articles) support or dispute your peer’s stance, and how? Did your peer provide insight or information that changed your opinion about TBL? If so, how?
Engaging in Peer Discussions
Engaging and responding to peers is vital, too. Follow the guidelines below for the peer responses in the QSO 321 1-2 Discussion: Is the Triple Bottom Line That Important?
- Agreeing or Disagreeing with Peers: When responding to peers, clearly state whether you agree or disagree with their viewpoint and why. Use specific arguments and examples to support your position.
- Supporting Your Stance with Examples: Provide examples from the textbook or external sources to support your arguments or challenge your peer’s stance.
- Reflecting on New Insights: Share if and how your peer’s perspective influenced your understanding of TBL. Mention any new information or insight that changed or reinforced your opinion.
Response
I read your post with great interest, and while I agree with many of your points, I have a different perspective on the potential challenges of implementing TBL (Burgess & Matar, 2023). You mentioned that the complexity and costs could deter businesses from adopting this model. However, examples, like the one by the Harvard Business Review titled “The Comprehensive Business Case for Sustainability” (Yadav & Mankavil Kovil Veettil, 2021) illustrate that companies integrating TBL principles often see a return on investment through enhanced brand loyalty, innovation, and risk management. This evidence suggests that the perceived drawbacks can be mitigated with strategic planning and a commitment to long-term goals. Your insights on the importance of TBL in driving social and environmental change were enlightening and reinforced my belief in adopting sustainable business practices.
Closing
By following QSO 321 1-2 Discussion: Is the Triple Bottom Line That Important? guide, students will be able to effectively engage with the concept of the Triple Bottom Line, understand its significance, and apply it in discussions and real-world contexts. This approach prepares you for academic success and equips you with a sustainable mindset for future business practices.
I hope you nail the QSO 321 1-2 Discussion post. Good luck! You can also read our next module, QSO 321 1-3 Assignment: Triple Bottom Line Industry Comparison.
References
Burgess, A., & Matar, E. (2023). Team-Based Learning (TBL): Theory, Planning, Practice, and Implementation. In D. Nestel, G. Reedy, L. McKenna, & S. Gough (Eds.), Clinical Education for the Health Professions: Theory and Practice (pp. 1325–1353). Springer Nature. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-3344-0_128
Tate, W. L., & Bals, L. (2018). Achieving Shared Triple Bottom Line (TBL) Value Creation: Toward a Social Resource-Based View (SRBV) of the Firm. Journal of Business Ethics, 152(3), 803–826. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10551-016-3344-y
Yadav, N., & Mankavil Kovil Veettil, N. (2021). Developing a comprehensive business case for sustainability: An inductive study. International Journal of Organizational Analysis, 30(6), 1335–1358. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJOA-04-2020-2146
Zaharia, R. M., & Zaharia, R. (2021). Triple Bottom Line. In D. Crowther & S. Seifi (Eds.), The Palgrave Handbook of Corporate Social Responsibility (pp. 75–101). Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-42465-7_2
QSO 321 1-3 Assignment: Triple Bottom Line Industry Comparison
Instructions for QSO 321 1-3 Assignment
1-3 Assignment: Triple Bottom Line Industry Comparison
Overview
In this module, you have learned about the benefits, drawbacks, and overall value of using the triple bottom line (TBL) in business. In this assignment, you will take a closer look at how strategies for incorporating this framework are similar and different across the manufacturing industry and the service industry.
Prompt
Imagine you are a sustainability consultant, and you’ve been asked to create a simple handout that clarifies the similarities and differences between strategies used to incorporate the TBL into the manufacturing industry and the service industry. The handout will be provided to individuals at large and small group trainings.
Specifically, you must address the following rubric criteria:
- Similarities: Explain the similarities that exist between incorporating the TBL framework into both the service industry and the manufacturing industry, and why.
- Differences: Explain the differences that exist between incorporating the TBL framework into the service industry and the manufacturing industry, and why.
- Example Strategies: Provide an example of a strategy that is appropriate to use across both the service and the manufacturing industries, and provide an example that is specific to either the service or the manufacturing industry when considering people, planet, or profit through the TBL framework. Include a brief explanation of what each example demonstrates.
Guidelines for Submission
Submit this assignment as a 350- to 500-word Word document. Use the course resource or external resources to support your comparisons. Sources should be cited according to APA style.
Introduction to QSO 321 1-3 Assignment
In QSO 321 1-3 Assignment: Triple Bottom Line Industry Comparison, we will briefly explain Triple Bottom Line as a sustainability framework emphasizing equal importance on People, the Planet, and Profit. This QSO 321 How-to guide will help you efficiently do your assignment.
Similarities: Explain the similarities between incorporating the TBL framework into the service and manufacturing industries and why.
Similarities in TBL Application
After briefly introducing the QSO 321 1-3 Assignment: Triple Bottom Line Industry Comparison, we will discuss the similarities in TBL applications.
- Discuss how both industries aim to reduce waste, enhance community engagement, and improve environmental stewardshipwhile remaining profitable.
- Highlight the importance of corporate social responsibility (CSR) programs that benefit employees and local communities as a common strategy.
Example
The manufacturing and service industries strive to minimize waste, engage with communities, and enhance environmental stewardship while maintaining profitability. Corporate Social Responsibility (Radzi et al., 2020) programs play a crucial role in this endeavor, focusing on improving the well-being of employees and the communities in which they operate, thus benefiting both sectors.
Differences in TBL Application
Let us discuss the differences in TBL applications.
- Explain how the manufacturing industry focuses more on environmental impacts due to its resource-intensive nature, while the service industry prioritizes social aspects like employee welfare and customer satisfaction.
- Point out the difference in measuring the environmental footprint, with manufacturing looking at production processes and service industries focusing on office operations and indirect activities.
Example
The manufacturing industry, being resource-intensive, concentrates more on mitigating environmental impacts, such as reducing emissions and managing waste effectively (Yang et al., 2023). In contrast, due to its less tangible environmental footprint, the service industry prioritizes social aspects, including employee welfare and customer satisfaction (Khalil et al., 2022). This leads to differing approaches in measuring environmental impacts, with manufacturing assessing direct production processes and service industries evaluating office operations and other indirect activities.
Example Strategies: Provide an example of a strategy appropriate for the service and the manufacturing industries and an example specific to either the service or the manufacturing industry when considering people, planet, or profit through the TBL framework. Include a brief explanation of what each example demonstrates.
Example Strategies
This section of QSO 321 1-3 Assignment: Triple Bottom Line Industry Comparison will provide examples for both Universal and Industry-specific strategies.
Universal Strategy Example
- A green procurement policy that applies to both sectors ensures sustainable, eco-friendly materials and services are purchased.
- Describe how this reduces the environmental impact and supports ethical labor practices, benefiting both the planet and people.
Industry-Specific Strategy Example
- Implementing a closed-loop recycling system to minimize waste and raw material usage.
- Introducing flexible working conditions to improve employee satisfaction and productivity.
- Discuss how each strategy specifically addresses the unique challenges and opportunities in the respective industries, demonstrating the application of TBL principles in different contexts.
Example
Universal Strategy Example
A green procurement policy is crucial for both sectors, advocating for acquiring sustainable, eco-friendly materials and services. This strategy aids in reducing environmental harm and supports fair labor practices, thus aligning with TBL’s goals (Lagnaoui, 2023)
Industry-Specific Strategy Example
For manufacturing, implementing a closed-loop recycling system addresses waste and resource usage, while in the service sector, flexible working conditions can boost employee satisfaction and productivity (Rachakatla & Garrepalli, 2024). These strategies cater to each industry’s unique challenges, demonstrating the versatile application of TBL principles.
Closing
By following QSO 321 1-3 Assignment: Triple Bottom Line Industry Comparison guide, students can comprehend and articulate how TBL similarities in service and manufacturing industry can be effectively tailored to the unique characteristics and demands of the manufacturing and service industries, supporting sustainable development across different sectors.
References
Khalil, N., Che Abdullah, S. N., Haron, S. N., & Hamid, M. Y. (2022). A review of green practices and initiatives from stakeholders’ perspectives towards sustainable hotel operations and performance impact. Journal of Facilities Management, ahead-of-print(ahead-of-print). https://doi.org/10.1108/JFM-03-2022-0025
Lagnaoui, T. (2023). CSR and Business Sustainability in the Finnish Textile Industry: A Path to a Sustainable Future [fi=AMK-opinnäytetyö|sv=YH-examensarbete|en=Bachelor’s thesis|]. http://www.theseus.fi/handle/10024/793524
Rachakatla, B., & Garrepalli, S. M. (2024). From Industry 4.0 to Industry 5.0. In Sustainability in Industry 5.0. CRC Press.
Radzi, N. A. M., Hezbollah, H. R., Normaizatul Akma, S., Hashim, H., & Ali, A. F. M. (2020). Wellness, Work, and Employee Assistance Programs as Part of CSR Initiatives among Corporate Companies. https://doi.org/10.48080/jae.v17i4.378
Yang, M., Chen, L., Wang, J., Msigwa, G., Osman, A. I., Fawzy, S., Rooney, D. W., & Yap, P.-S. (2023). Circular economy strategies for combating climate change and other environmental issues. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 21(1), 55–80. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-022-01499-6
QSO 321 2-2 Discussion: Cultural Comparisons and the Triple Bottom Line
Instructions for QSO 321 2-2 Discussion
2-2 Discussion: Cultural Comparisons and the Triple Bottom Line
In this module, you have learned about the ways organizations support their people, whether it be within the workplace or the local community. In this discussion, you will evaluate business practices that are not considerate of employees and communities, brainstorm reasons why the practices may have been established, and consider how they can be improved.
For your initial post, select one of the following practices to evaluate:
- Employee pay is low.
- Employee training is limited.
- Employee benefits are minimal; there is little paid time off or sick time available.
- The workplace culture is described by employees as stressful, competitive, or alienating.
- A business doesn’t give back to the local community in any way.
- A business outsources many of its suppliers even though many local suppliers are available.
In your initial post, evaluate your selected practice by addressing the following questions:
- What general factors may have contributed to an organization or business implementing this practice?
- What are some potential negative repercussions of the practice on employees, the local community, or the business or organization?
- What benefits might employees, the local community, or the business or organization experience if a more people-friendly practice were incorporated?
In your replies to at least two peers, address the following questions:
- What specific initiative, practice, or change to your peer’s evaluated practice could improve community or employee support?
- What are the benefits and risks of implementing your suggested initiative, practice, or change?
- If you were the primary decision-maker, would you implement your suggested initiative, practice, or change? In other words, do you feel the benefits outweigh the risks? Why or why not?
To complete this assignment, review the Discussion Rubric.
Introduction to QSO 321 2-2 DISCUSSION
Welcome to the How-To Guide QSO 321 2-2 Discussion: Cultural Comparisons and the Triple Bottom Line. This task will discuss the cultural comparisons and the triple bottom line. This QSO 321 How-To guide will provide brief and descriptive guidelines to solve the QSO 321 2-2 Discussion post and a dummy solution for each section. I will equip you with strategies and insights to tackle all the queries related to the Triple Bottom Line. Let us begin with the guide.
Introduction to the Issue
For the QSO 321 2-2 Discussion: Cultural Comparisons and the Triple Bottom Line, we must choose one of the issues given in the instruction guidebook. I chose the issue “Employee pay is low” for this discussion. I selected the issue of low employee pay because it directly impacts the well-being of workers and the local community, reflecting a significant challenge within business practices today (Diener & Seligman, 2004). Addressing this issue can enhance employee satisfaction, community welfare, and a more sustainable and equitable business model.
To start with the guide, let us start by understanding that low employee pay can affect the workforce, the broader community, and the organization’s sustainability.
What factors may have contributed to an organization or business implementing this practice?
Factors Contributing to Low Employee Pay
This section of the QSO 321 2-2 Discussion: Cultural Comparisons and the Triple Bottom Line will discuss the factors contributing to low employee pay.
- Consider the broader economic pressures, such as the desire to minimize operational costs or competitive pricing strategies, that might lead businesses to adopt lower pay scales.
- Analyze specific sectors or case studies where this practice is prevalent to understand its roots.
Example
Several factors might contribute to a business implementing low employee pay. Economically, businesses often aim to minimize operational costs to enhance profitability (Chen et al., 2023). Companies might lower wages in competitive markets to offer competitive pricing and maintain a cost advantage. This practice is particularly prevalent in sectors with high labor supply but low demand, such as retail or fast food, where the abundance of entry-level workers allows for lower wages. Additionally, a lack of union representation or weak labor laws can make it easier for businesses to adopt such practices. Understanding these dynamics requires looking at the specific industries and their operational challenges alongside broader economic pressures.
What are some potential negative repercussions of the practice on employees, the local community, or the business or organization?
Negative Repercussions of Low Employee Pay
For the next section of the QSO 321 2-2 Discussion: Cultural Comparisons and the Triple Bottom Line, we will look into the negative repercussions of the issue we selected above, i.e., low employment pay.
- Discuss how low pay can lead to employee dissatisfaction and high turnover rates, potentially affecting the local economy due to decreased spending power.
- Reflect on the potential for these practices to harm the organization’s reputation and long-term sustainability.
Example
Al-Qathmi and Zedan (2021) state that low employee pay can have several negative repercussions. For employees, it often results in dissatisfaction and a lack of motivation, leading to high turnover rates. This impacts the business through increased recruitment and training costs and affects the local economy due to decreased worker spending power. Furthermore, consistently low wages can harm an organization’s reputation, making it difficult to attract talented individuals. In the long run, these practices might jeopardize the company’s sustainability as public and consumer perceptions shift towards supporting businesses that treat their employees fairly (SimanTov-Nachlieli & Bamberger, 2021). Ultimately, low pay undermines employee well-being and the broader health of the community and business.
What benefits might employees, the local community, or the business or organization experience if a more people-friendly practice were incorporated?
Benefits of Improved Pay Practices
In this section of the QSO 321 2-2 Discussion: Cultural Comparisons and the Triple Bottom Line, we will shed light on the benefits of improved pay practices in the workplace.
- Explore how fair wages can improve employee morale, attract talent, and enhance community relations.
- Consider the potential for such practices to contribute to a positive brand image and long-term financial success.
Example
Incorporating fair wage practices can yield significant benefits. It boosts employee morale and job satisfaction, fostering a more motivated and productive workforce (Sorribes et al., 2021). This, in turn, attracts higher-quality talent looking for employers who value their contributions. From a community perspective, better pay increases workers’ spending power, benefiting local businesses and the economy. Fair wages can enhance the organization’s reputation, strengthening community relations and customer loyalty. This positive brand image is crucial for long-term financial success, as consumers increasingly support businesses prioritizing employee welfare (Bennett et al., 2021). Adopting people-friendly pay practices can lead to a virtuous cycle of benefits for employees, the community, and the business.
In your replies to at least two peers, address the following questions: What specific initiative, practice, or change to your peer’s evaluated practice could improve community or employee support? What are the benefits and risks of implementing your suggested initiative, practice, or change? If you were the primary decision-maker, would you implement your suggested initiative, practice, or change? In other words, do you feel the benefits outweigh the risks? Why or why not?
Replying to Peers
We must respond to peers for the last section of the 2-2 discussion.
- When responding to peers, propose specific initiatives, such as implementing a living wage policy or profit-sharing schemes, to address low employee pay.
- Discuss the benefits, such as improved employee loyalty and community support, against the risks, like increased operational costs. Conclude whether you believe the benefits outweigh the risks, justifying your stance.
Example
I appreciate your evaluation of the low pay issue. An initiative like a profit-sharing program could significantly improve employee and community support by directly linking company success to employee compensation. Increased spending could foster a more engaged and motivated workforce, enhance the company’s reputation, and stimulate local economies (Diener & Seligman, 2004). However, the risk lies in potential fluctuations in profitability that affect consistent employee earnings. In the QSO 321 Module Two Assignment Template, as a decision-maker, I would implement this change, believing that the benefits of increased employee engagement and loyalty outweigh the risks associated with profit variability (Tkalac Verčič, 2021). The key would be clear communication and setting realistic expectations. By ensuring that all stakeholders understand the long-term benefits of fostering a positive work environment and investing in employee satisfaction, the organization can minimize risks while boosting overall performance and retention.
Resources for Peer Response
Diener, E., & Seligman, M. E. P. (2004). Beyond Money: Toward an Economy of Well-Being. Psychological Science in the Public Interest, 5(1), 1–31. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0963-7214.2004.00501001.x
Tkalac Verčič, A. (2021). The impact of employee engagement, organizational support, and employer branding on internal communication satisfaction. Public Relations Review, 47(1), 102009. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pubrev.2021.102009
Closing
This How-To Owlisdom Guide will assist you in addressing low employee pay by
implementing fair wage practices that enhance worker satisfaction, attract talent, benefit the local economy, and
bolster the organization’s reputation and financial success. I hope you smash QSO 321 2-2 Discussion: Cultural
Comparisons and the Triple Bottom Line.
You can also read our QSO 321 next module 2-3 Assignment: Maintaining
Supplier Relationships.
References
Al-Qathmi, A., & Zedan, H. (2021). The Effect of Incentive Management System on Turnover Rate, Job Satisfaction, and Motivation of Medical Laboratory Technologists. Health Services Research and Managerial Epidemiology, p. 8, 2333392820988404. https://doi.org/10.1177/2333392820988404
Bennett, N. J., Blythe, J., White, C. S., & Campero, C. (2021). Blue growth and blue justice: Ten risks and solutions for the ocean economy. Marine Policy, p. 125, 104387. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpol.2020.104387
Chen, Y., kumara, E. K., & Sivakumar, V. (2023). RETRACTED ARTICLE: Investigation of finance industry on risk awareness model and digital economic growth. Annals of Operations Research, 326(1), 15–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-021-04287-7
Diener, E., & Seligman, M. E. P. (2004). Beyond Money: Toward an Economy of Well-Being. Psychological Science in the Public Interest, 5(1), 1–31. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0963-7214.2004.00501001.x
SimanTov-Nachlieli, I., & Bamberger, P. (2021). Pay communication, justice, and affect: The asymmetric effects of process and outcome pay transparency on counterproductive workplace behavior. Journal of Applied Psychology, 106(2), 230–249. https://doi.org/10.1037/apl0000502
Sorribes, J., Celma, D., & Martínez-Garcia, E. (2021). Sustainable human resources management in crisis contexts: Interaction of socially responsible labor practices for the well-being of employees. Corporate Social Responsibility and Environmental Management, 28(2), 936–952. https://doi.org/10.1002/csr.2111
Tkalac Verčič, A. (2021). The impact of employee engagement, organizational support, and employer branding on internal communication satisfaction. Public Relations Review, 47(1), 102009. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pubrev.2021.102009
QSO 321 2-3 Assignment: Maintaining Supplier Relationships
Instructions of QSO 321 2-3 Assignment
2-3 Assignment: Maintaining Supplier Relationships
Overview
In this module, you have learned about the importance of prioritizing people, whether it be employees, the local community, or customers. In this assignment, you will explore important considerations for culturally competent business practices, which can help strengthen and maintain relationships.
Scenario
You are a procurement manager working on training a new sourcing analyst. As part of their training, they will be traveling with you to meet with new and existing suppliers for specialized parts your company needs. This will allow your colleagues first-hand experience and help them develop relationships with the business professionals they will be working with in the future.
You need to make sure that they are familiar with cultural business practices for the places you will be visiting so that existing business relationships remain strong and new relationships start well. You have decided to create a brief guide that includes the cultural considerations they will need to be aware of while doing business.
Prompt
Use the Module Two Assignment Template Word Document to create a guide that provides a brief overview of culturally considerate business practices for three countries of your choosing that are outside of the United States. Use course and external resources (such as the Shapiro Library) to gather information on your selected countries and their cultural business practices.
Specifically, you must address the following rubric criteria:
- Authority Figures: Describe how figures of authority are treated and shown respect in each selected country, as well as actions or communications that may cause unintended offense.
- Levels of Formality: Describe the level of formality that business professionals follow in each selected country. Examples are things like language, dress, or etiquette.
- Social Norms: Identify common social norms that should be used in business in each selected country, as well as hand gestures and body language that should be avoided or that may cause unintended offense.
- Time and Scheduling: Describe how the concepts of time and scheduling are treated in each selected country, as well as considerations for business meeting etiquette that should be considered to avoid causing unintended offense.
- Business Practices: Describe general business practices that should be taken into consideration when conducting business in the selected countries. Examples include meals, cultural holidays and events, and the use of formal contracts.
Guidelines for Submission
Submit the Module Two Assignment Template to complete this assignment. Use bullet points when completing the template. Sources should be cited according to APA style.
Introduction to QSO 321 2-3 Assignment
In this How-To QSO 321 Guide, we will explore managing relationships with suppliers. We will be provided with a template for this assignment. I am using the SNHU template as an example. The template provided by your instructor will be the same as the one I am using.
We need to act as a procurement manager tasked with training a new sourcing analyst, and it is crucial to impart the significance of cultural competence in international business interactions. I will be focusing on the cultural business practices in Japan, Germany, and Brazil. QSO 321 2-3 Assignment: Maintaining Supplier Relationships guide will offer insights to ensure existing and new relationships thrive by respecting and understanding the selected countries.
Japan, Germany, and Brazil
For this section of the QSO 321 2-3 Assignment: Maintaining Supplier Relationships, we will evaluate the following points for the selected countries.
- Authority Figures
- Research how respect towards authority is demonstrated in the workplace.
- Identify specific titles or forms of address that are preferred.
- Note any actions or phrases that might be considered disrespectful.
- Levels of Formality
- Investigate the expected dress code for business meetings.
- Determine the appropriate level of language formalness (use of first names vs. titles).
- Understand any formal protocols for meetings or greetings.
- Social Norms
- Look into common behaviors considered polite or impolite in a business context.
- Find out about acceptable body language, including gestures that are welcome or should be avoided.
- Explore the role of personal space and physical contact during interactions.
- Time and Scheduling
- Assess the importance of punctuality for meetings and deadlines.
- Learn about the typical pace of business meetings and the scheduling flexibility.
- Understand how to arrange meetings and the etiquette for cancellations or delays.
- Business Practices
- Research any business rituals important in building relationships, like gift-giving or dining etiquette.
- Identify major cultural holidays that could affect business operations.
- Understand the importance and formality of contracts and agreements in business dealings.
Example
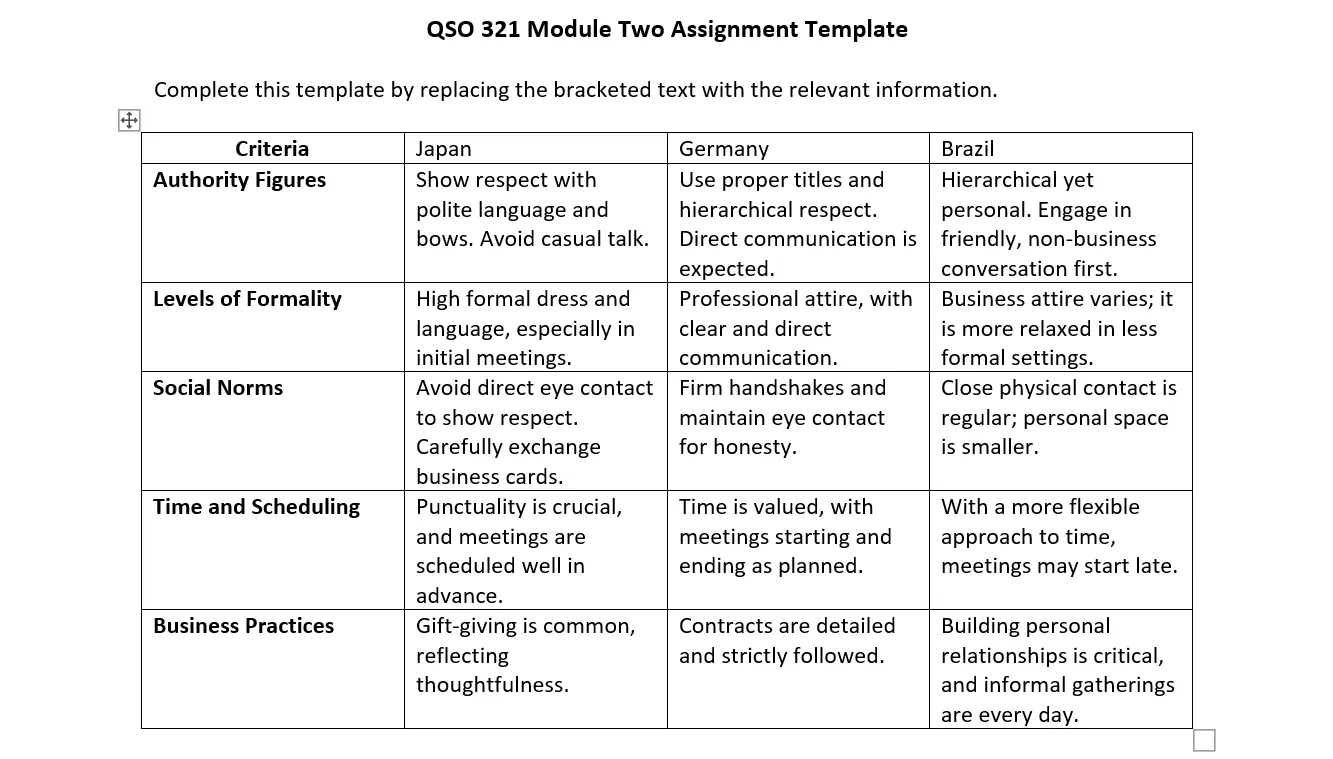
Closing
This How-To Owlisdom Guide will enable you to understand the QSO 321 2-3 Assignment: Maintaining Supplier Relationships and embrace cultural competence. As cultural competency is critical to fostering solid international business relationships, understanding and respecting the diverse practices outlined will pave the way for successful global interactions.
Use the Module Two Assignment Template Word Document to create a guide that provides a brief overview of culturally considerate business practices for three countries of your choosing that are outside of the United States. Use course and external resources (such as the Shapiro Library) to gather information on your selected countries and their cultural business practices. This guide will help you develop strategies for maintaining strong supplier relationships while respecting cultural differences to ensure effective collaboration and long-term success in global markets.
References
Edwards, J. (2012). Cultures and Languages in Contact: Towards a Typology. In The Handbook of Intercultural Discourse and Communication (pp. 37–60). John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118247273.ch3
Kubota, R. (2012). Critical Approaches to Intercultural Discourse and Communication. In The Handbook of Intercultural Discourse and Communication (pp. 90–109). John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118247273.ch6
Lincoln, J. R., & Kalleberg, A. L. (1992). Culture, Control, and Commitment: A Study of Work Organization and Work Attitudes in the United States and Japan. CUP Archive.
O’Keefe, H., & O’Keefe, W. M. (2004). Business behaviors in Brazil and the USA: Understanding the gaps. International Journal of Social Economics, 31(5/6), 614–622. https://doi.org/10.1108/03068290410529425
Witt, M. A., & Redding, G. (2009). Culture, meaning, and institutions: Executive rationale in Germany and Japan. Journal of International Business Studies, 40(5), 859–885. https://doi.org/10.1057/jibs.2008.81
QSO 321 3-2 Discussion: Risks and Benefits of Sustainable Operations
Instructions for QSO 321 3-2 Discussion
3-2 Discussion: Risks and Benefits of Sustainable Operations
Although sustainable operations have many benefits for organizations, consumers, and society, they also come with many business risks. In this discussion, you will explore the sustainability operations of major organizations to reflect on what they are doing well, the benefits their sustainable operations may bring, and the potential risks associated with their sustainable operations. In evaluating the risks and benefits of prioritizing sustainability, you will also learn the importance of justifying organizational priorities, which will assist you in completing the first section of your course project.
First, take some time to explore a few different organizations’ sustainable operations statements on their websites. You may explore organizations you are familiar with or use the following:
- Starbucks Stories
- Select Social Impact from the navigation bar, then select from the story topics in the drop-down menu to explore the stories. Be sure to explore the Sustainability topic.
- L’Oréal Group: Commitments and Responsibilities
- Dixie Cares: An Eye Toward the Future
- Peabody: Sustainability Approach
In your initial post, address the following questions:
- How did the organizations you explored address sustainability concerns inherent to their industry, if at all?
- For example, a company that manufactures plastic has inherent environmental risks regarding plastic waste and pollution.
- What other sustainable practices did the organizations you explored identify as priorities, and what kinds of business risks may they be taking on to prioritize those sustainable practices?
- Do you think that the business risks the organizations are taking to prioritize their identified sustainable operations are worthwhile from a business perspective? Why or why not?
In your replies to at least two peers, contribute to the discussion by sharing the potential repercussions of not taking risks to prioritize sustainability. Examples of how you could contribute to the discussion include the following:
- Provide examples of organizations that experienced the repercussions of not prioritizing sustainability.
- Reflect on how you or people you know might react to organizations and products that don’t prioritize sustainability from a consumer perspective. Consider how factors such as age, geographic location, and finances might affect consumers’ reactions.
- Name some specific impacts of not remaining competitive in the market based on what you learned from your reading in the Resources section.
- Provide other reasons to justify prioritizing organizational sustainability.
To complete this assignment, review the Discussion Rubric.
Introduction to QSO 321 3-2 Discussion
The How-To QSO 321 Guide for QSO 321 3-2 Discussion: Risks and Benefits of Sustainable Operations explores your understanding of the risks and benefits of sustainable operations. I will provide brief and descriptive guidelines to solve the 3-2 Discussion posts and a dummy solution for each section. This How-To Owlisdom Guide will equip you with guidelines to tackle all the queries related to the QSSO 321 3-2 Discussion post. Let us begin with the guide.
How did the organizations you explored address sustainability concerns inherent to their industry, if at all?
Introduction to Sustainable Operations
We will start off the discussion by introducing the organization we chose. We also need to add how the organization addresses sustainability concerns. I am selecting Starbucks for this discussion.
- Definition and Importance: Begin by understanding the concept of sustainable operations. Consider how they contribute to the triple bottom line of people, planet, and profit.
- Overview of Benefits and Risks: Acknowledge the positive impacts on society, the environment, and the potential business risks
Example
In our exploration, we chose Starbucks, a coffee industry leader known for its commitment to sustainability. Starbucks addresses sustainability by focusing on ethical sourcing, waste reduction, and energy efficiency, aligning with the triple bottom line of benefiting people, the planet, and profit. This approach mitigates environmental risks and reinforces its brand reputation, showcasing the harmonious balance between corporate responsibility and operational success.
What other sustainable practices did the organizations you explored identify as priorities, and what business risks may they be taking to prioritize those sustainable practices?
Exploring Organizational Sustainability Practices
For the next part of the QSO 321 3-2 Discussion: Risks and Benefits of Sustainable Operations, we will explore the sustainability practices of the organization we chose.
- Addressing Industry-Specific Sustainability Concerns: Use the Starbucks example to illustrate how an organization addresses sustainability. Please focus on the specific challenges in their industry, such as waste reduction and ethical sourcing.
- Identifying Other Priority Sustainable Practices: Investigate other sustainability efforts that Starbucks prioritizes, such as renewable energy use or community engagement.
- Evaluating Business Risks: Consider the risks Starbucks faces by prioritizing sustainability, like increased costs or operational changes, and how it manages these risks.
Example
Beyond addressing waste reduction and ethical sourcing, Starbucks prioritizes renewable energy and community engagement as part of its sustainability strategy. Embracing renewable energy, Starbucks aims to reduce its carbon footprint, a move critical for the coffee industry, which is heavily impacted by climate change. Community engagement initiatives, including support for local farmers and community projects, underscore Starbucks’s commitment to social sustainability. However, these practices introduce risks such as increased operational costs and complex supply chain management, which Starbucks mitigates through strategic planning and investment in sustainable innovations.
Do you think the business risks the organizations are taking to prioritize their identified sustainable operations are worthwhile from a business perspective? Why or why not?
Assessment of Sustainability Risks and Benefits
Now, we will assess the sustainability risks and benefits of the selected organization due to its sustainability operations.
- Business Perspective: Analyze whether Starbucks’s sustainability risks are justified from a business standpoint. Consider the long-term benefits against the immediate risks and costs.
- Justifying Organizational Priorities: Discuss the importance of sustainability in Starbucks’s operational strategy and how it aligns with its brand and values.
Example
From a business standpoint, the risks Starbucks takes by prioritizing sustainability are indeed justified. The immediate costs and operational adjustments are offset by long-term benefits, including enhanced brand loyalty, reduced operational costs through efficiency improvements, and a competitive edge in a market increasingly driven by consumer demand for ethical practices. Moreover, Starbucks’s commitment to sustainability aligns with its brand values, reinforcing its market position and supporting sustained growth.
Provide examples of organizations that experienced the repercussions of not prioritizing sustainability. Reflect on how you or people you know might react to organizations and products that do not prioritize sustainability from a consumer perspective. Consider how age, geographic location, and finances might affect consumers’ reactions. Name some specific impacts of not remaining competitive in the market based on what you learned from your reading in the Resources section. Provide other reasons to justify prioritizing organizational sustainability.
Engaging in Peer Discussions
Responding to peers is one of the vital parts of the QSO 321 3-2 Discussion: Risks and Benefits of Sustainable Operations discussion post. We need to provide at least two peer responses. I will provide one example post. You can write your peer responses by keeping the following points in mind.
- Reflecting on Neglecting Sustainability: Provide a short paragraph on the consequences companies face when they ignore sustainability, using examples from recent news or studies.
- Consumer Perspectives: Share insights on how different demographic factors influence consumer attitudes towards sustainability and how this impacts companies like Starbucks.
- Competitive Impacts: Briefly discuss how failing to prioritize sustainability can affect a company’s competitive edge and market position.
- Justifying Organizational Sustainability: Explain why companies should make sustainability a core part of their strategy, focusing on long-term benefits and societal impact.
Response 1
Focusing on sustainability is not just about environmental stewardship but also about ensuring long-term business viability. A striking example is the backlash fast-fashion brands face for not prioritizing sustainable practices, leading to consumer boycotts and brand damage. This illustrates the critical impact of sustainability on maintaining a competitive edge. Consumers, especially millennials and Gen Z, increasingly prefer brands with solid environmental ethics, showing how sustainability influences consumer choices and market competitiveness. Prioritizing sustainability, therefore, is essential for brand reputation, customer loyalty, and staying ahead in the market.
Closing
Finally, we will conclude your discussion with the key takeaways. Briefly recap the importance of understanding and implementing sustainable operations within an organization.
QSO 321 3-3 Assignment: Stakeholder Roles and Responsibilities
Instructions for QSO 321 3-3 Assignment
3-3 Assignment: Stakeholder Roles and Responsibilities
Overview
Knowing the expectations involved with maintaining operational sustainability and who is responsible for meeting these expectations is an important parKnowing t of being an effective practitioner. In this assignment, you will create a guide that can be used throughout this course and in the future to help you better understand the roles, influences, and responsibilities of internal and external stakeholders involved in maintaining ethical business practices related to the triple bottom line (TBL). This assignment will also support you in completing your course project, which is due in Module Seven.
Scenario
You are working on a collaborative project regarding sustainability initiatives. During recent meetings, the group has realized there is a lot of confusion surrounding who is responsible for what regarding regulations, governance, and responsibilities surrounding the new initiatives that are being planned. To help everyone understand the roles and responsibilities of both internal and external stakeholders, you have volunteered to create a brief guide.
Prompt
Use course and external resources to complete the Module Three Assignment Template Word Document, making sure to clearly and concisely identify key stakeholders and their roles, responsibilities, and level of influence in upholding sustainable business operations regarding each aspect of the TBL.
For this assignment, you can select one of the following industries to help contextualize your response:
- Foodservice
- Office supply
- Accounting and finance
Specifically, you must address the following rubric criteria:
- Identification:Identify key internal and external stakeholders, groups, and organizations involved in enforcing and maintaining operational sustainability regarding each aspect of the TBL.
- Roles:Briefly describe the role of identified internal and external stakeholders, groups, and organizations involved in enforcing and maintaining operational sustainability.
- Responsibilities:Briefly describe the responsibilities of identified internal and external
stakeholders, groups, and organizations involved in enforcing and maintaining operational sustainability
regarding each aspect of the TBL, specifically with their level of responsibility and accountability in the
following:
- Evaluating or enforcing sustainable operations
- Determining which aspects of the TBL framework they support most strongly
- Explaining how their responsibilities can help justify prioritizing the TBL
- Influence:Briefly describe the level of influence of the identified internal and external stakeholders, groups, and organizations involved in enforcing and maintaining operational sustainability regarding each aspect of the TBL. Make sure to note their ability to make decisions, enforce requirements, and justify prioritizing the TBL for an organization.
Guidelines for Submission
Submit the Module Three Assignment Template to complete this assignment. Use bullet points as appropriate when completing the template. Sources should be cited according to APA style.
Introduction to 3-3 assignment: stakeholder roles and responsibilities
This How-To QSO 321 Guide is crafted to assist you in solving the QSO 321 3-3 Assignment: Stakeholder Roles and Responsibilities. This Guide helps you navigate the complex landscape of stakeholder responsibilities and influences in maintaining operational sustainability. It focuses on the Triple Bottom Line (TBL) framework, emphasizing people, planet, and profit. Here, we outline a structured approach to identify, understand, and engage with the key stakeholders involved in sustainability initiatives.
I have chosen the Food Service Industry for this assignment. Note that this assignment is the first part of the Project we will complete in QSO 321 Module Seven. You will receive a template to solve the QSO 321 module 3 assignment 3-3. I am using the template by SNHU as an example here.
Identify key internal and external stakeholders, groups, and organizations involved in enforcing and maintaining operational sustainability regarding each aspect of the TBL.
Identification of Stakeholders
For the first part of the QSO 321 3-3 Assignment: Stakeholder Roles and Responsibilities, we will explore critical internal and external stakeholders of the industry we chose.
Internal Stakeholders
- Management and Employees: Directly involved in daily operations and decision-making processes.
- Shareholders/Investors: Financially invested in the company’s success and sustainability performance.
External Stakeholders
- Suppliers and Vendors: Provide goods and services and significantly impact the supply chain’s sustainability.
- Customers: Influence business practices through their purchasing decisions.
- Regulatory Bodies: Govern operational compliance with sustainability standards.
- Community and Environmental Groups: Advocate for sustainable practices and monitor the impact on society and the environment.
Briefly describe the roles of identified internal and external stakeholders, groups, and organizations in enforcing and maintaining operational sustainability.
Roles in Sustainability
Next, we will discuss the stakeholders’ roles in the sustainability of organizational management.
- Management and Employees: Drive sustainability initiatives and integrate TBL values into corporate strategy.
- Shareholders/Investors: Advocate for sustainability to enhance long-term value.
- Suppliers and Vendors: Adopt and adhere to sustainable production and distribution practices.
- Customers: Demand sustainable products and services, influencing market trends.
- Regulatory Bodies: Set and enforce sustainability standards and policies.
- Community and Environmental Groups: Raise awareness and push for sustainable business practices.
Briefly describe the responsibilities of identified internal and external stakeholders, groups, and organizations involved in enforcing and maintaining operational sustainability regarding each aspect of the TBL, specifically regarding their level of responsibility and accountability in the following: Evaluating or enforcing sustainable operations. Determining which aspects of the TBL framework they support most strongly. Explaining how their responsibilities can help justify prioritizing the TBL
Responsibilities Regarding the TBL
For this part of the QSO 321 3-3 Assignment: Stakeholder Roles and Responsibilities, we will explore the responsibilities of the stakeholders in operational management concerning TBL.
Evaluating/Enforcing Sustainable Operations
- Internal stakeholders ensure that operations align with sustainability goals.
- External stakeholders, like regulatory bodies, evaluate and enforce compliance.
Determining TBL Support
- Stakeholders prioritize aspects of the TBL based on their role and influence to balance people, planet, and profit.
Justifying the TBL
- Stakeholders justify TBL prioritization by demonstrating how sustainable practices contribute to long-term success and societal well-being.
Example
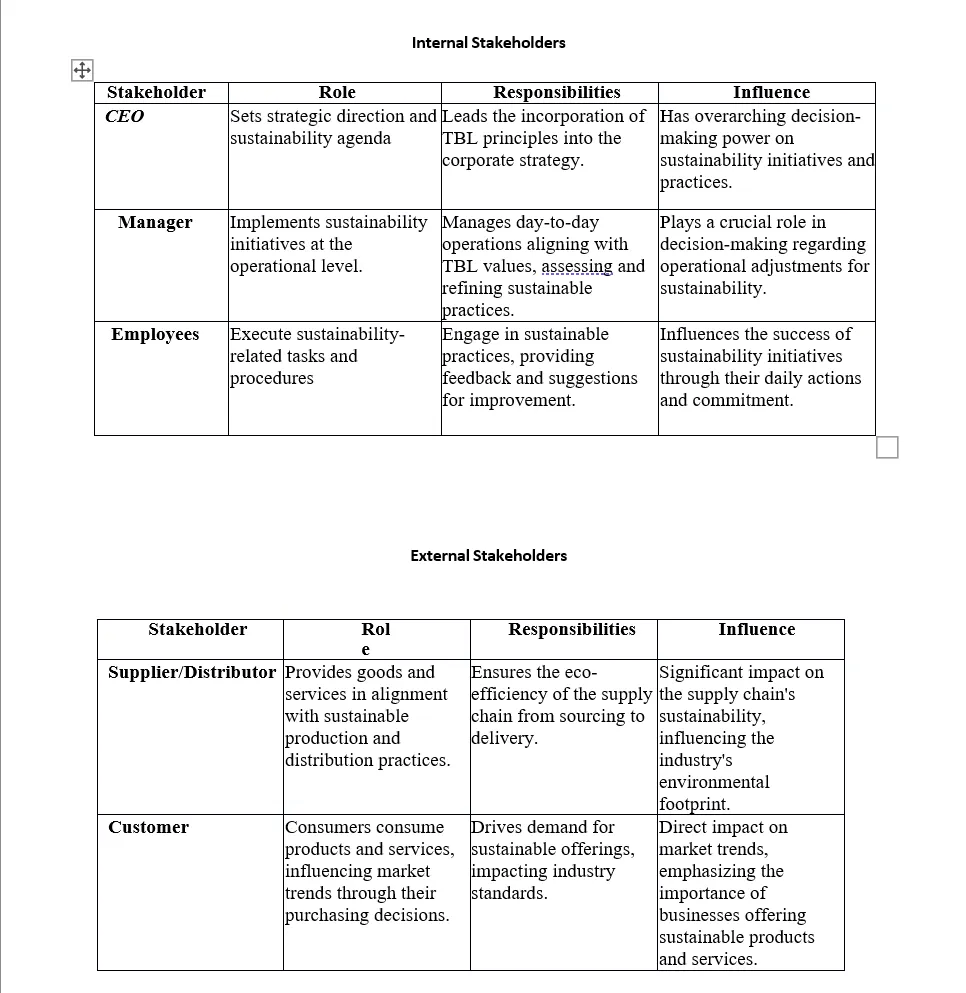
Closing
By following these guidelines, you will be able to understand how organizations in the food service industry can successfully navigate the complexities of maintaining operational sustainability. Also, you can ace your QSO 321 Course Project and QSO 321 3-3 Assignment: Stakeholder Roles and Responsibilities.
QSO 321 Module 4 Assignment 4-2 Discussion: Farm-to-Table and the Triple Bottom Line
Instructions for QSO 321 Module 4 Assignment 4-2 Discussion
4-2 Discussion: Farm-to-Table and the Triple Bottom Line
You are the chief operating officer (COO) of a local supermarket chain that has ten stores within a 100-mile radius. The farm-to-table movement has been gaining momentum locally, and now it’s a consumer demand as well as a good practice. This movement supports the use of local suppliers to limit the environmental impact caused by the long-distance transportation of food. It also supports small family farms that use sustainable practices, such as avoiding genetically modified organisms and pesticides or using organic fertilizers. The CEO of the supermarket chain has asked you to see if the supermarket can apply some of the farm-to-table principles to how it selects produce suppliers. Before moving too far in that direction, both you and the CEO agree that the inventory-management implications need to be understood.
Keep in mind that supermarket customers want a wide range of produce all year long—even produce that does not grow locally during parts of the year. For example, oranges cannot survive very cold weather, but local customers expect to be able to buy them even during snowstorms in winter.
In your initial post, address the following:
- What are a few different ways that the supermarket chain could incorporate farm-to-table principles into its operations while still meeting consumer demands?
- What are the benefits and risks associated with incorporating farm-to-table principles into the grocery chain’s supply chain?
- What data and communication with the local farms are necessary for the supermarket to implement this endeavour?
- What factors or metrics will determine whether you, as the COO, support applying farm-to-table principles to the supermarket, and why?
In your replies to at least two peers, address the questions below:
- What considerations should decision makers keep in mind or prioritize when components of the triple bottom line don’t agree, for example, when an environmentally beneficial decision may negatively affect profit or the reverse?
- Which approach do your peers suggest in their initial posts, and why do you feel would be the most effective?
To complete this assignment, review the Discussion Rubric.
Introduction to QSO 321 Module 4 Assignment 4-2
The QSO 321 Module 4 Assignment 4-2 Discussion: Farm-to-Table and the Triple Bottom Line discussion post revolves around your understanding of Farm-To-Table Principles. I will provide brief and descriptive guidelines to solve the 4-2 Discussion posts and a dummy solution for each section. This How-To QSO 321 Guide will equip you with guidelines to tackle all the queries related to the Module 4 Discussion post. Let us begin with the guide.
Introduction to Farm-to-Table Principles
We will briefly discuss the Farm-to-Table Principles to start the Discussion of QSO 321 Module 4 Assignment 4-2 Discussion: Farm-to-Table and the Triple Bottom Line.
- Understand the core values of the farm-to-table movement: local sourcing, supporting small-scale sustainable agriculture, and minimizing environmental impact.
- Acknowledge the challenge of meeting year-round consumer demand for a wide range of produce.
Example
The farm-to-table movement emphasizes the importance of local sourcing, supporting small-scale sustainable agriculture, and minimizing the environmental impact of food production (Pehin et al., 2021). This approach fosters community engagement and promotes healthier ecosystems. However, a significant challenge arises in satisfying the year-round consumer demand for diverse produce, some of which may not be locally available during certain seasons.
What are a few different ways that the supermarket chain could incorporate farm-to-table principles into its operations while still meeting consumer demands?
Strategies for Incorporation
For the next part of the QSO 321 Module 4 Assignment 4-2 Discussion: Farm-to-Table and the Triple Bottom Line, we will explore the strategies that help incorporate Farm-to-Table principles.
- Seasonal Product Highlighting: Rotate featured produce based on what is in season locally.
- Hybrid Sourcing Model: For non-local or out-of-season items, combine local sourcing with traditional methods, ensuring transparency about origins.
- Local Farmer Partnerships: Develop relationships with local farmers for consistent supply and support of sustainable practices.
Example
A supermarket chain could implement several strategies to align with farm-to-table principles while catering to consumer expectations. Highlighting seasonal produce encourages consumers to buy locally available foods, fostering a connection with seasonal eating. A hybrid sourcing model, combining local and traditional sourcing, ensures product availability with clear origin transparency (Pandey et al., 2022). Developing partnerships with local farmers secures a consistent supply of sustainable produce, reinforcing the chain’s commitment to supporting local agriculture and reducing environmental impact.
What are the benefits and risks of incorporating farm-to-table principles into the grocery chain’s supply chain?
Benefits and Risks Analysis
In this section of QSO 321 Module 4 Assignment 4-2 Discussion: Farm-to-Table and the Triple Bottom Line, we will analyze the benefits of farm-to-table principles.
- Benefits: Enhanced community relationships, reduced carbon footprint, and potential for fresher produce.
- Risks: Possible supply inconsistency, higher costs, and customer resistance to changes in product availability.
Example
Incorporating farm-to-table principles into the grocery chain’s supply chain offers significant benefits, including bolstering community relationships through local engagement, reducing environmental impact via a smaller carbon footprint, and enhancing product freshness (Gonzales-Yanac et al., 2024). However, this approach also presents risks, such as potential supply inconsistency due to reliance on local seasonal produce, increased operational costs stemming from premium pricing for sustainable practices, and the possibility of customer resistance to product availability and variety fluctuations.
What data and communication with the local farms are necessary for the supermarket to implement this endeavor?
Data and Communication Requirements
Here, we will discuss the necessary communication requirements.
- Collect data on local crop seasons, availability, and sustainable farming practices.
- Establish open lines of communication with local farmers for updates on crop yields and potential supply issues.
Example
To successfully implement farm-to-table principles, supermarkets must gather comprehensive data on local crop seasons, product availability, and local producers’ adherence to sustainable farming practices. Establishing robust, open lines of communication with local farmers is crucial for receiving timely updates on crop yields and identifying potential supply challenges. This proactive approach facilitates the anticipation of supply fluctuations. It allows for the adaptation of inventory strategies, ensuring the supermarket chain can maintain a consistent and diverse product offering while supporting local agriculture and sustainable practices.
What factors or metrics will determine whether you, as the COO, support applying farm-to-table principles to the supermarket, and why?
Decision Metrics for Implementation
For this QSO 321 Module 4 Assignment 4-2 Discussion: Farm-to-Table and the Triple Bottom Line section, we must discuss the decision matrices for implementing farm-to-table principles.
- Supply Stability: Ensure local sourcing can meet demand without significant gaps.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Evaluate the financial impact, including potential premium pricing for local, sustainable produce.
- Customer Satisfaction: Monitor feedback on product variety and quality.
- When faced with conflicts among the triple bottom line components, prioritize decisions that offer the best compromise and consider long-term benefits over short-term gains.
Example
As the COO, the decision to apply farm-to-table principles hinges on several critical factors. Supply Stability is paramount, ensuring that local sourcing reliably meets consumer demand. Cost-effectiveness involves assessing the financial viability, including the implications of premium pricing for sustainably sourced produce (Patel, 2023). Customer Satisfaction is crucial, requiring close monitoring of consumer responses to product range and quality. In instances of conflict within the triple bottom line elements, decisions should strategically balance short-term challenges against long-term benefits, prioritizing sustainable success and stakeholder well-being.
What considerations should decision makers consider when components of the triple bottom line do not agree, for example, when an environmentally beneficial decision may negatively affect profit or the reverse? Which approach do your peers suggest in their initial posts, and why do you feel would be the most effective?
Peer Responses
Responding to peers is one of the vital parts of the QSO 321 Module 4 Assignment 4-2 Discussion: Farm-to-Table and the Triple Bottom Line. We need to provide at least two peer responses. I will provide one example post. You can write your peer responses by keeping the following points in mind.
- Triple Bottom Line Considerations: Emphasize the importance of long-term vision and stakeholder engagement in making decisions that might sacrifice one component for the more significant benefit of another.
- Evaluating Peers’ Strategies: Highlight approaches that effectively balance supply chain sustainability with consumer demand and operational viability, explaining why these strategies seem most sustainable and adaptable.
Response 1
Adopting a long-term perspective and engaging stakeholders are crucial when navigating the triple bottom line’s complexities, especially when environmental and financial goals seem at odds. The hybrid sourcing model you proposed stands out for its pragmatic approach to balancing sustainability with consumer demand. It is adaptable and capable of evolving with changing preferences and technologies, making it a sustainable choice for the future.
Closing
By following these guidelines, you can fulfill all the requirements of QSO 321 Module 4 Assignment 4-2 Discussion: Farm-to-Table and the Triple Bottom Line. This guide will allow you to understand the Farm-to-Table principles and how incorporating them influences the TBL.
References
Gonzales-Yanac, T., Nagadeepa, C., Jaheer Mukthar, K. P., Castillo-Picón, J., Manrique-Cáceres, J., Ramirez-Asis, E., & Huerta-Soto, C. (2024). Minimalist Farm-To-Table Practices: Connecting Consumers with Local Agriculture. In B. Alareeni & A. Hamdan (Eds.), Technology and Business Model Innovation: Challenges and Opportunities (pp. 109–122). Springer Nature Switzerland. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-53998-5_9 Pandey, V., Pant, M., & Snasel, V. (2022). Blockchain technology in food supply chains: Review and bibliometric analysis. Technology in Society, 69, 101954. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techsoc.2022.101954 Patel, K. R. (2023). Harmonizing Sustainability, Functionality, and Cost: Navigating Responsible Packaging Innovations in Modern Supply Chains. American Journal of Economic and Management Business (AJEMB), 2(8), 287–300.
Pehin Dato Musa, S. F., & Chin, W. L. (2021). The role of farm-to-table activities in agritourism towards sustainable development. Tourism Review, 77(2), 659–671. https://doi.org/10.1108/TR-02-2021-0101
QSO 321 Module 4 Assignment 4-3: Project Management Strategies
Instructions of QSO 321 Module 4 Assignment 4-3
4-3 Assignment: Project Management Strategies
Overview
In this assignment, you will apply what you have learned about key concepts regarding operations management. You are encouraged to leverage your work and instructor feedback on this assignment in your course project, which is due in Module Seven.
Scenario
You work as the chief supply chain officer at NationaliTeas, a large international corporation that manufactures and sells tea worldwide. Its mission is to “Make the world more awake through rejuvenating and refreshing beverages and sustainable practices that uplift workers, communities, and souls.” You have recently hired the company’s first project manager and have given them their first project: Revise current workflows related to packaging at one of your tea factories to be more sustainable and leaner. As this is their first project, you will be helping them complete their task.
Prompt
Read through the Project Charter for Workflow Improvement Word Document, then review the Process Workflow for Tea Production Word Document graphic. A text-only version is available: Process Workflow for Tea Production Text-Only Version Word Document. Based on these documents, we recommend removing a total of four steps from the process flowchart that can help make the process more efficient and sustainable. Explain the implications of the proposed changes, and then help the NationaliTeas team address current items in the Issue Log located in the project charter.
Specifically, you must address the following rubric criteria:
- Lean Manufacturing: Evaluate the process flowchart to identify steps that do not add value based on the principles of lean manufacturing. Explain why you selected each step.
- Sustainability: Evaluate the process flowchart and identify steps that should be removed or changed to improve environmental sustainability. Explain why you selected each step.
- Process Changes: Explain the implications, both positive and negative, of removing or changing the steps from the process flowchart you identified in the previous two bullet points. Also, explain how those changes would help align with the triple bottom line (TBL).
- Issue Log: Analyze all entries in the Issue Log from the perspective of a project manager and explain the recommended course of action based on the project charter, noting the impact of the issue on scope, planning, communications, and resourcing.
- Operations Management Techniques: Discuss how operations management techniques, including project management and lean manufacturing, can add value to NationaliTeas.
Guidelines for Submission
Submit this assignment as a 350- to 500-word Word document. Sources should be cited according to APA style.
Introduction to QSO 321 Project Assignment 4-3
For QSO 321 Module 4 Assignment 4-3: Project Management Strategies, you will be provided with some supporting material documents. I am using the SNHU instructions as an example for this How-To QSO 321 Guide. Here, we are given the QSO 321 Project Assignment 4-3 Process Workflow for Tea Production Document and the Project Charter for the Workflow Process Improvement Document. We will first read and understand the Process Workflow and then review the Project Charter.
After reading and understanding the given documents, we will follow these guidelines. We recommend removing four steps from the process flowchart that can help make the process more efficient and sustainable.
Based on these documents, we recommend removing four steps from the process flowchart that can help make the process more efficient and sustainable. Explain the implications of the proposed changes, and then help the NationaliTeas team address current items in the Issue Log located in the project charter.
Reviewing Project Documents
- Familiarize yourself with the Project Charter and Process Workflow documents. Understand these documents’ executive summary, scope, business objectives, and current workflow to ground your analysis and recommendations.
Evaluate the process flowchart to identify steps that do not add value based on lean manufacturing principles. Explain why you selected each step.
Lean Manufacturing Analysis
After reading the documents provided for this section of the QSO 321 Module 4 Assignment 4-3: Project Management Strategies, we will evaluate the process flowchart to analyze the steps.
- Identify Steps to Remove: Examine the tea production process, identifying steps that do not add value or are redundant. Focus on processes that may cause delays, excess inventory, or unnecessary motions.
- Justification: Explain why each step was selected for removal or modification, referencing lean principles such as waste elimination and value stream mapping.
Example
Steps Identified for Removal
- Re-weighing Bags at the Processing Facility: This step seems redundant and does not add direct value to the product. Eliminating it can streamline the process and reduce time wastage.
- Multiple Re-weighing of Tea Leaves: After spreading across pans, after the first drying, and after removing from special rolling trays, these steps could be consolidated to minimize handling and processing time.
- Visual Inspection Post-Oxidation: Assuming quality control mechanisms are in place at various stages, this step could be integrated with earlier quality checks to enhance efficiency.
Evaluate the process flowchart and identify steps that should be removed or changed to improve environmental sustainability. Explain why you selected each step.
Sustainability Evaluation
Next, we will explore how to improve the sustainability of the environment by removing or changing the steps.
- Identify Unsustainable Practices: Look for steps in the workflow that have a high environmental impact, such as excessive energy consumption, use of non-renewable resources, or generation of waste.
- Justification: Provide reasons for each selection, considering the environmental impact and how modifications or eliminations contribute to sustainability goals.
Example
Steps Identified for Modification for Sustainability
- Use of Plastic in Packaging: Changing plastic to biodegradable or compostable materials for tea bagging and sealing can significantly reduce environmental impact.
- Energy Consumption in Multiple Drying Processes: Optimizing drying processes or utilizing renewable energy sources could enhance sustainability.
Explain the positive and negative implications of removing or changing the steps from the process flowchart you identified in the previous two bullet points. Also, explain how those changes would help align with the triple bottom line (TBL).
Process Changes and Implications
This QSO 321 Module 4 Assignment 4-3: Project Management Strategies section will explore the positive and negative impacts of changing the steps.
- Outline Proposed Changes: Describe how removing or modifying the identified steps will alter the workflow.
- Discuss Implications: Assess positive (e.g., reduced waste, lower costs, improved sustainability) and negative (e.g., initial investment, training needs) implications. Highlight how these changes align with the Triple Bottom Line (TBL).
Example
Proposed Changes
- Eliminate redundant weighing and visual inspection steps to streamline operations, reducing energy and labor costs.
- Switch to sustainable packaging materials and optimize drying processes for energy efficiency.
Implications
Positive: Reduced operational costs, improved efficiency, and lower environmental footprint align with TBL.
Negative: Initial costs associated with changing packaging materials and potential downtime during process optimization.
Analyze all entries in the Issue Log from the perspective of a project manager and explain the recommended course of action based on the project charter, noting the impact of the issue on scope, planning, communications, and resourcing.
Issue Log Analysis
Here, we will analyze the issue log and recommend steps to address those issues effectively.
- Review the Issue Log: Analyze the issues in the Project Charter, focusing on their impact on scope, planning, communication, and resources.
- Recommend Actions: For each issue, propose a solution or decision-making process that aligns with project goals, considering the potential impact on project timelines and deliverables.
Example
Confusion Among Stakeholders: Clear communication and defined roles can resolve confusion, and regular project updates and stakeholder meetings could be beneficial.
Change to Shiny Foil Packaging: While aesthetically pleasing, this contradicts sustainability goals. Recommend maintaining or finding sustainable alternatives that meet aesthetic and environmental criteria.
Budget Increase Request by Procurement: A detailed cost-benefit analysis should assess the feasibility. If compostable packaging significantly enhances sustainability metrics, exploring budget adjustments or alternative funding could be justified.
Discuss how operations management techniques, including project management and lean manufacturing, can add value to NationaliTeas.
Leveraging Operations Management Techniques
For the last step of QSO 321 Module 4 Assignment 4-3: Project Management Strategies, we will discuss how such operations management can add value to NationaliTeas.
- Discuss Value Addition: Reflect on how integrating lean manufacturing and project management principles can enhance efficiency, sustainability, and overall value for NationaliTeas.
- Emphasize the role of these techniques in achieving the project’s objectives and the company’s mission.
Example
Integrating lean manufacturing principles, such as waste elimination and process optimization, directly contributes to operational efficiency and sustainability. Employing project management principles ensures that the project aligns with strategic objectives, manages resources effectively, and adheres to timelines. These techniques, combined, can significantly improve NationaliTeas’ operational sustainability, aligning with its mission and bolstering its candidacy for B Corp Certification.
By addressing these steps and considerations, NationaliTeas can enhance its production efficiency and sustainability, furthering its mission and positively impacting the environment, society, and its bottom line.
Closing
By following QSO 321 Module 4 Assignment 4-3: Project Management Strategies guide, project managers will be equipped to make informed decisions that enhance NationaliTeas’ commitment to sustainability and lean operations, paving the way for B Corp Certification and long-term success.
QSO 321 5-2 DISCUSSION: Benefits and Risks of Outsourcing the Global Supply Chain
Instructions of QSO 321 5-2 DISCUSSION
5-2 Discussion: Benefits and Risks of Outsourcing the Global Supply Chain
Globalization has created many opportunities for organizations. There are many advantages and ways to create value through outsourcing portions of one’s global supply chain. For each opportunity, there are also many ways for the project to run into problems.
In your initial post, address the following:
- Identify one example of an organization that created value for itself through outsourcing part of its supply
chain. Provide a link to one resource.
- Identify the benefit that occurred.
- How did this benefit help the organization create value? Who was the value created for—the organization, or the customer?
In your replies to at least two peers, discuss potential risks of outsourcing for the examples they provided—for example, risks to supplier quality or stability, intellectual property, or reputation. The following questions may help develop your responses:
- Can you provide an example of an organization that started outsourcing the supply chain and then stopped? What risks did the organization face that caused it to stop the project?
- Can you provide an example of an organization that outsourced similarly and faced reputational damage due to the project?
To complete this assignment, review the Discussion Rubric.
Introduction to QSO 321 5-2 Discussion
In this How-To QSO 321 Guide, we will understand the concept of outsourcing and its significance in globalization. We will also focus on acknowledging how outsourcing offers opportunities and challenges for organizations.
Identify one example of an organization that created value for itself through outsourcing part of its supply chain. Provide a link to one resource.
Identifying Outsourcing Opportunities
For the first step of QSO 321 5-2 DISCUSSION: Benefits and Risks of Outsourcing the Global Supply Chain, we will identify an example of an organization that outsources its operations. For this Discussion, I am choosing Apple Inc.
- Briefly describe the organization and the specific part of its outsourced supply chain.
Example
Apple outsources the manufacturing of its hardware components to various suppliers globally, notably in China and Taiwan, to leverage cost efficiencies and specialized manufacturing capabilities. (Apple, n.d.). This strategic move allows Apple to leverage cost efficiencies and specialized manufacturing skills unavailable in-house, enabling the tech giant to focus on innovation, design, and software development, core areas that drive its market success.
Identify and detail the primary benefit the organization gained from outsourcing.
Evaluating the Benefits of Outsourcing
For this QSO 321 5-2 DISCUSSION: Benefits and Risks of Outsourcing the Global Supply Chain section, we will evaluate the benefits of the outsourcing opportunities Apple Inc. gets.
- Consider benefits such as cost reduction, improved efficiency, access to skilled labor, or enhanced focus on core competencies.
Example
Apple Inc.’s outsourcing strategy primarily benefits from cost reduction and access to specialized manufacturing skills, which are crucial for maintaining its high standards of product quality and innovation; by outsourcing the manufacturing of components to suppliers, especially in Asia, Apple leverages lower labor costs and specialized expertise that would be more expensive or difficult to develop in-house. This approach significantly reduces production costs while ensuring the manufacturing process uses state-of-the-art technology and expertise. Furthermore, it allows Apple to focus its resources on core competencies such as design, technology development, and market strategy. This strategic allocation of resources enhances Apple’s operational efficiency and enables it to invest heavily in research and development, driving innovation. Consequently, Apple maintains its competitive edge in the tech industry, consistently offering cutting-edge products to its customers.
Discuss how the benefit of outsourcing contributed to value creation for the organization or its customers.
Analyzing the Creation of Value Through Outsourcing
This section will analyze how Apple Inc. creates value through outsourcing.
- Reflect on whether the value was lower prices, better product quality, faster delivery times, or increased shareholder value.
Example
Apple Inc.’s strategic outsourcing contributes to value creation in several ways, notably by enhancing shareholder value and improving product quality. The cost savings realized through outsourcing enable Apple to allocate more resources towards research and development, driving innovation. This focus on innovation leads to high-quality, cutting-edge products that stand out in the competitive market. While the lower production costs do not necessarily translate to lower prices for consumers, the value comes in the form of advanced features, reliability, and the prestige associated with owning Apple products. Additionally, the efficiency of Apple’s global supply chain ensures the timely delivery of the latest devices to the market, further solidifying its market position. Overall, outsourcing supports Apple’s mission to deliver exceptional products, thereby creating significant value for the organization and its customers, ultimately contributing to increased shareholder value.
In your responses to peers, discuss the potential risks associated with the outsourcing examples they provided. Consider mentioning risks like quality issues, supply chain disruptions, loss of intellectual property, or reputational damage. Use hypothetical examples or well-known cases to illustrate potential outsourcing pitfalls.
Peer Responses
- Risk Identification: For peers’ examples, identify specific risks related to quality, stability, intellectual property, or reputation.
- Organizational Responses to Risks: If possible, mention organizations that reverted to outsourcing decisions due to these risks or faced significant challenges.
- Brief and Focused Response: Keep your analysis concise, aiming to enlighten the discussion with insightful observations on potential outsourcing risks.
Example
Outsourcing can indeed offer benefits, but it’s crucial to consider potential risks like quality control issues, which Boeing faced with the 787 Dreamliner, leading to significant project delays. Such examples highlight the importance of maintaining stringent quality checks and having contingency plans to manage and mitigate these outsourcing risks effectively.
Closing
QSO 321 5-2 DISCUSSION: Benefits and Risks of Outsourcing the Global Supply Chain How-To Owlisdom Guide aims to provide a structured approach to understanding and analyzing the role of outsourcing in creating value and the associated risks. Remember, the goal is not to advocate for or against outsourcing but to critically assess its impacts on the global supply chain.
References
Apple. (n.d.). Apple. Retrieved April 5, 2024, from https://www.apple.com/
QSO 321 5-3 Assignment: Evaluating Potential Partnerships
Instructions for QSO 321 5-3 Assignment
5-3 Assignment: Evaluating Potential Partnerships
Overview
As globalization has become increasingly common, so has the importance of analyzing opportunities to create value through outsourcing the supply chain. In this assignment, you will create a checklist to help determine which country might be the best location for parts of your organization’s supply chain.
Scenario
You are a consultant who specializes in helping U.S.-based businesses expand into new international locations. You have a new client who’s looking to outsource their company’s manufacturing of hard drives and computer memory, and it’s your job to assist in selecting the new locations. The company is very focused on quality, sustainability, and equality, and your client would like these attributes upheld in the new manufacturing locations.
Your task is to evaluate two of the following countries:
- India
- Mexico
- Thailand
Then, recommend one country you believe would be the most suitable for the company’s new manufacturing facility, and one country that would be considered the least suitable.
Prompt
Evaluate both countries being considered for a new manufacturing facility through exploration of course and outside resources. Then, recommend the most and least suitable location based on the company’s attributes and requirements.
Specifically, you must address the following rubric criteria:
- Sustainability Measures and Environmental Regulation:Briefly describe sustainability measures
and regulations in each country, and analyze how they may work well with or create conflict or tension with your
U.S.-based company.
- Examples of items to consider include regulations around pollution, waste, and power sources.
- Cost and Workforce:Briefly describe each country’s workforce for the creation of computer
components and the cost of that labor.
- Examples of items to consider include workforce education levels, the overall cost of labor, types of manufacturing available in the country, and the existence of a specialized workforce that can create computer components.
- Government Regulation:Briefly describe the overall regulatory environment of each country. Take
the most likely mode of entry into consideration for each country.
- Examples of items to consider include the types of manufacturing operations allowed in the country, the labor regulations, and the overall business regulations.
- Intellectual Property:Briefly describe the risk of intellectual property being stolen by
creating a manufacturing location in each country.
- Examples of items to consider include each country’s reputation when it comes to intellectual property, intellectual property regulations, and any other legal protections for intellectual property.
- Reputation:Briefly describe the ways an organization can face reputational risk through
outsourcing its manufacturing to each country.
- Examples of items to consider include if and why other organizations have closed manufacturing locations in each country, how your organization’s customer base will view manufacturing in each country, and the protections each country provides to its workforce and the environment.
- Recommendations:Based on your evaluations of the key attributes and requirements, recommend one country that is the most suitable location for your client’s new manufacturing facility, and one country that would be the least suitable location. Justify your recommendations with evidence from your evaluations and the course resources.
Guidelines for Submission
Submit this assignment as a 500- to 750-word Word document. Sources should be cited according to APA style.
Introduction to QSO 321 5-3 Assignment
This How-To QSO 321 Guide aims to assist you in analyzing and selecting the most appropriate international location for outsourcing parts of a company’s supply chain. This Guide will help you solve the QSO 321 5-3 Assignment: Evaluating Potential Partnerships.
For the 5-3 Assignment, I will evaluate the potential partnership between India and Mexico. I will be providing dummy solutions according to the countries I choose. By following the guidelines, you can easily solve QSO 321 5-3 Assignment: Evaluating Potential Partnerships for the countries you decide to choose.
Introduction to Global Supply Chain Outsourcing
We will start the QSO 321 5-3 Assignment: Evaluating Potential Partnerships by introducing and giving a brief overview of Global Supply Chain Outsourcing.
- Brief Overview: Start with a concise introduction to the globalization of supply chains and the significance of outsourcing. Highlight how it aids companies in achieving efficiency and cost reduction.
- Purpose: Clarify the goal of selecting an optimal location for manufacturing components, considering sustainability, quality, and equality.
Example
In the evolving global commerce landscape, supply chain outsourcing has emerged as a strategic lever for companies aiming to enhance operational efficiency and reduce costs. By integrating global markets into their supply chains, businesses can leverage comparative advantages across countries, such as lower labor costs and specialized manufacturing capabilities (Saragih et al., 2020). This globalization of supply chains fosters economic efficiency and presents opportunities for sustainability and quality enhancement, aligning with corporate commitments to environmental and social responsibility.
Briefly describe sustainability measures and regulations in each country and analyze how they may work well with or create conflict or tension with your U.S.-based company. Examples of items to consider include regulations around pollution, waste, and power sources.
Evaluating Sustainability Measures and Environmental Regulation
In the next section of QSO 321 5-3 Assignment: Evaluating Potential Partnerships, we will discuss the sustainability measures and environmental regulations to analyze the working operations of the countries.
- India and Mexico: Research and summarize each country’s sustainability measures and environmental regulations. Consider pollution controls, waste management, and sustainable power initiatives.
- Analysis: Discuss how these measures align or conflict with a U.S.-based company’s values and practices in sustainability.
Example
India and Mexico have progressively implemented sustainability measures and environmental regulations to mitigate pollution, enhance waste management, and promote sustainable power (Mor & Ravindra, 2023). India’s National Green Tribunal and its policies on renewable energy reflect a commitment to environmental stewardship, aligning with global sustainability goals. However, challenges such as regulatory enforcement in India and Mexico’s dependency on fossil fuels could pose conflicts (Bresnihan & Millner, 2022). Aligning operations with these countries requires navigating their sustainability landscapes, ensuring compliance, and leveraging opportunities to bolster a company’s commitment to environmental responsibility.
Briefly describe each country’s workforce for creating computer components and the labor cost. Examples of items to consider include workforce education levels, the overall cost of labor, types of manufacturing available in the country, and the existence of a specialized workforce that can create computer components.
Analyzing Cost and Workforce Characteristics
Next, we will evaluate the cost and workforce characteristics of the countries we chose for the QSO 321 5-3 Assignment: Evaluating Potential Partnerships.
- Labor Cost and Skill Level: Investigate and present the average cost of labor and the workforce’s education level in both countries, specifically in the tech manufacturing sector.
- Specialized Workforce Availability: Examine the presence of a specialized workforce capable of producing high-quality computer components in India and Mexico.
Example
India and Mexico offer competitive advantages in the tech manufacturing sector, distinguished by their labor costs and workforce capabilities (Liu et al., 2020). Renowned for its vast pool of highly educated tech talent, India offers a significant advantage in software development and computer component manufacturing, coupled with relatively low labor costs. Mexico, with its proximity to the U.S., offers logistical benefits and has developed a specialized workforce in manufacturing (German, 2023), particularly in electronics, facilitated by educational programs tailored to the industry’s needs. However, Mexico’s labor costs, while competitive, are generally higher than India’s but offer the advantage of geographical and temporal proximity to the U.S. market.
Briefly describe the overall regulatory environment of each country. Consider the most likely mode of entry for each country. Examples of items to consider include the types of manufacturing operations allowed in the country, the labor regulations, and the overall business regulations.
Assessing Government Regulation and Its Impact
For the next section of the QSO 321 5-3 Assignment: Evaluating Potential Partnerships, we will assess the impact of government regulations on outsourcing the workforce.
- Regulatory Environment Overview: Provide an overview of the regulatory environment in each country, focusing on manufacturing and labor laws.
- Entry Modes: Consider the most likely modes of entry (e.g., joint ventures, wholly-owned subsidiaries) and how government regulations affect these choices.
Example
The regulatory environments in India and Mexico significantly influence the strategic approach to outsourcing and establishing manufacturing operations. India’s regulatory landscape is characterized by a complex web of labor laws and business regulations that require careful navigation. The country supports foreign direct investment (FDI) in manufacturing, often through joint ventures or wholly-owned subsidiaries, encouraged by policies to simplify the business establishment (Haudi et al., 2020). Under the USMCA, Mexico offers streamlined access for U.S.-based companies to establish manufacturing facilities, with favorable conditions for wholly-owned subsidiaries and manufacturing contracts (Quintana et al., n.d.). Both countries have specific regulations governing labor practices, environmental compliance, and business operations.
Briefly describe the risk of stealing intellectual property by creating a manufacturing location in each country. Examples of items to consider include each country’s reputation regarding intellectual property, intellectual property regulations, and any other legal protections for intellectual property.
Understanding the Risks Related to Intellectual Property
In this section of QSO 321 5-3 Assignment: Evaluating Potential Partnerships, we will assess and understand the risks associated with intellectual property.
- IP Regulations: Summarize the intellectual property laws in both countries and evaluate their effectiveness in protecting foreign investments.
- Risk Analysis: Discuss the historical and current risks of intellectual property theft in India and Mexico.
Example
India and Mexico have frameworks for intellectual property (IP) protection, yet these laws’ effectiveness and enforcement levels vary, posing different risks to foreign investments (Auriol et al., 2023). However, challenges persist with enforcement and occasional counterfeiting issues (Gantz, 2020). The risk of IP theft exists in both countries, but is mitigated through careful legal planning, understanding local IP laws, and implementing robust IP protection strategies within manufacturing operations. For a U.S.-based company, navigating these risks requires diligence, local legal expertise, and potentially leveraging international agreements that protect IP across borders.
As a consultant specializing in helping U.S.-based businesses expand into new international locations, my task is to assist a new client who is looking to outsource their company’s manufacturing of hard drives and computer memory. The company is very focused on quality, sustainability, and equality, and would like these attributes upheld in the new manufacturing locations. After evaluating various countries, I will assist them in selecting between India, Mexico, and Thailand as potential manufacturing hubs, ensuring that the chosen location aligns with the company’s values and operational goals.
Briefly describe how an organization can face reputational risk by outsourcing manufacturing to each country. Examples of items to consider include if and why other organizations have closed manufacturing locations in each country, how your organization’s customer base will view manufacturing, and the protections each country provides to its workforce and the environment.
Considering Reputation and Outsourcing Impacts
Next, we will discuss the impacts of outsourcing the workforce.
- Reputational Risks: Identify potential reputational risks for a company outsourcing to either country, including public perception and historical precedents of other companies.
- Environmental and Social Governance (ESG): Reflect on how each country’s practices in workforce treatment and environmental protection could affect the company’s reputation.
Example
Outsourcing manufacturing to India or Mexico presents unique reputational risks tied to public perceptions of labor and environmental standards. Companies that proactively engage with local communities, adhere to stringent Environmental and Social Governance (ESG) standards, and transparently report their operations can mitigate these risks (Clementino & Perkins, 2021). Emphasizing commitment to fair labor practices and environmental stewardship in these countries can safeguard and potentially enhance a company’s reputation, aligning with the growing consumer demand for responsible corporate conduct.
Based on your evaluations of the key attributes and requirements, recommend one country that is the most suitable location for your client’s new manufacturing facility and one that would be the least suitable. Justify your recommendations with evidence from your evaluations and the course resources.
Making Recommendations Based on Evaluation
We will make key recommendations based on our evaluation for the next part of QSO 321 5-3 Assignment: Evaluating Potential Partnerships.
- Suitable Location: Recommend the most appropriate country for the new manufacturing facility, providing a rationale based on the above evaluations.
- Least Suitable Location: Identify the least suitable option and justify this choice with evidence from your analysis.
- Evidence and Resources: Support your recommendations with data, examples, and references to course materials and reputable external sources.
Example
Considering the evaluations on sustainability measures, workforce capabilities, government regulations, intellectual property risks, and reputational implications, Mexico emerges as the most suitable location for the new manufacturing facility. Additionally, Mexico’s proximity to the U.S. reduces logistical costs and simplifies supply chain management, complemented by a skilled workforce adept in electronics manufacturing (Villarreal & Fergusson, 2020). Conversely, despite its lower labor costs and high-skilled workforce, India presents challenges in regulatory complexity and enforcement, posing higher risks for intellectual property security and operational hurdles.
Closing
This How-To Owlisdom Guide will help you solve the QSO 321 5-3 Assignment: Evaluating Potential Partnerships by effectively analyzing and recommending the most suitable international location for a company’s supply chain outsourcing, focusing on manufacturing hard drives and computer memory in India and Mexico.
References
Auriol, E., Biancini, S., & Paillacar, R. (2023). Intellectual property rights protection and trade: An empirical analysis. World Development, 162, 106072.
Bresnihan, P., & Millner, N. (2022). Decolonising environmental politics. In Handbook of Critical Environmental Politics (pp. 521–539). Edward Elgar Publishing. https://www.elgaronline.com/edcollchap/book/9781839100673/book-part-9781839100673-48.xml
Clementino, E., & Perkins, R. (2021). How do companies respond to environmental, social and governance (ESG) ratings? Evidence from Italy. Journal of Business Ethics, 171(2), 379–397.
Gantz, D. A. (2020). USMCA Provisions on Intellectual Property, Services, and Digital Trade. Mexico Center, Rice University’s Baker Institute for Public Policy (2020), Arizona Legal Studies Discussion Paper, 20–03.
German, A. (2023). Supply Chain Risks at the US/Mexico Border. https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11875/4241
Haudi, H., Wijoyo, H., & Cahyono, Y. (2020). Analysis of Most Influential Factors To Attract Foreign Direct Investment (SSRN Scholarly Paper 3873718). https://papers.ssrn.com/abstract=3873718
Liu, X., Mattoo, A., Wang, Z., & Wei, S.-J. (2020). Services development and comparative advantage in manufacturing. Journal of Development Economics, 144, 102438. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdeveco.2019.102438
Mor, S., & Ravindra, K. (2023). Municipal solid waste landfills in lower- and middle-income countries: Environmental impacts, challenges and sustainable management practices. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 174, 510–530. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2023.04.014
Quintana, A. R., Roberts, J. M., & Kim, A. B. (n.d.). A U.S.–Mexico–Canada (USMCA) Economic Partnership Recovery Plan. 3494.
Saragih, J., Tarigan, A., Pratama, I., Wardati, J., & Silalahi, E. F. (2020). THE IMPACT OF TOTAL QUALITY MANAGEMENT, SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT PRACTICES, AND OPERATIONS CAPABILITY ON FIRM PERFORMANCE. Polish Journal of Management Studies, 21(2), 384–397. https://doi.org/10.17512/pjms.2020.21.2.27
Villarreal, A. M., & Fergusson, I. F. (2020). NAFTA and the United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA). Congressional Research Service Report.
QSO 321 6-2 Discussion: Balancing Business and Customer Expectations
Instructions for QSO 321 6-2 Discussion
6-2 Discussion: Balancing Business and Customer Expectations
Customers are at the centre of every company, and therefore, it is important for businesses to be influenced by customer requests and pushes for different products, product features, or services. However, customers frequently do not consider people, planet, and profit when making requests. In this discussion, you will consider how businesses can influence their customers to consider ethical approaches to people, the planet, and profit.
In your initial discussion post, address the following questions:
- What are the positive and negative impacts of the “Amazon effect” on customers?
- As ethical concerns regarding business practices such as poor employee treatment, negative environmental impacts of production, and decreasing use of local storefronts are recognized, how much, if any, of the responsibility for these unethical practices falls to the customers, and how much, if any, falls to businesses?
In your replies to at least two peers, continue the discussion surrounding the influence and impact of customer demands. You may use the following questions to guide your response:
- How can organizations influence consumer behaviours and increase awareness of the value of the triple bottom line?
- How can an organization leverage its mission, vision, and values in its communications with customers?
- Should organizations ignore customers with unethical demands? What are the potential benefits and drawbacks of doing so?
To complete this assignment, review the Discussion Rubric.
Introduction to QSO 321 6-2 Discussion
This How-To QSO 321 Guide will equip you with the analytical tools to assess and influence ethical consumer behaviors to solve QSO 321 6-2 Discussion post. This post revolves around your understanding of aligning business practices with the broader values of sustainability and social responsibility.
What are the positive and negative impacts of the “Amazon effect” on customers?
Understanding the “Amazon Effect”
To start QSO 321 6-2 Discussion: Balancing Business and Customer Expectations, we will discuss the Amazon Effect and its impacts.
- Positive Impacts: Briefly describe the benefits customers experience from the Amazon effect, such as convenience, variety, and potentially lower prices. Use examples to illustrate your points.
- Negative Impacts: Discuss the downsides, including potential harm to local businesses, environmental consequences of increased shipping, and the implications of aggressive competition on employee treatment.
Example
The “Amazon effect” has significantly altered consumer experiences, blending convenience with an unmatched variety of products at competitive prices. Customers now enjoy shopping from the comfort of their homes, accessing a vast selection that brick-and-mortar stores cannot match. This accessibility and speed of delivery have set new standards in customer expectations. However, this shift has drawbacks, notably affecting local businesses unable to compete with Amazon’s pricing and efficiency, leading to closures and economic shifts in local communities. Moreover, the environmental toll of increased shipping and packaging waste, alongside aggressive competition that often pressures employee working conditions, reflects the negative consequences of this phenomenon. While redefining retail, the Amazon effect prompts a complex balance between consumer convenience and broader socioeconomic impacts.
As ethical concerns regarding business practices such as poor employee treatment, negative environmental impacts of production, and decreasing use of local storefronts are recognized, how much, if any, of the responsibility for these unethical practices falls to the customers, and how much, if any, falls to businesses?
Assessing Ethical Responsibility
Now, we will assess the ethical responsibility of businesses.
- Customer vs. Business Responsibility: Analyze the division of ethical responsibility between customers and businesses.
- Consider factors like the awareness level of customers about the ethical implications of their purchases and the role of businesses in promoting ethical consumerism.
Example
The ethical responsibility for practices impacting employees, the environment, and local economies is shared between businesses and consumers. Businesses are responsible for deciding on operational practices, employee treatment, and environmental policies. They are pivotal in fostering sustainable and ethical consumerism through transparent practices and education about the implications of their operations. Conversely, consumers, equipped with varying levels of awareness, also hold responsibility. Their purchasing decisions can either endorse or challenge business practices. However, the onus is on businesses to guide and inform consumers, making ethical choices accessible and appealing. Thus, while consumers play a role in ethical consumption, companies have a more substantial impact on shaping these practices and should lead by example in promoting a more ethical marketplace.
Peer Responses
Responding to peers is one of the vital parts of the QSO 321 6-2 Discussion: Balancing Business and Customer Expectations discussion posts. We need to provide at least two peer responses. I will provide one example post. You can write your peer responses by keeping the following points in mind.
- Collaborate and Educate: Advocate for joint efforts between businesses and consumers to promote ethical practices through educational initiatives.
- Integrate Values in Communication: Encourage using a company’s mission, vision, and values in all customer interactions to foster ethical consumer behavior.
- Navigate Unethical Demands with Care: Consider the implications of refusing service to customers with unethical demands, focusing on education and dialogue to encourage a shift toward ethical practices.
Response 1
Great points about the role of businesses in ethical consumerism! I agree that organizations have a pivotal role in shaping consumer behaviors. They can guide consumers towards more ethical choices by embedding their commitment to the triple bottom line into every aspect of their business—from transparent marketing strategies to sustainable product development. Leveraging their mission and values in communication helps to educate customers about the impacts of their purchases, fostering a culture of responsibility. While ignoring customers with unethical demands is complex, it presents an opportunity for businesses to stand firm on their principles and possibly influence consumer values for the better, albeit with the risk of alienating some customers. Ultimately, the focus should be on education and dialogue to shift perspectives over time.
QSO 321 6-3 Assignment: Adding Customer Value
Instructions for QSO 321 6-3 Assignment
6-3 Assignment: Adding Customer Value
Overview
An important part of any organization’s priorities, as well as an important category of B Corp Certification, is the consideration of added value for customers. In this assignment, you will apply what you have learned about customer expectations and consider how it can be applied to your course project, which is due in Module Seven.
Prompt
You work in the operations department at NationaliTeas, a large international corporation that manufactures and sells tea worldwide. Based on customer feedback and a push to work toward B Corp Certification, the board of directors is looking for new initiative ideas that would increase value to customers. Examples include offering product guarantees, seeking product quality certifications, monitoring customer satisfaction, and so on. You have been asked to outline two customer-focused initiatives that can be evaluated by impacted teams for feasibility.
Specifically, you must address the following:
- Added Customer Value: Briefly describe the added value your initiative idea brings to customers. Use supporting evidence from course materials in your response.
- Added Business Value: Briefly describe the added value your initiative idea brings to the organization. Make sure to note the impact of the added customer value on the business, and use evidence from the course materials to support your response.
- Potential Resources: Identify resources that would likely be needed to complete the initiative. In this case, resources might refer to the amount of funding, the materials available, the allocation of employees and their time, and so on.
- Monitoring and Evaluation: Briefly describe how the success of the initiative would be monitored over time and how you’d evaluate the criteria for success.
Guidelines for Submission
Submit this assignment as a 500- to 750-word Word document. Sources should be cited according to APA style.
Introduction to QSO 321 module 6 assignment 6-3
This How-To QSO 321 Guide will help you understand how to solve the QSO 321 6-3 Assignment: Adding Customer Value. Note that the QSO 321 module 6 assignment 6-3 is that you will apply what you have learned about customer expectations and consider how it can be used in your course project, due in Module Seven.
You have been asked to outline two customer-focused initiatives that can be evaluated by impacted teams for feasibility.
Customer-Focused Initiatives
To start the QSO 321 6-3 Assignment: Adding Customer Value, we will explore customer-focused initiatives. Then, we will align two initiatives with the customer expectations and the company’s values.
- Start with a brief introduction to the concept of customer-focused initiatives.
- Mention aligning these initiatives with customer expectations and the company’s values, especially in striving for B Corp Certification.
Example
Customer-focused initiatives are strategic endeavors to enhance the value and experience provided to consumers, pivotal for fostering loyalty and differentiating a brand within competitive markets. For NationaliTeas, these initiatives are essential for meeting and surpassing customer expectations and embodying its commitment to ethical, sustainable practices as it pursues B Corp Certification. Such certification underscores a balance of profit with purpose, reflecting the company’s dedication to benefiting people and the planet. Therefore, the initiatives proposed must seamlessly integrate with customer desires and the broader ethical framework that NationaliTeas aspires to uphold, ensuring a harmonious alignment with the organization’s core values and long-term sustainability goals.
Briefly describe the added value your initiative idea brings to customers. Use supporting evidence from course materials in your response.
Added Customer Value
The next section of the QSO 321 6-3 Assignment: Adding Customer Value revolves around how to add customer value.
- Select and describe two initiatives that could potentially increase value for NationaliTeas’ customers. For instance, you might consider a product guarantee program or obtaining a quality certification for your tea products.
- Use evidence from course materials to support why these initiatives are expected to meet customer expectations and how they align with current trends or demands in the tea industry.
Example
Introducing a product guarantee program adds significant value to NationaliTeas’ offerings by bolstering consumer confidence and loyalty. This approach aligns with evidence suggesting that guarantees increase customer trust, as they feel assured of product quality and company accountability. Additionally, obtaining environmental and ethical quality certifications, like Organic or Fair Trade, meets the rising consumer demand for sustainably sourced products. Such certifications resonate with current trends in the tea industry.
Briefly describe the added value your initiative idea brings to the organization. Ensure you note the impact of the added customer value on the business and use evidence from the course materials to support your response.
Added Business Value
This section of the QSO 321 6-3 Assignment: Adding Customer Value will explore how to add business value to organizations.
- Discuss how the proposed initiatives will add value to the organization. This could include brand differentiation, customer loyaltyincreases, or alignment with sustainability goals that could improve market positioning.
- Analyze the potential impact of enhanced customer value on the business, such as increased sales, better customer retention rates, or more favorable brand perception.
Example
Adopting initiatives that emphasize sustainability and ethical practices significantly enhances an organization’s brand differentiation. By integrating these values into our operations, we signal to consumers a commitment beyond mere profit, aligning with increasing customer expectations for responsible business conduct. This alignment not only fosters deeper customer loyalty but also opens up new markets interested in sustainable and ethical products, potentially boosting sales and improving customer retention rates. Moreover, these initiatives contribute to a more favorable brand perception, as demonstrated by evidence from marketing studies that show consumers are more willing to support and advocate for brands that demonstrate a commitment to social and environmental causes. This enhanced brand perception, coupled with increased customer loyalty, can lead to substantial long-term benefits for the organization, including improved market positioning and competitive advantage. Implementing these initiatives represents a strategic investment in the organization’s future, aligning business operations with broader societal values and expectations.
Identify resources that would likely be needed to complete the initiative. In this case, resources might refer to the amount of funding, the materials available, the allocation of employees and their time, and so on.
Potential Resources
Next, we will identify some potential resources needed to complete the initiatives.
- Identify the resources required for each initiative. This may encompass financial investments, materials for product improvement, or the workforce for program implementation.
- Provide a brief overview of how these resources could be allocated effectively to ensure the initiative’s success.
Example
For the product guarantee program, resources such as financial reserves for refunds or replacements and a dedicated customer service team are essential (Liao, 2022). Effective allocation involves training customer service staff on program specifics and setting aside a budget to cover guarantee claims, ensuring customer trust and satisfaction. Regarding quality certifications, necessary resources include funding for certification processes, investment in sustainable materials, and employee training on new production standards. Allocation should focus on integrating sustainable practices into the production process, securing certification fees, and conducting employee training sessions to uphold certification standards, thus enhancing the brand’s market positioning and consumer appeal through demonstrated commitment to sustainability and quality.
Briefly describe how the initiative’s success would be monitored over time and how you’d evaluate the criteria for success.
Monitoring and Evaluation
For the next section of QSO 321 6-3 Assignment: Adding Customer Value, we will discuss how to monitor and evaluate the success of initiatives.
- Describe the methods for monitoring the initiative’s progress over time. This could involve regular customer feedback surveys, sales tracking, or social media engagement metrics.
- Outline how you would evaluate the success of each initiative, including specific criteria and benchmarks for measuring impact on customer satisfaction and business performance.
Example
The success of the initiatives will be monitored through a combination of regular customer feedback surveys, sales data analysis, and social media engagement metrics. For the product guarantee program, success criteria include increased customer satisfaction scores and reduced return rates, indicating trust in product quality. In the QSO 321 Module Six Assignment, for the quality certifications initiative, benchmarks such as sales growth in certified products and enhanced social media positive mentions will signal increased consumer appreciation for sustainability efforts. Regularly scheduled reviews of these metrics will provide insights into the initiatives’ effectiveness, allowing for adjustments to strategies to maximize impact on customer satisfaction and overall business performance. These reviews will be crucial in refining the approach to ensure alignment with sustainability goals and ongoing customer engagement.
Closing
This guide will help you understand how to add customer and business value. How-To Owlisdom Guide will allow you to solve QSO 321 6-3 Assignment: Adding Customer Value easily.
QSO 321 7-2 PROJECT SUBMISSION
Instructions for QSO 321 7-2 Project Submission
7-2 PROJECT SUBMISSION
Competencies
In this project, you will demonstrate your mastery of the following competencies:
- Recommend operations management methods and techniques to increase value for customers
- Evaluate how operations management generates value for an organization
- Explain local, national, and global sustainability in relation to functional areas of business
Scenario
You work as the chief supply-chain officer at the large international corporation, NationaliTeas. NationaliTeas manufactures and sells tea worldwide. Its motto is “Keeping people and their taste buds awake (when they want to be awake).” Its mission is “Make the world more awake through rejuvenating and refreshing beverages and sustainable practices that uplift workers, communities, and souls.” Its vision is “to be the most respected tea manufacturer across at least three continents for our tea and our actions, which will be driven by a commitment to ethical sourcing, minimal waste, and empowerment of our employees.”
You would like to establish an operational goal of having your corporation apply for a B Corp Certification within the next two years. You believe this would add value to the organization and help it prioritize a stronger focus on sustainable operational practices. You have conducted a pre-assessment based on the recommendations for applying for B Corp Certification, and you’ve evaluated the corporation’s current strengths and areas for improvement.
Now you need to develop a proposal for the board of directors that explains why prioritizing the triple bottom line (TBL) through working toward B Corp Certification has organizational value. You must also propose three high-impact initiatives to help strengthen the corporation’s commitment to people, planet, and profit based on your evaluations.
Directions
- Part One: Justification of Benefits:Justify the value of working toward more
intentionally incorporating the TBL framework into organizational decision making, specifically how ethical
business practices regarding people, planet, and profit can benefit society, the environment, and the
company’s profit. Specifically, address the following:
- Key Components: Explain the three key components of the TBL framework and how each component benefits businesses and society.
- Organizational Value: Justify the value and benefits of using the TBL framework to inform corporate decision-making, and explain connections between the organizational mission and the organizational vision.
- B Corporation Benefits:Briefly describe the organizational benefits of attaining B Corp Certification.
- Part Two: Operational Recommendations:Read through the Preassessment Evaluation
Summary (located in the Supporting Materials section) for each aspect of the TBL (people, profit, and
planet). You will need to provide a detailed description of the initiatives that will create the needed
improvement. You should note the organizational and societal value of the initiative, along with the
operational management techniques recommended to plan and complete each initiative. For each of your three
initiatives, address the following:
- Organizational Impacts:Describe the organizational benefits of each initiative, specifically noting the expected positive impact of completing each. Examples of positive impacts include better alignment with the organization’s mission, vision, and culture statements; increased amounts of funds or resources saved; and improvements to the organization’s brand.
- Societal Impacts:Describe the societal benefits of each initiative, specifically noting the expected positive impact of completing each. Examples of positive impacts include increased community building and positive environmental impact.
- Customer Impacts:Describe the consumer benefits of each selected initiative, specifically noting the expected positive impact of completing each. Examples of positive impacts include increased alignment with target markets, improved product access and availability, and improved customer satisfaction.
- Business Risks:Explain the business risks associated with prioritizing, planning, and resourcing each initiative and how these risks will be considered and monitored.
- Operational Management Techniques:Recommend an operational management strategy or technique (e.g., project management, lean manufacturing, or Six Sigma) that is appropriate to implement for each selected initiative, and explain why.
- Defining Requirements and Scope:Define the requirements for the successful implementation of each selected initiative as well as the scope of each. Describe how changes to the requirements and scope would impact timelines, budget, and risk.
- Roles and Responsibilities: Explain the key internal and external stakeholders who would be involved in planning and implementing each selected initiative, as well as why each identified stakeholder is needed to successfully implement the initiatives.
What to Submit
To complete this project, you must submit the following:
Submit your project using one of the two formats listed below. Please note that your submission should include both Part One and Part Two of your project. For either format, sources should be cited according to APA style.
- Written Report: Submit a 1,500- to 1,700-word Word document. Use APA style.
- Slideshow Presentation: Submit a 10- to 12-slide presentation with speaker's
notes. Your slideshow should be submitted as a PowerPoint or PDF document. Example tools that could be used
to create your slideshow include:
- PowerPoint
- Canva
- Prezi
Supporting Materials
The following resource supports your work on the project:
Reading: Project
Preassessment Evaluation Summary PDF
This
document presents the results of NationaliTeas’ preassessment for attaining B Corp
Certification.
Introduction to QSO 321 7-2 Project
This guide provides a structured approach for students tasked with developing a proposal to integrate the Triple Bottom Line (TBL) framework into NationaliTeas’ operations, aiming for B Corp Certification. The guide covers the justification of TBL benefits and outlines operational recommendations for impactful initiatives. Part One: Justification of Benefits
Explain the three key components of the TBL framework and how each component benefits businesses and society.
Key Components of the TBL Framework
We will start Part One of the QSO 321 7-2 Project Submission by explaining the three key components of TBL. People: Focus on the well-being of employees and communities. Demonstrate how ethical treatment and empowerment lead to a motivated workforce and positive community impact. Planet: Emphasize sustainable environmental practices. Highlight the importance of minimizing waste, using sustainable resources, and reducing carbon footprint. Profit: Discuss how ethical practices and sustainability can lead to long-term profitability through brand loyalty, innovation, and operational efficiencies.
Example
The Triple Bottom Line (TBL) framework emphasizes People, Planet, and Profit, guiding businesses toward sustainable success (Zaharia & Zaharia, 2021). By prioritizing People, companies ensure ethical treatment and empowerment of employees and communities, fostering a motivated workforce and generating positive social impacts. Focusing on the Planet, businesses adopt sustainable practices, minimizing waste and carbon emissions, which benefits the environment and enhances corporate responsibility (Molthan-Hill et al., 2020). Lastly, Profit derived from ethical practices and sustainability secures long-term business viability through increased brand loyalty, innovation, and operational efficiencies. This holistic approach advances business performance and contributes to societal well-being and environmental preservation, demonstrating the interconnectivity of corporate success with broader societal and environmental health.
Justify the value and benefits of using the TBL framework to inform corporate decision-making and explain connections between the organizational mission and the organizational vision.
Organizational Value
Next, we will discuss the values and benefits of using TBL in organizations. Link the TBL framework to NationaliTeas’ mission and vision. Illustrate how adopting TBL can enhance respect and reputation globally, contribute to achieving the vision, and reflect the company’s commitment to ethical sourcing and minimal waste.
Example
Adopting the Triple Bottom Line (TBL) framework aligns closely with NationaliTeas’ mission “to make the world more awake through rejuvenating beverages and sustainable practices” and its vision to be a respected leader across continents (Burgess & Matar, 2023, page number). By integrating TBL into decision-making, NationaliTeas underscores its commitment to ethical sourcing and waste reduction, enhancing its global reputation and respect. This approach directly contributes to achieving its vision by promoting a sustainable operational model that equally values people’s well-being, environmental stewardship, and financial health. It reflects a strategic alignment between the company’s day-to-day operations and broader ambitions. It showcases a genuine dedication to ethical business practices that resonate with consumers and stakeholders, fostering a sustainable and profitable future.
Briefly describe the organizational benefits of attaining B Corp Certification.
B Corporation Benefits
This section of the QSO 321 7-2 Project Submission revolves around our understanding of the organizational benefits of B Corp Certification. Outline benefits such as enhanced brand credibility, access to a like-minded business community, improved investor relations, and alignment with consumer expectations for ethical business practices.
Example
Attaining B Corp Certification significantly benefits an organization by enhancing brand credibility through demonstrated commitment to social and environmental responsibility. It grants access to a community of like-minded businesses, fostering collaboration and shared growth opportunities. Improved investor relations stem from the certification’s rigorous standards, attracting investment from those prioritizing sustainability and ethical practices (Villela et al., 2021). Moreover, aligning with consumer expectations for ethical business practices, B Corp Certification helps to meet the growing demand for transparency and corporate responsibility, reinforcing customer trust and loyalty. This alignment enhances the company’s competitive edge in a market increasingly driven by conscious consumerism.
Part Two: Operational Recommendations. For each initiative, consider the impacts on people, planet, and profit, and address operational strategies for implementation.
Describe the organizational benefits of each initiative, specifically noting the expected positive impact of completing each. Positive impacts include better alignment with the organization’s mission, vision, and culture statements, increased funds or resources saved, and improvements to the organization’s brand.
Organizational Impact
For Part Two of the QSO 321 7-2 Project Submission, we will discuss the organizational benefits of these initiatives. Discuss how each initiative aligns with the company’s mission, vision, and values. Estimate potential savings and brand improvement outcomes.
Example
Implementing a product guarantee program aligns with NationaliTeas’ mission to “make the world more awake” by ensuring customer satisfaction and trust, enhancing brand loyalty, and potentially increasing sales. This initiative supports the vision of being a respected tea manufacturer through ethical practices, reflecting the company’s commitment to quality and customer care (Marschall, 2023). Additionally, acquiring quality certifications like Organic or Fair Trade directly supports the mission of sustainable practices and uplifts workers and communities, aligning with the company’s values. These certifications could lead to brand differentiation, opening new market segments, and improving the brand’s reputation. Both initiatives promise cost savings through efficient resource use and waste reduction, contributing positively to the organization’s profitability and brand perception (Villela et al., 2021).
Describe the societal benefits of each initiative, specifically noting the expected positive impact of completing each. Examples of positive impacts include increased community building and positive environmental impact.
Societal Impacts
Next, we will discuss the impact of B Corp Certifications on society. Describe how initiatives will contribute to community development and environmental sustainability. Examples could include local employment opportunities and reduced environmental degradation.
Example
The product guarantee program fosters a culture of trust and reliability, indirectly promoting community building by setting a standard for consumer rights and corporate accountability. It encourages other organizations to adopt similar ethical practices, contributing to a more consumer-friendly market environment (Villela et al., 2021). Quality certifications like Organic or Fair Trade significantly benefit societies by supporting fair labor practices and environmental sustainability. These certifications ensure that farmers and workers receive fair compensation, fostering community development and economic stability in producing regions. Moreover, they promote environmental stewardship by reducing chemical usage and degradation, contributing to healthier ecosystems and sustainable agricultural practices. Both initiatives enhance NationaliTeas’ societal impact and set a precedent for industry-wide responsibility towards communities and the environment.
Describe the consumer benefits of each selected initiative, specifically noting the expected positive impact of completing each. Examples of positive impacts include increased alignment with target markets, improved product access and availability, and enhanced customer satisfaction.
Customer Impacts
After discussing the business and Social impacts, in this section of the QSO 321 7-2 Project Submission, we will discuss the customer impacts of B Corp Certification. Explain how initiatives will meet customer expectations for ethical products, possibly enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Example
Implementing a product guarantee program significantly enhances customer satisfaction by ensuring that the tea products meet or exceed expectations, fostering trust and loyalty within the consumer base. This initiative directly aligns with customer desires for high-quality and reliable products, boosting confidence in the brand (Munyoro et al., 2023). Obtaining quality certifications like Organic or Fair Trade meets the growing consumer demand for ethically produced goods, resonating with environmentally and socially conscious customers. These certifications improve product access and availability for niche markets seeking sustainable options, enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty. Both initiatives underscore NationaliTeas’ commitment to ethical practices, aligning closely with target market values and expectations and likely leading to increased customer retention and brand advocacy.
Explain the business risks associated with prioritizing, planning, and resourcing each initiative and how these risks will be considered and monitored.
Business Risks
Now, let us describe the risk associated with B Corp Certification. Assess potential risks such as financial implications, market reception, and implementation challenges. Include risk mitigation strategies.
Example
Prioritizing the product guarantee program and quality certifications presents risks, including financial burdens from upfront costs and potential market resistance. Implementing the guarantee could lead to increased returns, impacting short-term profits. Quality certifications might face hurdles like high certification costs and stringent compliance requirements. Continuous market analysis will ensure alignment with consumer expectations to mitigate these risks, while phased implementation can help manage financial outlays (Borden & Mead, 2023). Regular audits and feedback loops will monitor market reception and operational challenges, enabling timely adjustments. Risk mitigation strategies involve setting aside contingency funds and leveraging marketing to educate consumers on the added value of these initiatives, ensuring a positive reception and sustainable implementation.
Recommend an appropriate operational management strategy or technique (e.g., project management, lean manufacturing, or Six Sigma) to implement for each selected initiative and explain why.
Operational Management Techniques
For this section of Part Two, we will discuss different operational techniques and strategies recommendations. Recommend strategies like Six Sigma for quality improvement or lean manufacturing for waste reduction. Justify each choice based on its suitability for the initiative.
Example
Implementing a Six Sigma approach is recommended for the product guarantee program due to its focus on reducing defects and improving quality. Six Sigma’s data-driven methodology will ensure that any issues leading to product returns are systematically identified and rectified, enhancing product reliability and customer satisfaction (Condé et al., 2023). Lean Manufacturing is the suggested strategy for obtaining quality certifications. Lean’s emphasis on waste reduction and efficiency aligns with the goals of quality certifications like Organic or Fair Trade, which often require sustainable and efficient production processes. Lean Manufacturing will streamline operations, reduce waste, and ensure compliance with certification standards, supporting the initiative’s success and sustainability objectives.
Define the requirements for successfully implementing each selected initiative and its scope. Describe how changes to the requirements and scope would impact timelines, budget, and risk.
Defining Requirements and Scope
This section of Part Two QSO 321 7-2 Project Submission defines the requirements for implementing the selected initiatives. Detail what is necessary for each initiative’s success, including time, budget, and resources. Discuss how changes might affect project outcomes.
Example
Success for the product guarantee program requires a clear policy, training for customer service teams, and an allocated return budget. The initiative’s scope encompasses all tea products. Changes in scope or policy could extend timelines for training and policy adjustments, impacting the budget due to increased operational costs (Agarwal, 2021). For quality certifications, requirements include audit fees, modifications to production processes, and employee training. Expanding the scope to include more certifications or products would necessitate additional time and financial investment, potentially elevating the risk of project delays and budget overruns. Effective project management and contingency planning are essential to mitigate these risks and ensure adaptive change responses.
Explain the key internal and external stakeholders involved in planning and implementing each selected initiative and why each identified stakeholder is needed to implement the initiatives successfully.
Roles and Responsibilities
Now, for the last section of Part Two QSO 321 7-2 Project Submission, we will discuss the roles and responsibilities of stakeholders in implementing the initiatives. Identify internal teams and external partners crucial for implementation. Explain their roles and why their involvement is critical.
Example
For the product guarantee program, key internal stakeholders include the customer service team, which is responsible for managing claims and feedback, and the marketing team, which is tasked with communicating the program to customers. Their involvement ensures efficient execution and awareness of the guarantee. External stakeholders might include third-party logistics providers, vital for handling returns and exchanges swiftly (Darko & Vlachos, 2022). For quality certifications, the production team is crucial internally for aligning manufacturing processes with certification standards, while external certifying bodies are essential for granting the certifications and providing credibility (Shi et al., 2020). Both sets of stakeholders are critical for successfully implementing the initiatives, ensuring operational alignment with objectives, and enhancing brand reputation.
Closing
By following this QSO 321 guide, students can craft a compelling and coherent proposal demonstrating the value of integrating the TBL framework into NationaliTeas’ operations, aligning with the company’s ethical, environmental, and profitability goals.
References
Agarwal, A. (2021). Investigating design targets for an effective performance management system: An application of balanced scorecard using QFD. Journal of Advances in Management Research, 18(3), 353–367. Borden, D. S., & Mead, T. (2023). Rural Small and Medium Enterprises: Maximising the Value of Benefit Corporation Certification. International Journal of Rural Management, 19(3), 456–472. Burgess, A., & Matar, E. (2023). Team-Based Learning (TBL): Theory, Planning, Practice, and Implementation. In D. Nestel, G. Reedy, L. McKenna, & S. Gough (Eds.), Clinical Education for the Health Professions: Theory and Practice (pp. 1325–1353). Springer Nature. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-3344-0_128 Condé, G. C. P., Oprime, P. C., Pimenta, M. L., Sordan, J. E., & Bueno, C. R. (2023). Defect reduction using DMAIC and Lean Six Sigma: A case study in a manufacturing car parts supplier. International Journal of Quality & Reliability Management, 40(9), 2184–2204. Darko, E. O., & Vlachos, I. (2022). Creating valuable relationships with third-party logistics (3PL) providers: A multiple-case study. Logistics, 6(2), 38. Marschall, T. C. M. (2023). The global relevance of Afghan migration: A state-of-the-art review and repository. Molthan-Hill, P., Robinson, Z. P., Hope, A., Dharmasasmita, A., & McManus, E. (2020). Reducing carbon emissions in business through Responsible Management Education: Influence at the micro-, meso-and macro-levels—the International Journal of Management Education, 18(1), 100328. Munyoro, G., Makotore, D., & Zingunde, M. (2023). The Role of Brand Equity in Enhancing Customer Retention in Buying Tea Products in Zimbabwe: A Case Study of Ariston Holdings. ADRRI Journal of Arts and Social Sciences, 20(1 8), January 2023-March 2023), 1–36. Shi, Y., Waseem, R., & Shahid, H. M. (2020). Third-Party Logistics. Transportation Systems Analysis and Assessment, p. 45. Villela, M., Bulgacov, S., & Morgan, G. (2021). B Corp certification and its impact on organizations over time. Journal of Business Ethics, 170, 343–357.
Zaharia, R. M., & Zaharia, R. (2021). Triple Bottom Line. In D. Crowther & S. Seifi (Eds.), The Palgrave Handbook of Corporate Social Responsibility (pp. 75–101). Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-42465-7_2
QSO 321 8-2 Assignment Request for Professional Development Funds
Instructions for QSO 321 8-2 Assignment
8-2 Assignment: Request for Professional Development Funds
Overview
An important part of any career is professional development. Professional development can consist of attending conferences, taking additional courses, reading professional texts, or earning industry credentials. Many workplaces not only encourage professional development but also provide employees with funds to be used for this purpose. Use what you have learned about relevant credentials in your course resources to complete this assignment.
Prompt
Your manager has asked that you submit a request for professional development funds for an industry credential related to sustainability, business ethics, or operations management. Select one of the credentials covered in your course resources or a relevant credential you find online that meets your manager’s requirements. Explore the purpose, requirements, and career benefits of the credential, then complete the request using the Module Eight Assignment Template Word Document.
Specifically, you must address the following rubric criteria:
- Purpose:Briefly describe the purpose of your selected credential from a business
perspective. The following questions can be used to help guide your description:
- What knowledge, skills, or expertise does it help recognize?
- What fields or industries is it relevant to?
- How widely known or recognized is it?
- Requirements:Identify the requirements for earning the credential. The following
questions can be used to help guide your response:
- What is the financial cost for the credential?
- What is an estimate of the time required to earn it?
- What evidence needs to be provided to earn it, such as a portfolio, paperwork, exams, work experience, and so on?
- Does the credential require renewal, and if so, how does one renew the credential?
- Career Benefits:Describe the general career benefits for both professionals and
organizations related to the credential. The following questions can be used to help guide your
response:
- How might the credential impact a job application, or the types of jobs you could reasonably apply to?
- How might the credential impact your pay or expected salary for a new role?
- What specialized knowledge or skills would you gain from earning the credential, and how might they benefit the organization?
- Is the credential required or preferred for regulatory requirements your organization must adhere to?
Introduction to QSO 321 8-2 Assignment
This QSO 321 assignment revolves around your understanding of professional development funds. We will be provided with a template for writing requests. I will be using the SNHU example template.
Selecting a Credential
First, we will choose a credential that aligns with our sustainability and career goals.
- Choose a credential that aligns with your sustainability, business ethics, or operations management career goals.
- Consider credentials mentioned in course materials or conduct research online to find one that meets your manager’s criteria and your professional aspirations.
Example
I’ve chosen the Certified Sustainability Officer (CSO) credential. This certification aligns with my career aspirations in sustainability and business ethics, offering a comprehensive understanding of integrating sustainable practices within corporate strategies.
Briefly describe the purpose of your selected credential from a business perspective. The following questions can be used to help guide your description: What knowledge, skills, or expertise does it help recognize? What fields or industries is it relevant to? How widely known or recognized is it?
Describing the Purpose
For the next section of QSO 321 8-2 Assignment Request for Professional Development Funds, we will briefly describe the purpose of the credentials chosen.
- Knowledge, Skills, Expertise: Explain how the credential recognizes specific knowledge, skills, or expertise in your field. Mention its relevance to particular fields or industries and its recognition within the professional community.
- Relevance: Discuss the industries or fields where the credential is most valued and how it supports business objectives or ethical standards in those areas.
- Recognition: Highlight the credential’s recognition in the industry, emphasizing any notable organizations or professionals that endorse it.
Example
The purpose of the CSO credential is to recognize professionals with a high level of expertise in implementing sustainable practices across organizations. It’s highly relevant to industries committed to environmental stewardship and corporate responsibility. The credential is widely acknowledged in the business community and endorsed by leading sustainability organizations, signifying a professional’s commitment to ethical business practices and sustainability.
Identify the requirements for earning the credential. The following questions can be used to help guide your response: What is the financial cost of the credential? What is an estimate of the time required to earn it? What evidence needs to be provided to earn it, such as a portfolio, paperwork, exams, work experience, and so on? Does the credential require renewal, and if so, how does one renew the credential?
Identifying the Requirements
This QSO 321 8-2 Assignment Request for Professional Development Funds section identifies the requirements for earning the chosen credential.
- Financial Cost: Provide details on the cost of obtaining the credential, including examination fees, study materials, or any other associated expenses.
- Time Investment: Estimate the time required to complete the credentialing process, including study time, examination hours, and any required professional experience.
- Evidence and Renewal: Outline the proof required to earn the credential (e.g., exams, portfolio, work experience) and detail the renewal process, if applicable, including frequency and requirements.
Example
To obtain the CSO credential, candidates must invest approximately $1,500 and dedicate around 6 months to complete the required coursework and project work. The process includes passing a comprehensive exam and submitting a project demonstrating the application of sustainable practices. The credential requires renewal every three years, which involves completing continuing education units to stay abreast of the latest in sustainability.
Describe the general career benefits for professionals and organizations related to the credential. The following questions can be used to help guide your response: How might the credential impact a job application, or what types of jobs could you reasonably apply for? How might the credential impact your pay or expected salary for a new role? What specialized knowledge or skills would you gain from earning the credential, and how might they benefit the organization? Is the credential required or preferred for your organization’s regulatory requirements?
Outlining the Career Benefits
Next, we will outline the career benefits by describing the impacts and types of jobs we will apply for concerning the chosen credentials. Job Market Impact: Describe how the credential could enhance your job applications and the range of positions it may qualify you for. Emphasize its potential to open up new career opportunities. Salary Impact: Discuss the potential impact on your salary or compensation, citing industry standards or statistics if available. Knowledge and Skills Benefits: Explain the specialized knowledge and skills you will gain and how these could benefit your current or future organization. Regulatory Compliance: If relevant, mention how the credential aligns with regulatory requirements or industry standards your organization must comply with.
Example
The CSO credential significantly enhances job prospects, particularly in sectors prioritizing environmental conservation and ethical business operations. It can lead to better job positions and potentially higher salaries due to the specialized knowledge it represents. This credential equips professionals with the skills to contribute meaningfully to their organizations’ sustainability goals, aligning business operations with global sustainability standards and regulatory requirements, thus benefiting both the individual and the organization.
Closing
Following these guidelines for QSO 321 8-2 Assignment Request for Professional Development Funds guide will help you craft a persuasive request for professional development funds, demonstrating the credential’s value to your career and your organization.




